Along with diseases of the cardiovascular system throughout the world, joint diseases hold the palm. Many of them are chronic and often lead to disability. Orthopedists and rheumatologists prefer conservative methods, and diet plays an important role in therapy. Nutrients directly affect how intense the inflammatory process will be in tissues. What nutritional recommendations do doctors give for arthrosis, arthritis, gout?
Nutrition is part of conservative therapy for joint pathologies
Subtleties of therapeutic nutrition for gout
In gout, the metabolism of purine bases is disrupted. The disease is manifested by damage to the joints and internal organs, the cause of which is the deposition of uric acid salts.
Gout can be primary, which is also called idiopathic, and secondary, when the disease is caused by medication. Excessive amounts of uric acid are formed due to the fact that a person consumes a lot of foods that contain purine bases. The second option is that these substances are synthesized in the body in increased quantities. In this case, the kidneys cannot cope with excretion.
Before the advent of drug treatment, diet therapy was perhaps the only effective way to influence the course of the disease. Its main principles are:
- it is necessary to limit the consumption of meat and fish, since they contain a lot of purine bases;
- milk and cereals are introduced into the diet, which contain a minimum amount of these bases;
- the person is advised to drink plenty of fluids;
- If you are overweight, you need to get rid of it.
Walnuts
Walnuts contain a significant amount of compounds that have anti-inflammatory effects.
Scientific work shows that their addition to the diet has a positive effect on the course of rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune intestinal diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis). The effects are associated with the omega-3 fatty acid content of the nuts.
Healthy polyunsaturated fats also reduce the intensity of pain, stiffness after sleep and improve general condition.
In addition to walnuts, scientists recommend eating pistachios, peanuts, hazelnuts and almonds. They contain a lot of useful substances and are recommended for use by rheumatological patients.
Walnuts contain a lot of omega-3 fatty acids, which effectively eliminate inflammatory processes in the joints and are a means of symptomatic therapy.
What is the difference between nutrition during an exacerbation and outside of an acute exacerbation of gout?
During an exacerbation, a person is recommended to take mainly liquid food - lactic acid drinks (kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt), milk, homemade compotes, juices, simple liquid porridges and vegetable soups. It is necessary to completely abandon meat and fish products. Hunger and moisture deficiency are contraindicated: it is important to drink at least 2 liters of liquid, especially mineral waters with an alkaline composition.
When an acute attack of gout subsides, you can eat 100-150 g of boiled meat no more than twice a week, and on other days you can gradually add dairy products to your diet (lactic acid products are preferred), cereals, eggs, fruits and vegetables.
If gout flares up, you need to stick to a strict liquid diet for at least 1-2 weeks.
Garlic
The active substances contained in garlic have pronounced chondroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
Garlic has been noted to have a positive effect on the symptoms of arthritis by improving the functioning of immune system cells.
Particular attention is paid to sulfur compounds. They suppress the destruction of the matrix (intracellular fluid) in chondrocyte-like cells by inhibiting a number of enzymes, thereby preventing the manifestation of osteoarthritis.
Korean scientists have concluded that thiacremonone, contained in garlic, reduces the intensity of pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reduces the severity of edema (including in the periarticular tissues), and accelerates the healing of damaged segments.
In addition, with regular addition of garlic to food, the risk of developing atherosclerosis and type II diabetes mellitus is reduced.
It is recommended to eat 2-3 cloves of garlic per day.
Regular addition of garlic to the diet can improve the condition of the musculoskeletal system and the entire body due to its pronounced anti-inflammatory properties.
Outside of an exacerbation of an attack, a person is recommended to:
- limit the intake of proteins and refractory fats into the body;
- reduce salt consumption to 5-7 g, including that contained in foods;
- increase the volume of seasonal vegetables, fruits and dairy products;
- exclude from the diet foods that contain purines that are hazardous to health in large quantities: meat extracts, beef innards, small shrimp, sardines and mackerel, legumes;
- reduce the intake of meat, fish, legumes - peas, beans, lentils;
- practice fasting days;
- If you are overweight, give up sugar and baked goods.
