Home — Rules for preparing a patient for laboratory and ultrasound examinations — Preparation for blood tests
Food restrictions | Capillary blood | General clinical analysis | Biochemistry | Coagulogram | Hormones | Infections | Glucose tolerance test | TSH | Vitamin D
Blood counts can change significantly throughout the day, so it is recommended to take tests in the morning. For this period, reference intervals for many laboratory parameters have been calculated. This is especially important for hormonal studies.
- All blood tests are done before radiography, ultrasound and physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Do not smoke 2 hours before donating blood.
- For 2-3 days, do not overeat, especially fatty foods, avoid alcohol, intense physical activity, and also do not visit the bathhouse or sauna.
General rules for preparing for blood tests
In all cases, before donating blood, it is recommended to adhere to several rules:
- Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach (or in the afternoon and evening, 4-5 hours after the last meal). Blood counts can change significantly throughout the day, so it is recommended that all tests be taken in the morning.
- Do not eat fatty foods several hours before the test, it is advisable not to eat for 4 hours - a high concentration of fats in the blood can interfere with any test.
- Shortly before taking blood, drink 1-2 glasses of ordinary still water; this will reduce the viscosity of the blood, and it will be easier to take a sufficient volume of biomaterial for research; in addition, it will reduce the likelihood of clots forming in the test tube.
- If possible, stop taking medications at least a day before the test.
- When taking tests while taking medications, you must indicate this fact on the referral form.
- It is recommended not to exercise on the day of the test.
- On the day of the test, it is recommended to exclude increased emotional stress.
- On the day of the test, it is recommended to take a comfortable position (sit down), relax, and calm down a few minutes before taking blood.
- Avoid drinking alcohol for 72 hours before taking the test.
- Do not smoke at least 30 minutes before blood collection.
- Clarify the optimal days of the menstrual cycle (or pregnancy period) for donating blood for sex hormones.
- FSH is follicle stimulating hormone. A woman should be tested for this sex hormone on days 3-7 of the cycle. To determine the possibility of follicle growth, FSH is taken on days 5-8 of the cycle;
- LH – luteinizing hormone. LH in men is responsible for increasing the permeability of the seminiferous tubules to testosterone. LH in women ensures completion of egg maturation in the follicle and ovulation, secretion of estrogen and formation of the corpus luteum. Women should undergo a blood test for LH on days 3-8 of the cycle;
- Prolactin . If prolactin levels are elevated in a man, sexual function may be impaired. In women, prolactin takes part in the ovulation process and stimulates lactation in the period after childbirth. To determine the level of this hormone, the analysis should be carried out in phases 1 and 2 of the menstrual cycle, and the sample should be taken only in the morning on an empty stomach. Before blood sampling, the patient is recommended to spend 30 minutes at rest, since prolactin is a stress hormone, as a result of which slight physical activity or anxiety can affect its level;
- Estradiol . In women, analysis can be taken at any phase of the menstrual cycle. Estradiol in women ensures the formation and regulation of menstrual function and the development of the egg;
- Progesterone . This hormone is responsible for ensuring the final preparation of the uterine lining for the embryo to attach. Progesterone provides optimal conditions for pregnancy to develop. The test is scheduled for days 19-21 of the menstrual cycle;
- Testosterone . Testing of this hormone in women can be carried out on any day of the cycle. If a man’s concentration has decreased, this entails a decrease in sperm quality and insufficient virility;
- DHEA sulfate . If the concentration of the hormone is increased in a woman, this may cause disruption of the ovaries and infertility. A woman’s hormone levels can be checked on any day of her cycle.
Hormones
Blood collection is carried out strictly on an empty stomach: at least 8 hours must pass from the last meal (preferably at least 12 hours). You are allowed to drink water (non-mineral, non-carbonated). It is forbidden to drink juice, tea, coffee. 2-3 days before the test, do not overeat, especially fatty foods. Avoid alcohol, intense physical activity, and do not visit the sauna or bathhouse.
- On the day of blood collection, avoid taking medications; if withdrawal is not possible, inform the laboratory.
- When studying hormones over time, it is advisable to take blood samples at the same time of day.
- Some hormones need to be taken by women on certain days of the menstrual cycle. This information can be obtained from your doctor.
Attention!Q Blood collection for cortisol is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, strictly in the interval from 8:00 to 11:00 (the exact time of venipuncture is indicated).
General rules for preparing for urine tests
Single sample urine tests
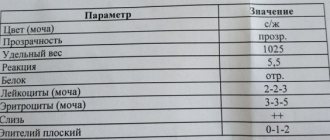
Depending on the required laboratory tests, the first, middle, third (usually morning) or “one-time” (independent of the collection sequence) portion of urine can be used for analysis. Urine for testing is collected by the patient in a sterile plastic container.
