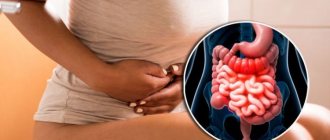
Why might my right side hurt?
The causes of this symptom are usually associated with internal organs. “This is a sign that something located on the right side of the abdomen is suffering,” says Bulat Yunusov, a surgeon at GMS Clinics and Hospitals. “The cause of damage to these organs can also be different, for example, inflammation, oncological processes, trauma, consequences of previous operations, neurological disorders.”
However, this symptom may have other reasons. “An unpleasant sensation in the right side can be muscular in nature, especially if it occurs after physical activity. If a person falls on their right side, the pain may be associated with muscle contusion or injury, such as myositis. Gallstones can also cause an uncomfortable tingling sensation in your side. The stones close the ducts, which leads to swelling of the bladder and, as a consequence, to the occurrence of calculous cholecystitis, that is, an inflammatory process. All this, of course, is accompanied by pain,” commented an invited specialist from another medical center. Let's look at the main causes of pain in the right side.
Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Hepatitis
Jaundice
Vomit
37948 05 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The right hypochondrium is one of nine areas into which the anterior abdominal wall is conventionally divided. This area belongs to the so-called “upper floor” of the abdominal cavity.
In the right hypochondrium there are the liver, gallbladder, hepatic angle of the colon, and swollen loops of the small intestine can also be projected into this area. The organs listed above belong to the digestive system.
The liver is a parenchymal (spongy) organ with a very good blood supply. The outside of the liver is covered with a capsule in which nerve endings are located. The liver is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and plays a vital role in detoxification of the body.
Harmful substances that enter the liver are subjected to “chemical” processing, which makes them less toxic to the body and promotes faster elimination through the gastrointestinal tract and urine.
In addition, liver cells produce bile necessary for digesting food, primarily fats. Bile enters the gallbladder, located on the lower surface of the liver, where bile accumulates, which is released from it into the duodenum during the next meal.
From above, the liver is adjacent to the diaphragm - a kind of muscular partition between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. From below, from the side of the abdominal cavity, the diaphragm is lined with peritoneum (which covers the entire abdominal cavity and organs located in it from the inside), and from above, from the side of the lungs, by the pleura, which lines the pleural cavity from the inside and covers the lungs from the outside. Both the pleura and peritoneum have good innervation, which is important to know to understand the causes of pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The peritoneum also covers the gallbladder and intestinal loops.
Types of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
The pain in the right hypochondrium can be acute, sometimes “dagger-like”, which makes you think about a serious illness. This pain is characteristic of hepatic colic and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, increased heart rate and a drop in blood pressure.
In chronic diseases and the gradual development of acute diseases, the pain is often dull, bursting in nature, or is described by the patient as “heaviness, discomfort” in the area of the right hypochondrium.
Pain syndrome can be spontaneous, or it can be provoked by food intake, alcohol, physical activity, change in body position, etc.
Possible causes of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
There is only one mechanism for the development of pain: stimulation of pain receptors. As mentioned above, the peritoneum has good innervation. Also, a large number of nerve endings are localized in the wall of hollow organs (intestines, gall bladder). Therefore, inflammatory processes in these organs naturally manifest themselves as pain.
Pain also occurs when the liver capsule is stretched. This can occur due to an increase in the volume of the organ (which in most cases is associated with tissue swelling), due to the accumulation of any fluid (most often blood) under the capsule (with a traumatic rupture of the liver), or damage to the capsule.
Unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium are caused by excessive distension of the intestinal loops by intestinal contents or gases. In addition, since the organs of the chest are located close to the right hypochondrium, in case of development of pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura), the pain syndrome can also be localized in the right hypochondrium and imitate diseases of the abdominal organs.
Diseases that cause pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Among acute diseases accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning first of all those that require emergency surgical intervention.
These include
acute calculous cholecystitis
and
renal colic
.