For gout, the meat of young animals, which contains a lot of purines, is especially contraindicated.
Olive oil
Olive oil has an extremely beneficial effect on the course of arthritis. Studies on rodents have found that consuming oil for 1.5 months slows down the process of destruction of cartilage tissue and helps to delineate the source of inflammation.
Using olive oil instead of sunflower and other types reduces the concentration of C-reactive protein by almost 40%.
Adding olive oil to food is an independent factor preventing the manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis.
Olive oil reduces inflammatory changes and prevents the development of arthritis of any origin.
What nutrition is indicated for arthrosis?
A comprehensive treatment regimen for osteoarthritis always includes nutritional recommendations. A thoughtfully designed diet allows you to avoid excess weight and provides the body with the necessary supply of vitamins and minerals. Antioxidants are of particular importance for joints, namely vitamins A and E, omega-3 fatty acids. Also, in order for the body to produce chondroitin and glucosamine, a person must receive sufficient amounts of vitamin C and manganese.
TOP 10 products that must be present in the diet for arthrosis:
- Fresh vegetables.
- Seasonal fruits.
- Greenery.
- Lean fish.
- Whole grains.
- Dairy products with low fat content.
- Various nuts.
- Low-fat butter.
- High quality olive oil.
- Jelly.
With arthrosis, it is important to get enough vitamin C so that chondroitin and glucosamine are produced
Broccoli
Since ancient times, broccoli has been considered one of the healthiest foods and has been used to treat many diseases.
According to the accumulated data of Chinese scientists, the plant reduces the concentration of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-a, interleukins 1 and 6). As a result, the course of the inflammatory reaction in the joints and its symptoms quickly disappear.
Broccoli contains a special component - sulforaphane. It, according to researchers, prevents the formation of immune cells that secrete inflammatory mediators.
Eating broccoli leads to a decrease in the severity of any inflammatory processes in the body. Positive properties have been proven specifically for joints.
What is recommended for osteoporosis?
With osteoporosis, bone density decreases and the risk of bone fracture increases. The cause of the disease is insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D into the body, consumption of alcohol in large quantities, medications of the glucocorticoid group, as well as the postmenopausal period.
Diet therapy for osteoporosis involves the following rules:
- taking calcium, which reduces the progression of the disease (the main source is milk and dairy products);
- consumption of foods with a high content of the microelement magnesium, which also promotes better absorption of calcium by the body (foods such as sesame, almonds, hazelnuts, watermelon, sunflower seeds, oatmeal contain it);
- taking vitamin D (fatty fish, caviar, liver of various origins, milk fats, eggs);
- Postmenopausal women are recommended soy-based products that have an estrogen-like effect;
- It is important to reduce your salt and coffee intake.
In osteoporosis, calcium comes first
Grape
Grapes have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, prevent the development of atherosclerotic changes in the walls of large vessels.
As a result of one experiment, it was proven that when consuming 250 g of fresh grapes daily for 3 weeks, there is a decrease in the concentration of inflammatory markers (adiponectin, interleukin 10) in the blood, which has a beneficial effect on the course of autoimmune diseases of the joint and ligamentous apparatus.
In addition, the skins of grapes, as well as wines based on them, contain a significant amount of resveratrol, a special substance that has a negative effect on the release of mediators of the inflammatory response into the bloodstream.
Grapes improve the clinical course of arthritis by inhibiting inflammatory processes.
Nutrition secrets for rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is thought to be caused by autoimmune disorders. With this disease, it is important to establish a daily routine and nutrition, and most importantly, to ensure sufficient intake of protein and amino acids into the body.
