Published: 11/09/2018 Updated: 04/15/2021
Acute viral intestinal infections (AVI) are similar in initial symptoms to acute respiratory infections or influenza: sore throat, fever, weakness. The first thing that comes to mind is that I have a cold! However, after some time, more unpleasant circumstances appear - severe nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, which is not easy to cope with. Many people mistakenly believe that they ate something wrong and got poisoned due to a “cold.” This is wrong.
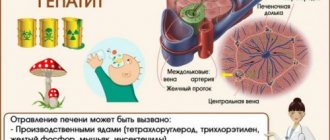
The reason for the development of this scenario of events is the intestinal group of viruses - enteroviruses, noroviruses, rotoviruses. Self-medication in this case is not recommended, especially if the case concerns a child or an elderly person. What is important? Promptly perform the necessary tests and begin treatment!
Symptoms and consequences of intestinal infections
Viruses that cause intestinal or stomach flu are transmitted through the air, are highly contagious and widespread, especially during the cold season. If there is a sick person in the team (even at the initial stage), most likely, several more people will “catch” the virus in the next 1-2 days. The disease can become epidemic.
When the pathogen enters the body, intoxication and damage to the gastrointestinal tract occurs, such as acute gastroenteritis. As a result, dysbiosis develops and the process of water absorption is disrupted, which leads to dehydration. Together with water, a person also loses vital minerals - sodium, potassium, chlorine, magnesium. And without these substances, metabolism is impossible, blood clotting function is impaired, and it is difficult to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
What do we call "stomach flu"? Its features
July 26, 2021
What is stomach flu?
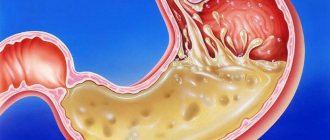
Most often, this is the colloquial name for painful sensations in the stomach, which doctors call gastroenteritis. As a rule, this is a viral disease, but it is not caused by the influenza virus, and therefore is not a stomach flu in the literal sense of the word. In addition to viruses, gastroenteritis can be caused by bacteria and parasites.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis
Viral gastroenteritis causes diarrhea, nausea and even vomiting. The patient may experience flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, headache, accompanied by abdominal pain. With viral gastroenteritis, the above symptoms begin to appear 12–48 hours after the first contact with the infection. It all starts with nausea, which can last up to 3 days. If gastroenteritis has a bacterial or parasitic etiology, nausea may last for a longer period of time. This condition can pose a risk of infecting others, and is especially dangerous for people with chronic diseases, infants and the elderly.
Gastroenteritis of viral etiology
Viral gastroenteritis is the process of infection of cells of the gastrointestinal tract by a virus, resulting in inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. Viral gastroenteritis is highly contagious and can be easily contracted simply by touching an infected person or something they have touched. It is especially dangerous to eat food prepared by a sick person. It is noteworthy that shellfish are also distributors of the virus that causes gastroenteritis. It is possible to become infected by eating shellfish in contaminated water, or vegetables and fruits washed with water from the same source.
Viruses that cause gastroenteritis:
- Norovirus is the most common cause of illness in adults.
- Rotavirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis in infants and young children. Adults can also become infected with this type of virus, but they tolerate it more easily.
- Adenovirus and astrovirus both affect children more often than adults. Less common than the previous two, but their symptoms appear much later, approximately on the 10th day from the moment of infection.
Gastroenteritis of bacterial etiology
Not all bacteria can cause gastroenteritis. Many of them are harmless, and some are even necessary for our body. The danger is posed by salmonella and E. coli, which can enter the gastrointestinal tract along with food. They are the most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis, causing inflammation in the stomach. Salmonella and E. coli can enter the digestive system through foods contaminated at virtually any stage of preparation: during growing, harvesting, processing, storage, transportation, or even cooking. The easiest way to become infected with bacterial gastroenteritis is through infections in food from untreated kitchen surfaces or unwashed dishes.
How to keep food safe?