Both conditions are a consequence of cholelithiasis
. Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) develops against the background of an already advanced process of stone formation or, conversely, is the cause of the formation of stones. With renal colic, a calculus (stone) becomes wedged into narrow segments of the biliary tract, which is accompanied by severe pain, impaired bile outflow, and in more severe cases – jaundice (yellowing of the sclera and skin).
Other diseases of the biliary tract, such as
biliary dyskinesia
,
chronic cholecystitis
, cause recurrent pain in the right hypochondrium, usually associated with an error in diet.
Another disease classified as an “acute abdomen” that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium is appendicitis.
(inflammation of the appendix).
Despite the fact that the classic position of the appendix corresponds to the right iliac region, an abnormal position of the appendix in the right hypochondrium is quite common, especially in children.
Overdistension of intestinal loops can develop as part of
intestinal obstruction
.
Swelling of the liver tissue is characteristic of hepatitis (inflammation of the liver parenchyma). Hepatitis can have a variety of origins: viral hepatitis A, B, C, etc., autoimmune, toxic, incl. alcoholic. These diseases are usually accompanied by pain, as well as weakness, nausea and vomiting, yellowing of the skin and sclera, change in the color of urine and feces.
Subcapsular hematomas of the liver (accumulation of blood between the liver tissue and its capsule), as well as ruptures of the liver capsule, are usually traumatic in nature.
Among the diseases of the chest that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning pleuropneumonia (inflammation of the lung tissue and pleura), heart failure, intercostal neuralgia and herpes zoster. The latter is characterized by the appearance of blistering-type skin rashes, which are preceded by severe pain.
Which doctors should you contact if you experience pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium?
If sudden, progressively increasing pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, you should contact a doctor to exclude acute surgical pathology. If the pain is not acute, the examination can begin at or. If necessary, the patient can get advice from a hepatologist (a specialist in liver diseases) and other specialized specialists.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
After a detailed survey and comprehensive clinical examination, the doctor, as a rule, needs laboratory and instrumental confirmation of the diagnosis. For this purpose, the following studies are used:
- A clinical blood test with determination of the leukocyte formula, based on the results of which one can suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and determine its severity.
Inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Pain and cramps in the right side can be caused by a whole “bouquet” of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. “These are, for example, appendicitis, diverticulitis, colitis, gastroenteritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Most often, with these diagnoses, the pain is felt as aching, moderate, with gradually increasing intensity. With appendicitis, pain may increase when walking, coughing, changing body position and decrease at rest. Also with this diagnosis, there is an increase in temperature, nausea, and vomiting.
With a stomach ulcer, the pain becomes more noticeable after eating fatty, spicy or fried foods, alcohol, and intense physical activity. Additional symptoms may include heartburn, nausea, and vomiting.
With colitis (inflammation of the intestines), the pain can be nagging or paroxysmal. The disease is also accompanied by diarrhea, fever, general weakness, headaches, and the presence of mucus in the stool.
With diverticulitis (protrusion of the intestinal walls), acute pain is felt to the right of the navel, the temperature rises, and diarrhea (with blood and mucus) appears.
With gastroenteritis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine), pain in the right side is accompanied by lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, etc.
With pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), the pain begins suddenly and is constant and intense. Sometimes it can “give” to the left side or get worse after eating heavy, fatty or spicy foods.
Diseases of the urinary system
Often the side on the right side hurts due to the organs of the excretory system. “These include urolithiasis and pyelonephritis,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which, in addition to pain in the right side, weakness, nausea, vomiting, “jumping” pulse, dry mouth, and high temperature may also occur.
Pain in the side due to urolithiasis can be constant or wave-like, dull or sharp, it can only bother you at rest or intensifies when walking. It depends on the location of the stone, but sometimes the pain may first be felt in the lumbar region (so-called “renal colic”), and only then “settle” in the right side.
Liver diseases
“Pain in the right side can occur with damage to the liver and organs of the hepatobiliary system,” notes Bulat Yunusov. “Such diseases include cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice, liver cysts, hepatitis, and cirrhosis.” All of these diagnoses are characterized by fairly sharp pain in the right side, which can “radiate” to the right shoulder, neck or shoulder blade.