For arthritis, the following nutritional rules are fundamentally important:
- limit the amount of fat in the diet, but so that the body receives animal - twice as much as vegetable;
- reduce the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates in the diet, in particular sugar and sweets;
- reduce table salt consumption to 3-4 g per day;
- Among vitamins, antioxidants come to the fore;
- strong meat and fish broths, it is better not to eat smoked meats;
- It is recommended to eat fractionally – ideally up to 6 times a day;
- if a person is overweight, cereals and pasta are replaced with raw or boiled vegetables, sugar is completely eliminated, and the amount of bread and bakery products is reduced to 100 g per day.
For arthritis, doctors strongly recommend giving up a number of foods. You will see the 10 most dangerous for joints in the video below:
Do not underestimate the importance of proper nutrition for joint diseases. The main thing is to correctly determine your priorities, since they will be different in the treatment of ankle arthrosis, knee arthritis or gout.
Useful and harmful foods for the spine
Essential vitamins and microelements
Food should not just go into the stomach. It must be well absorbed, dissolve, enter the blood and reach the bones of the spinal column. The comprehensive use of certain vitamins will help to significantly facilitate this process.
- So, most people know that vitamin D helps calcium absorption.
- Vitamin A is an essential element of the calcium cycle. It is listed as fat soluble and cannot be absorbed in the absence of fat.
- The B group of vitamins is important for the breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates.
- C (ascorbic acid) – necessary for collagen synthesis. This vitamin converts calcium from an inorganic compound to an organic one.
The supply of certain microelements and vitamins to the structure of the spine is very important. Among microelements, the presence of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and manganese .
Enemies of the spine and joints - foods that need to be limited in the diet
- Table salt Contained in any canned food, semi-finished products, fried potatoes, frozen foods, cheeses. Salt does not allow calcium to integrate normally into the bone tissue of the spine and corrodes it, forming holes. Moreover, it creates its excessive extraction from the bones. Osteoporosis occurs.
- Alcohol What effect does alcohol have on our spine? Calcium is found in human blood in two forms. 50 percent is ionized active calcium, which is well absorbed into the blood, and calcium bound to transport proteins that move it. This calcium, no matter how much it is, will never get into the bones of the spine. Alcohol blocks the conversion of calcium into an active form and all calcium in our blood becomes inactive. Osteoporosis sets in and bones begin to break.
- Margarine Margarine is an artificially created hydrogenated fat in a semi-solid form. Our body processes them with great difficulty. Trans fat, which is margarine, when it enters the stomach, blocks the actions of vitamins K and D. Bones become fragile and can break even with light stress.
- Refined sugar and grains after industrial processing These products contribute to excess weight gain, which has a harmful effect on the spine and the entire musculoskeletal system. You should see as little as possible in your diet of confectionery, creams, chocolate, white rice and semolina porridge, white bread and buns.
- Coffee This common and beloved product by many interferes with the normal absorption of calcium in the body, and therefore large quantities of this drink are a direct threat to the health of the spine and joints.
- All canned foods , pickles, smoked meats, sausages, fast food, sweet soda.
- Nitrates, vinegar, glutamate, salt, sugar substitutes, dyes and food additives with the symbol E found in these foods help wash calcium out of the bones and interfere with its absorption from food in the intestines.
The key to healthy joints and ligaments
- avoid hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather;
- for women to minimize walking in heels and uncomfortable shoes;
- do not ignore your doctor’s recommendations on wearing orthopedic insoles;
- control body weight (obesity is the main enemy for joints);
- lead a healthy lifestyle and eat well.
It is important to know! Scientists have long proven that reducing body weight by 5 kg reduces the risk of developing joint diseases by 35-45%. And if you spend one week in bed, the strength of joint tissue decreases by 15%.
To improve bone, cartilage, and joint tissue, rheumatologists recommend consuming vitamins, for example, Calcium - D3 Nycomed. The vitamin is vital for the health of the muscular, circulatory and digestive systems; essential for normal bone growth, supports the synthesis and function of blood cells.
Does cracking your fingers harm your joints?