Bacteria begin to actively multiply already in the refrigerator at a temperature of +4ºС. The process of bacterial reproduction accelerates in room conditions, not stopping until the air temperature reaches +60ºС. There are two ways to counteract this process: by freezing food in the freezer or by cooking it at high temperatures in the oven. It should be remembered that in both refrigerated and frozen foods, bacteria remain viable, becoming active at room temperature. If you overlook this, you may miss the shelf life and allow some bacteria to start releasing toxins into the food before you eat it. In such cases, signs of bacterial gastroenteritis will not be long in coming within the next few hours from the moment of eating.
Tourist's diarrhea
Tourist's diarrhea is a common disease among travelers visiting exotic countries. This fairly common way to contract gastroenteritis is through local cuisine or water contaminated with local bacteria. Therefore, when traveling to developing countries in Asia, Africa, the Caribbean or Latin America, it is better not to eat raw fruits, vegetables, and street foods such as dried meats, fish, shellfish, etc. Try to brush your teeth often using bottled water, and Drink drinks without ice in restaurants and bars: it is unknown what kind of water it is made from.
Gastroenteritis of parasitic etiology
Parasitic gastroenteritis, that is, an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract caused by parasites, is a relatively rare phenomenon in developed countries such as the USA, Canada, and EU countries. However, Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia are found everywhere. Parasites, that is, tiny creatures that live inside other living things, can move through water and thus infect more and more individuals. You can get sick if you use contaminated water to grow or cook food, or if you swim or bathe in it.
Treatment of gastroenteritis
Regardless of the cause of the disease, it is generally possible to recover from gastroenteritis within a few days. To do this, you first need to get plenty of rest and drink plenty of fluids. If the symptoms really intensify or prolong, consult a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe adequate treatment aimed at eliminating the infection, i.e., eliminating the cause of the disease, and will also give a referral for tests to rule out other diseases that cause similar symptoms and stomach problems.
Diet for gastroenteritis
Eating the right diet can relieve symptoms of gastroenteritis. The peculiarity of the disease is that due to the inflammatory process on the gastric mucosa, the digestion process is difficult and causes discomfort. However, you can get nutrients, calories, fluid, and along with it vital minerals (electrolytes) from fruit juices, isotonic, soft and caffeine-free drinks, as well as from broths. When the patient feels ready to eat solid foods, they can start eating rice, potatoes, bread, applesauce and bananas. You should avoid fatty or sweet foods, dairy products, caffeine and alcohol, which can make you feel worse.
Dehydration as a result of gastroenteritis
Dehydration occurs only when the body loses too much fluid through vomiting and diarrhea. This is the main health problem caused by gastroenteritis. Dehydration is especially dangerous for infants, the elderly and chronically ill people. Symptoms of dehydration include a strong desire to drink, dark-colored urine, feeling tired, and dizziness. The child may complain of dry mouth and have sunken eyes and cheeks.
Fight against dehydration
With gastroenteritis, water is poorly absorbed into the body. Therefore, the patient needs to be given fluids containing rehydrating drugs (electrolytes), sold in pharmacies. The drink must also contain essential nutrients. When it comes to adults, they can be given isotonic drinks, juices and soups, and they can also be offered to dissolve ice specially frozen in the freezer. If the patient's body cannot maintain the required level of fluid, dizziness and a rapid pulse are observed, perhaps these are signs of severe dehydration. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance or consult a family doctor. It will likely be necessary to prescribe parenteral nutrition to replace lost fluids.
Possible serious consequences of gastroenteritis
It rarely happens that a consequence of gastroenteritis is hemolytic-uremic syndrome. This applies to a greater extent to patients under 10 years of age. The disease is caused by E. coli, which, when ingested, releases toxins that negatively affect the production of red blood cells and platelets, thereby causing a decrease in their levels in the body, which, in turn, negatively affects blood clotting and can cause bleeding. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome can cause kidney failure and damage to the nervous system. Symptoms of hemolytic uremic syndrome include paleness, irritability, infrequent urination, and blood in the stool. This is a good reason to seek emergency medical care.