To obtain reliable results, it is recommended to comply with the following conditions:
- It is not recommended to consume on the eve of the study (10–12 hours before): alcohol, spicy, salty foods, foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots);
- If possible, avoid taking diuretics;
- Before taking the test, perform a thorough toileting of the external genitalia;
- For women, the study is recommended to be carried out before menstruation or 2 days after its end;
- The PCR method for diagnosing urogenital infections in urine is suitable exclusively for men; in women, this diagnostic method is much inferior in its information content to the study of a urogenital smear and is not used.
Daily urine tests
urine sample is all urine collected over a 24-hour period.
Daily urine is most often collected by the patient independently at home using a special kit for collecting and transporting a daily urine sample. Before the collection begins, the patient is given the necessary instructions about the collection procedure and the necessary measures to prepare for the test.
To obtain reliable results, it is recommended to comply with the following conditions:
- It is not recommended to consume on the eve of the test (10–12 hours before): alcohol, spicy, salty foods, foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots).
- If possible, avoid taking diuretics.
- Before taking the test, perform a thorough toileting of the external genitalia.
- For women, testing is not recommended during menstruation.
Where do they get it from?
Usually from a finger. To do this, one of the fingers, usually the ring finger (since a large blood vessel approaches it), is lubricated with an antiseptic, a puncture is made up to three millimeters deep, and the blood is collected on glass and in a test tube.
Less commonly, from a vein: they tighten the forearm with a tourniquet, pierce the vessel in the elbow area and collect it in a flask. This method is less painful and is usually used in commercial laboratories.
In 2015, scientists from Rice University (USA) proved that the standard method of drawing blood from a finger is not informative. The small volume of biological material does not allow one to accurately determine the level of hemoglobin, and for 40% of diseases, the volume of blood tested must be at least 20 ml. Biological material from the vein is sufficient for clinical tests and obtaining reliable results.
pixabay.com/
General rules for preparing for stool tests
To collect and transport stool, the patient is given a sterile plastic container with a spoon. The container may contain a nutrient medium (peptone) or a preservative, depending on the type of study.
The release of helminth eggs and protozoan cysts in feces directly depends on the life cycle of the parasites. For this reason, the test results may be negative even if infection is present. For the most reliable results, three stool examinations are recommended with an interval of 3–7 days.
Important Notes
Material for research
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications).
Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood.
Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications).
According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Microbiological and PCR studies
- The study is recommended to be carried out before starting antibiotics and other antibacterial chemotherapy drugs (if this is not possible, then no earlier than 12 hours after discontinuation of the drug).
- Avoid taking laxatives, administering rectal suppositories, oils, limit taking medications that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine, etc.) and drugs that affect the color of stool (iron, bismuth, barium sulfate) for 72 hours before stool collection .
- The material obtained after an enema, after taking radiopaque substances (barium during X-ray examination) is unsuitable for research.
General clinical and antigen studies
- Avoid taking laxatives, administering rectal suppositories, oils, limit taking medications that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine, etc.) and drugs that affect the color of stool (iron, bismuth, barium sulfate) for 72 hours before stool collection .
- The study should be carried out before performing sigmoidoscopy and other diagnostic procedures in the intestines and stomach.
- To test stool for occult blood, exclude meat, fish, green vegetables, and tomatoes from the diet for 72 hours before the test.
Urogenital urethral smear in men
- For 2 weeks before the study, exclude the local use of antiseptics and/or antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
- For 3 hours before the examination, refrain from urinating and do not toilet the external genitalia.
- It is recommended to analyze a urogenital smear in a man no earlier than 2 weeks after taking antibacterial drugs.
- In men with urethral discharge, the surface of the glans and the external urethral meatus should be cleaned with a gauze pad and the foreskin pulled back to prevent contamination.
General rules for preparing for sputum tests
- The patient collects sputum independently through deep coughing.
- Sputum collection is recommended to be carried out in the morning.
- Before collecting sputum, it is recommended to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth and throat with boiled water.
- Smears (scrapings) from the surface of the cervix (external uterine pharynx) and cervical canal for atopy.
- It is advisable to take smears no earlier than on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
- You cannot obtain smears within 24 hours after sexual intercourse, the use of lubricants, vinegar or Lugol's solution, tampons or spermicides, douching, insertion of medications, suppositories, creams into the vagina, including gels for ultrasound examination.
- In case of acute infection, it is advisable to obtain material for the purpose of examination and identification of the etiological agent; after treatment, but not earlier than 2 months, cytological control is necessary.
For prevention
What tests should I take to “just check my health”?