Some people like to intentionally crack their knuckles, but putting too much pressure on your knuckles is harmful. The unnatural load they experience can lead to damage to cartilage tissue and the development of inflammatory and degenerative processes.
The Elena Malysheva Clinic of Traumatology and Orthopedics points out that if you already have signs of arthrosis, arthritis and other joint diseases, you should definitely consult a doctor. This article is suitable for those who want to prevent joint diseases, but not treat them. The pathological process cannot be stopped by eating jellied meat and cartilage. It can only be slowed down or completely cured with the help of qualified professionals.
More detailed information and registration by phone: 8.
NUTRITION FOR CONNECTIVE TISSUE HEALTH
Many of us have heard about connective tissue in our bodies, but few know how important it is and how to preserve it. But connective tissue is not only one of the main components of our skin and subcutaneous tissue, but also the “building blocks” of blood vessels, bones, teeth, cornea and sclera of the eye, and cartilage. There is a connective tissue component in the myocardium, layers of connective tissue are found between muscle fibers, even part of the brain and adipose tissue are connective tissue. Connective tissue is the connecting link between all tissues of the body. 85% of a person’s body weight is this tissue!
Unfortunately, highly specialized doctors are rarely interested in our concomitant diseases, but damage to the eyes, teeth or spine are links in one chain, caused by a violation of the strength of connective tissue components as a result of hereditary or acquired metabolic disorders.
There are so many types of connective tissue:
- bone - cartilage (hyaline, elastic and fibrous cartilage) - blood, lymph - connective tissue itself (loose fibrous, dense fibrous, reticular). - fatty
Today we are most concerned with collagens and elastins - vital proteins that form the basis of connective tissue and the main amorphous substance. Collagens and elastins are “springs”; our appearance and the condition of all connective tissues of the body depend on their healthy elasticity, and the amorphous substance is a “gel” that performs the most important functions.
It is through the main substance of connective tissue that water and nutrients are transported. Every cell of our body needs nutrition and cleansing from waste products, which are carried out through the smallest capillaries of the bloodstream. But capillaries are not able to “encompass” every cell, so from the capillaries nutrients enter the intercellular substance, and only from there to the cells, and waste from the cells first enters the intercellular substance.
Now imagine that instead of the desired gel (jelly-like) consistency of the main substance of the connective tissue - cement, or vice versa, broth, will the nutrients and hormones reach the cell membrane? How will waste be released into the lymphatic system? How will other functions of connective tissue be performed? What will happen to articular cartilage, which must withstand enormous loads - pressure of hundreds of atmospheres? What will happen to the permeability of the walls of blood vessels - after all, nutrients must penetrate through the walls of blood vessels into the intercellular substance? What about the cells of the immune system - phagocytes, macrophages, etc., which act not only in the blood, but also in the intercellular fluid? But what if the intercellular fluid is cement, through which it is impossible to get through? How then will the immune system detect these bad cells?
What can we do to ensure that the connective tissues of our body remain healthy and strong for a long time?
First of all, take care of the “health” of our collagen, of its sufficient quantity. In the body, collagen is formed from a precursor called procollagen.
Beverly Hills dermatologist Dr. David Emron has found that excessive sun exposure during tanning negatively affects the collagen fibers contained in the skin, leading to premature wrinkles and aging of the skin. Dr. Debra Jailman, a dermatologist in New York City, has discovered that the development of cellulite is closely linked to the weakening of the collagen elements that attach the skin to underlying structures and keep the skin in a smooth, taut state. Almost all experts who have studied collagen agree that a decrease in flexibility and mobility in joints with age is a consequence of the “aging” of collagen in connective tissues.
Can you get it from food? For many years, collagen was considered insoluble in water and therefore indigestible. The reason for this is that collagen supplied to the body from foods resists the effects of trypsin contained in the gastric environment, however, it is hydrolyzed by the bacterial enzyme collagenase. When collagen is boiled in water, it hydrolyzes, and the product becomes gelatin.