The need for medical care for gastroenteritis
It is imperative to seek medical help if the following illness occurs:
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- the body does not retain fluid for more than 24 hours;
- diarrhea lasts more than two days in an adult or 24 hours in a child;
- dehydration is accompanied by excessive thirst, dry mouth, and excessive weakness;
- urine is dark yellow, there is very little or no urine;
- severe pain in the intestines or rectum;
- temperature above +38ºС;
- stool with blood, pus, or black color;
- any nervous system symptoms such as loss of balance, coordination or numbness.
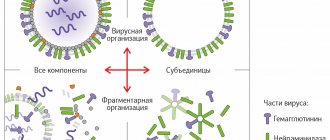
Types of viruses
Intestinal viruses are divided into several types:
- Rotaviruses. They belong to the Reoviridae family and provoke outbreaks of disease during the cold season. The virus causes severe diarrhea with dehydration, especially in children under three years of age. In some cases, urgent hospitalization and intensive rehydration therapy (restoring fluid balance in the body) are required.
- Noroviruses. It is believed that up to 50% of acute intestinal infections are caused by these viruses (family Caliciviridae). In children, noroviruses are the second most common cause of disease after rotaviruses. The virus was first identified in 1972. Clinical symptoms are similar to rotavirus infection. You can become infected not only through airborne droplets, but also through household contact, for example, through a handshake, a kiss, unwashed hands, any objects, toys used by an infected person or a carrier in the recovery stage. A person is contagious in the first two days from the moment of infection. But it may still be “dangerous” for some time, since eliminating the norovirus from the body can take up to two weeks. The first symptoms of the disease appear within 12-48 hours. Immunity is formed, but it is not stable; it lasts for about eight weeks. So you can get sick again if you don’t follow the rules of hygiene.
- Enteroviruses. Representatives of the family Picornaviridae. Most often, the pathogen attacks children, including those in the first year of life, as well as people with weakened immune systems. It is transmitted in the same way as other intestinal viruses.
Course of the disease
The incubation period of rotavirus is 3-5 days. If the microbe enters a weakened body, the first symptoms will develop within 12 hours. It is enough to ride in the same elevator with a sick neighbor in the evening to wake up in the morning from sudden vomiting.
After two or three attacks of nausea, ending with vomiting, the patient develops diarrhea and the body temperature rises to 39˚C. A serious condition can last up to 4 days, during which a number of recommendations should be followed that will allow you to safely cope with the disease at home, excluding a trip by ambulance to the infectious diseases department.
Laboratory diagnosis of intestinal infections
The most susceptible to intestinal infections are young children under 5 years of age, people with weakened immune systems and/or those suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therefore, when the first symptoms and discomfort appear, you should not hesitate; it is better to immediately consult a doctor, get tested and begin restorative treatment. To diagnose acute intestinal infections, CITILAB can perform a number of necessary studies using the PCR method. They reliably allow us to identify the genetic material of the pathogen:
- 97-84-104 — Acute viral intestinal infections (enterovirus, rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus).
- 97-84-102 - Rotavirus types A, C.
- 97-84-103 — Enterovirus.
- 97-84-105 - Norovirus types 1 and 2.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first appointment, the therapist listens to the patient’s complaints, studies the medical history, conducts a visual examination and palpation of the abdomen, measures body temperature and blood pressure.
To differentiate viral gastroenteritis from bacterial and determine the severity of the condition, laboratory diagnostics are performed, which may include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- examination of stool and vomit.
If necessary, the therapist refers the patient for consultation with a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist.
Prevention of intestinal flu
There is no vaccine for intestinal viruses. Therefore, the only way to avoid infection and prevent further spread of the infection is to follow the rules of hygiene:
- Always wash your hands after returning from the street, the toilet, or traveling on public transport.
- Wash all vegetables and fruits (even bananas and kiwis) before eating.