Women often experience pain on the lower right side due to malfunctions of the pelvic organs. “Such work disorders include inflammatory diseases (salpingitis, salpingoophoritis) and non-inflammatory (corpus luteum cyst, ovarian tumors, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy),” notes Bulat Yunusov.
With salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes) and salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries), the pain is most often felt as a pulling in the groin area, but it can also “radiate” to the right or left side. Accompanied by fever, nausea, severe headache, vaginal discharge and intensifies during sexual intercourse.
With ovarian or corpus luteum cysts, pulling or stabbing pain is mainly localized in the lower abdomen or lower back, but can also be felt in the right side.
With endometriosis, the pain is most often acute, cramping, and can disappear and return. It is felt, as a rule, in the lower abdomen, in the left or right side (closer to the lower back).
Causes of abdominal pain on the right in women
Pain in the lower abdomen in women occurs before menstruation and is caused by contractions of the uterus. The discomfort goes away after 2-3 days. Often, on the 14th day from the start of menstruation during the period of ovulation (maturation and release of the egg into the uterine cavity), women complain of nagging pain or cramps in the lower abdomen on one side. In this case, there is slight bloating and an increase in vaginal discharge. The condition does not require medical intervention. If pain on one side (right or left) is not associated with menstrual bleeding, gynecological pathology should be excluded. In this case, the nature of the pain will help make a preliminary diagnosis.
- Acute pain - ectopic pregnancy, rupture of an ovarian cyst, adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages). The pain syndrome is often accompanied by bloody discharge, and the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates.
- Aching pain - fibroids, uterine flexion, endometriosis, corpus luteum cyst. The pain intensifies during sexual intercourse and is accompanied by pathological discharge from the vagina. If the intensity of the pain increases sharply and blood appears, you should urgently seek medical help.
Important! All women who complain of pain in the lower abdomen are referred to a gynecologist for consultation.
Pain in the right side may be associated with pregnancy - the growing uterus puts pressure on the abdominal organs. There is an unpleasant, throbbing pain, frequent urination, and heartburn. Fetal movements are often mistaken for pulsation. The first conscious movement is recorded at 18-20 weeks; before this period, fetal movements are usually not felt. Pain in the abdomen on the right and in the groin area during pregnancy is caused by the divergence of the pelvic bones. However, with severe abdominal pain on the right side in a pregnant woman, acute surgical pathology cannot be ruled out: cyst torsion, intestinal obstruction, abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Important! If there is pain in the lower abdomen on the right or left, warming procedures (using a heating pad) are strictly prohibited. This will only increase bleeding during menstruation, and in pregnant women it can cause a miscarriage. Expectant mothers should not take medications (painkillers, antispasmodics) without a doctor’s prescription. Many modern medications negatively affect the fetus and uterine tone.
Cramping pain in the abdomen after childbirth, which intensifies during breastfeeding, is a normal phenomenon caused by contractions of the uterus. However, due to overstretching of the ligamentous apparatus in the postpartum period, an umbilical hernia often forms. Protrusion of the abdominal wall is accompanied by painful sensations in the navel area on the right or left, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen.
Constipation can cause abdominal pain in women giving birth. Therefore, it is important to do squats after childbirth, in consultation with your doctor. Abdominal exercises will speed up uterine contractions, reduce blood loss and strengthen the abdominal wall.
Important! Taking laxatives is contraindicated for nursing mothers. This will lead to diarrhea in the baby. Prunes, oatmeal, fermented milk products and consuming 1 tbsp. will help improve defecation after childbirth. l. sunflower oil in the morning. Of the medications, the safest are glycerin suppositories.
The development of postpartum endometritis cannot be ruled out. After cesarean section, inflammation of the uterus occurs in 43% of cases. The disease is manifested by fever, purulent discharge and increased bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen and groin. The risk of disease is reduced by a prophylactic course of antibiotics.