Health is a fairly stable complex of various functions of the body, which for a long time compensates for all the “problems” that arise. In this regard, it is not surprising that most diseases develop over years, or even decades, without manifesting themselves clinically.
At the same time, identifying abnormalities at an early stage makes it possible to prevent the development of serious complications, and the examination itself, as a rule, takes no more than an hour.
The main thing
The list of annual screening for absolutely all groups of patients includes:
- general analysis with leukocyte formula (control of anemia, platelet levels and general inflammatory processes),
- analysis of liver condition (ALT, AST, total bilirubin, gamma-GT, total protein) and
- kidneys (urea, creatinine),
- atherosclerosis risk assessment (LDL, VLDL, atherogenicity coefficient) and
- diabetes mellitus (glucose, glycated hemoglobin),
- assessment of thyroid hormone levels (TSH).
For women, this list is supplemented by screening for cervical cancer with HPV, and for men - PSA (prostate-specific antigen).
Screening is recommended from the age of 25, and its “composition” is determined by morbidity statistics for the listed organs and systems.
Thus, diabetes mellitus can manifest itself in childhood (especially type 1 diabetes), and its complications are always severe and, more often, irreversible (for example, amputation of limbs).
The liver and kidneys are so “busy with work” that they can “fail” already at a young age. Thyroid dysfunction is more common in women. Atherosclerosis has long ceased to be an “age-related” disease and threatens with stroke and infarction.
Cervical cancer is becoming increasingly “younger” and is increasingly being detected in women under 29 years of age. And the prevalence of prostatitis and prostate adenoma in men dictates the need to control this organ.
All of these studies (except for cervical cancer screening) can be completed either individually or in a convenient complex format: “Women, level 1” and “Men, level 1”.
Liquid cytology with HPV will help assess the risk of cervical cancer.
With age
Screening of women and men aged 40-49 years includes the same indicators as the 1st level + examination:
- osteoporosis risk assessment (25-OH vitamin D, phosphorus, calcium),
- cardiovascular disease risk assessment (homocysteine),
- assessment of magnesium and zinc levels.
Preventive examination at 50-65 years old, compared with the previous age group, has been supplemented:
- assessment of the risk of rheumatological diseases and systemic inflammation (C-reactive protein),
- as well as an additional indicator of calcium metabolism (parathyroid hormone).
The complex is called “Without unnecessary problems” and is also presented for women and men.
The complex for the age group 65+ years has been expanded:
- identifying hidden iron deficiency (ferritin) - as a sign of possible oncology and chronic inflammatory processes,
- marker of heart failure (brain natriuretic peptide)
and is called “The Most Important Thing” (for men and women).
In addition, for both sexes at the age of 40+, screening for intestinal cancer is recommended - stool analysis for transferrin and hemoglobin and tumor pyruvakinase.
Of course, it is unfortunately not possible to cover all possible pathologies with one analysis. However, even regular “general” examinations can help in the timely detection of the most common pathologies.
General rules for preparing for hair analysis
Scalp hair is the most preferred biomaterial for research. Hair from other areas of the body should only be used if there is no hair on the head.
- Stop using hair treatments 2 weeks before submitting your hair for analysis. Dyed, bleached, permed hair is not suitable for research. You must wait until enough hair has grown back to collect a hair sample.
- Hair should be clean and dry (it is advisable to wash your hair no later than 24 hours before collecting hair). Before the study, it is not allowed to apply any cosmetic or medicinal products (creams, oils, gels, etc.) to the hair.
- Avoid professional contact of hair with external contaminants (welding, mining) between shampooing and hair collection.
- Before collecting hair, thoroughly wash and dry your hands and scissors.
Tests for women
Women, first of all, need to visit a gynecologist once a year, or better yet, once every six months. Only regular preventive visits can preserve women's health and avoid negative consequences, because Some diseases go away with virtually no symptoms - a woman may not be bothered at all - this is the specificity of female diseases.
Annual preventive examinations of women should include:
- Examination of the mammary glands: up to the age of 40, it is enough to regularly do ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs: evaluates the size, shape, structure, location, blood supply of the following organs and parts: uterus, uterine cavity, cervix, ovaries and fallopian tubes. The study allows the doctor to obtain information about changes in organs in the shortest possible time and determine effective treatment tactics.
- Colposcopy is a technique for examining the vaginal part of the cervix using a special device - a video colposcope and simultaneously conducting diagnostic tests. Allows you to identify precancerous and cancerous diseases, cervical polyps, condylomas, endometriosis, atrophy, and inflammatory changes at the early stages of development.
It is also recommended to have a smear to infections and a test for papillomavirus (HPV or human papillomavirus), which causes the formation of warts and papillomas. For women, HPV is especially dangerous because... it can provoke cervical cancer and other cancers, and this risk only increases with age.