- Drink only boiled and bottled water, not raw (!).
If someone in the house is sick:
- Carry out wet cleaning daily. Wipe all surfaces and objects that a sick person comes into contact with (door handles, plumbing fixtures, especially the toilet seat, children's potty). Viruses are resistant to alcohol and ordinary detergents, so use disinfectant and chlorine-containing household chemicals.
- Dishes, bed linen, and hand towels must be individual.
- Wash all clothes that may have traces of vomit or feces on them immediately at a temperature of at least 60°.
Be healthy!
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Rotavirus in infants
Children of the first year of life are susceptible to infection from the age of 6 months. The course of the disease and recovery time do not differ from those in adults. High fever and diarrhea persist for 3-4 days. Vomiting, as a rule, occurs once, at the very beginning of infection. A small child is also contagious to others, so it is important to protect him from communicating with children on the playground or in kindergarten.
After recovery, parents need to switch the child to a lactose-free formula to eliminate pain in the abdominal area. It will take 9 to 14 days before digestive functions are restored. After which the child can be returned to natural feeding or an adapted milk formula.
What can parents do before the doctor arrives?
Even before the doctor arrives, parents should start giving their sick child something to drink. You can try to do this in various ways. Some children drink well during illness using a spoon. Someone will have to slowly pour liquid into their mouth from a syringe. The main thing is not to rush and do it evenly and regularly - 5-20 ml every few minutes. If the baby continues to have nausea or vomiting, you need to make the intervals between drinks a little longer, but do not stop offering the patient something to drink. In addition to saline solutions, it is useful to drink dried fruit compote and chamomile decoction.
To reduce the symptoms of the disease, sorbents and preparations containing probiotics are used. Sorbents ensure binding and removal of the pathogen from the body. For this purpose, carbon, fibrous, mineral or synthetic sorbents can be used, which effectively sorb and remove from the body food decomposition products formed during enzymatic deficiency, help accelerate epithelial regeneration, reduce flatulence and pain, and also do not affect the composition of normal intestinal flora .
In some situations, enzymes may be used in treatment if the child has difficulty digesting food due to severe damage to the intestines and pancreas.
In addition to medications, it is important to pay attention to diet during illness. To prevent nausea, food should be given to the child in small quantities and more often. For about a month, you should exclude dairy products, fresh vegetables, fruits, pasta, baked goods, pastries, sweets, and fried foods from your diet.
Food is served to the patient boiled, stewed or baked without crust. The child should have such food for about a month, and then the diet can be gradually expanded.
If you rush and do not follow a diet, recovery will slow down. Complications may arise and chronic diseases of the liver, stomach, intestines or pancreas may develop.
What is the danger of rotavirus infection for children?
In a short time, intoxication and rapid dehydration of the child’s body develop, which leads to a rather severe course of the disease. Therefore, the baby runs the risk of receiving not entirely pleasant procedures in the form of injections and intravenous drips.
The maximum incidence of rotaviruses occurs in winter and spring. However, it also occurs during the rest of the year, when it would seem that the “season” has come for other intestinal infections - for example, salmonellosis or dysentery.
Moreover, it is important to distinguish a bacterial infectious disease from a rotavirus infection. Because antibiotics must be used to fight bacteria. Whereas their use for viral infections is not only inappropriate, but also harmful, weakening the functioning of the baby’s already immature immune system.
Photo: www.pexels.com
How to recognize rotavirus infection?
- The incubation period for this disease is from one to two days - the time from the moment of infection until the appearance of the first signs of the disease.
- Sometimes the disease begins gradually with the development of the prodrome period - when the disease does not manifest itself with typical symptoms, but the baby has signs of slight malaise.
“At the same time, infants become capricious, refuse to eat, and develop a slight runny nose and cough. Older children complain of fatigue, poor appetite, rumbling and discomfort in the stomach, headache, chills, nasal congestion, sore throat, and slight cough. Only after 12-72 hours do typical signs of rotavirus infection develop.