Response to physical activity
Sometimes the right side hurts not due to malfunctions in the internal organs (which we discussed above). If you feel pain on the right side during (or immediately after) physical activity, there is a chance that it is:
- Muscle spasm caused by weakness in the muscles of the back or abdomen.
- Diaphragm spasm. It is most often encountered while running: rapid breathing causes the diaphragm to contract faster, which can cause it to spasm and “give off” pain in the right side.
- Increased liver function. This organ is considered the “blood” depot of the body. During training, the liver may increase slightly in volume and “press” on its outer capsule, where there are many nerve endings, which will be felt as pain in the right side. And such discomfort can also arise due to an incorrect diet: for example, if before training you “got too much” with carbohydrates or fats. In this case, during exercise the liver will be forced to work under increased load, which can also provoke pain.
How to determine why you have pain in your right side
Of course, you won’t be able to make an accurate diagnosis on your own. However, you can get some idea about it based on exactly how your right side hurts. “In acute diseases, pain occurs suddenly, increasing in intensity in a short period of time (hours, sometimes days),” notes Bulat Yunusov. “If the cause is some kind of chronic disease, then the pain syndrome is either constant or wave-like in nature, not very intense.”
It is also important to check for additional symptoms. “To correctly determine the cause of pain in the right side, you need to listen to the nature of this pain. For example, muscle pain is usually dull and aching,” the invited specialist commented. “However, muscle pain can also be acute, since in addition to the muscles in the right side there are intervertebral joints that can be a source of discomfort. In case of cholelithiasis or acute cholecystitis, the pain is accompanied by fever. This situation can be called “pain-plus” - pain and fever. Discomfort caused by renal colic can also be “pain-plus,” but pain plus frequent urination or the presence of blood in the urine. Pain caused by intestinal problems—pain plus diarrhea.”
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce pain in the right hypochondrium, it is recommended to follow a diet limiting fried, fatty, smoked foods, preserved foods and spices. Alcohol consumption is prohibited. The diet should consist of fruits and vegetables, lean fish and meat. If the pain syndrome intensifies, it is necessary to reduce physical activity and adhere to a gentle or semi-bed rest.
To stop an attack of spastic pain, you can use a warm (not hot!) heating pad, which is applied to the right hypochondrium. Cramping pain is well relieved with antispasmodics. Persistent pain is a reason to consult a doctor, since the symptom can be caused by dozens of different diseases that, without treatment, lead to serious complications.
Conservative therapy
Moderate pain in the right hypochondrium, arising from chronic diseases of the hepatobiliary tract, is treated on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is required for patients with severe pain and severe general condition. In the hospital, narcotic analgesics are used to relieve unbearable pain, and detoxification therapy is carried out. To eliminate the causes of pain, several groups of medications are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. They have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, so they quickly relieve pain. For functional biliary disorders, NSAIDs are combined with antispasmodics. - Cholekinetics
. Medicines that improve the flow of bile are necessary to relieve pain and discomfort and improve digestive processes. To enhance their effectiveness, they are combined with choleretics. - Antibiotics
. Medicines are prescribed for exacerbation of cholecystitis and cholangitis, which is caused by activation of pathogenic microflora. The selection of antibacterial agents is carried out taking into account the data of bacterial culture and bacterioscopy of bile. - Interferons
. Recombinant drugs are indicated for the treatment of chronic forms of viral hepatitis B and C. For the treatment of HCV, modern drugs from the group of protease inhibitors are effective, which provide complete cure. - Hepatoprotectors
. Products with UDCA and ademetionine are intended to protect healthy liver cells from damage and stimulate the regeneration of hepatocytes. The drugs increase the organ’s resistance to toxic factors and improve its detoxification function.
For chronic diseases of the gallbladder, courses of medicinal mineral waters are prescribed. Hepatobiliary pathologies in remission are an indication for physiotherapeutic treatment: reflexology, electrophoresis, SMT therapy. Herbal medicine methods are recommended to improve digestion. Sanatorium-resort treatment is widespread.