Principles of treatment of rotavirus infection
1. Lost fluid is replenished
In case of moderate dehydration, the child is “hydrated” using solutions used orally.
In case of severe dehydration, fluid is administered intravenously in a hospital setting. Also, if the child is able to drink and is conscious, then he is simultaneously continued to be given oral solutions.
How to “desolder”?
It is better to use ready-made pharmaceutical preparations (for example, Regidron, Reosolan or Gidrovit) in powders for dissolution. Because they have an optimal ratio of salts and dextrose.
You can also make a sugar-salt solution at home. To do this, add one teaspoon of salt, half a teaspoon of soda and 8 teaspoons of granulated sugar to one liter of boiled warm water. Then mix everything thoroughly, cool to room temperature and “drink” the baby.
It is necessary to give the baby 1-2 teaspoons of liquid every 5-10 minutes. If you exceed the volume and frequency, you can provoke vomiting, which will lead to even greater loss of fluid from the body.
Moreover, the earlier “wetting” is started, the more favorable the outcome of the disease. Therefore, as soon as the first signs of the disease appear, offer your baby something to drink before going to the doctor.
2. Enzyme preparations are prescribed because the production and activity of digestive enzymes is impaired: Pancreatin, Creon and others.
3. It is advisable to adhere to a diet so as not to increase the fermentation processes in the intestines. To do this, it is recommended to refrain from feeding the child milk and fermented milk products, exclude fruits, and also limit foods rich in easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, pasta made from first-grade flour, and others).
4 . Due to the fact that rotavirus infection disrupts the intestinal microflora, it is advisable to use bacterial biological preparations containing lactobacilli: Lactobacterin, Acylact and others.
5. An immunoglobulin complex preparation (ICP) for oral use , containing antibodies (proteins) against rotaviruses, salmonella, Escherichia and some other pathogens of intestinal infections, has proven itself well Moreover, its use significantly reduces the duration of diarrhea, and also reduces the signs of intoxication. Therefore, recovery occurs many times faster.
6. To accelerate the removal of viruses and toxins from the body, enterosorbents are used: Lactofiltrum, Enterosgel and others.
7. Body temperature is lowered using medications containing paracetamol or ibuprofen. They are used in the form of suppositories (if stool allows, this manipulation may cause it to become more frequent) or syrup (if vomiting is rare). In case of excessive vomiting and diarrhea, an antipyretic mixture is injected intramuscularly.
Causes
The causative agent of rotavirus infection in children and adults is rotavirus, which has the ability to survive even when treated with potent disinfectant solutions. In the feces of a sick person, its vital activity persists for 7 months, in environmental conditions - for more than a month. The infection is transmitted from a carrier or a sick person through the fecal-oral route through water, food and household items, especially when the sanitary and hygienic condition of the premises is unsatisfactory.
Patients at risk for rotavirus include:
- childhood;
- with disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, when it is suppressed;
- with chronic intestinal diseases;
- with violations in the diet, as well as when changing baby food;
- working or visiting large groups;
- not observing the rules of personal hygiene.
What consequences can rotavirus have?
In mild cases, the infection usually ends without complications, and the body recovers in one to two weeks. In severe cases of the disease and untreated, the disease can be complicated by severe manifestations of dehydration: kidney failure, shock, malabsorption of nutrients in the stomach and intestines, blood thickening, interruptions in heart function, decreased body defenses and secondary infection.
Long-term consequences of untreated rotavirus infection include:
- dysbacteriosis;
- chronic gastritis;
- chronic colitis;
- avitaminosis;
- insomnia;
- anemia.
As a result of weakening the body's defenses, herpes, skin acne and fungal infections can develop.
If you seek medical help in a timely manner and treatment is started on time, the prognosis for rotavirus infection is favorable.
A few words for pregnant women: as a rule, rotavirus is not dangerous to the fetus. The main threat of this infection is dehydration of the expectant mother!