Collagen biosynthesis and the subsequent formation of connective tissue is a complex, multi-stage and relatively slow process (this is why connective tissue and cartilage injuries heal so slowly, especially in adults). Violation of individual stages of this process - in the case of blockade or lack of individual factors - leads to the synthesis of atypical, easily destroyed collagen. Thus, a lack of vitamin C inhibits the hydroxylation of proline and lysine, and therefore causes such a serious disease as scurvy. In case of other disorders, diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, scleroderma and a number of other equally serious diseases arise.
The most important factor necessary for the construction of a full-fledged collagen molecule is the structural subunits of the protein - amino acids formed as a result of the breakdown of food proteins.
You certainly know that there are about three dozen amino acids that are nutritional factors. In the body, many of them are synthesized in the liver. However, some amino acids cannot be synthesized in the body, and a person must obtain them from food. The following amino acids are essential for humans: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, valine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine and tryptophan. The body is constantly in the process of protein synthesis, and in the absence of at least one essential amino acid, the formation of proteins is suspended.
Therefore, it is extremely important for the health of our connective tissues to have complete proteins in our diet. Complete proteins include proteins from animal products, such as eggs, dairy products, meat, poultry, and fish. Vegetable protein from different types of legumes, soybeans, peas, various cereals and vegetables is considered incomplete. The disadvantage of incomplete protein is its relatively poor amino acid composition and a rather low degree of absorption. For example, soy contains relatively a lot of protein, but it is absorbed by the body by 30–40%, while egg white is almost completely absorbed. Therefore, a person’s diet should contain a sufficient amount of animal protein, and if your goal is to lose excess weight, then this protein should be combined with a minimum amount of fat. The following products meet this requirement: egg whites, lean meat (beef, chicken, turkey), fish (pollock, cod, haddock, flounder, pike perch, hake, pink salmon, salmon), milk and low-fat fermented milk products.
In addition to complete proteins, other nutritional components are also extremely important:
Vitamin C – participates in the synthesis of collagen by promoting special enzymes. The human body does not produce vitamin C and it must be obtained from food. The consequence of impaired collagen synthesis is an increase in the permeability of the walls of blood vessels, which leads to hemorrhages in the skin, joints, bleeding gums, etc.
Sources of vitamin C: dried rose hips, black currants, red and bell peppers, horseradish, citrus fruits, sorrel, strawberries, radishes, gooseberries, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, broccoli, mango, parsley, domestic apples, apricots, peaches, persimmons, sea buckthorn, rowan, oats, spinach, pomelo, melon.
Minerals:
Sulfur is part of structural proteins (collagens), certain glycosaminoglycones that are present in cartilage, in the sclera of the eye (they give strength to the sclera, participating in supporting the shape of the eye), in the cornea of the eye (provide transparency of the cornea), and also prevent the formation of blood clots.
Sources of sulfur:
Vegetables: cabbage, onions, cereals, cereals, legumes, mustard, horseradish, gooseberries, grapes, apples, garlic, asparagus, baked goods.
Animals: lean beef, fish, chicken eggs, milk and dairy products.
Silicon is included in the composition of elastin, a substance that determines the strength, elasticity and permeability of blood vessels.
Sources of silicon
Plant-based: whole grains, cereal products, beets, soybeans, turnips, radishes, green beans, potatoes, onions, Jerusalem artichokes, seaweed, bran, wild berries, greens, brown rice, apricots, bananas, cherries, raisins, figs, cabbage , corn, celery, nuts.
Silicon is also present in grape juice, wines and beer.
Animals: caviar, eggs.
Some amount of silicon is found in mineral waters
Copper - strengthens the cross-links of collagen (collagen fiber consists of “threads” - collagen fibrils, the “cross-linking” of which requires an enzyme activated by copper ions).
It is clear that the body must receive such an important element daily from the outside - with food, water or through the skin.
It’s clear about water - passed through copper pipes, the water arrives enriched with copper ions - approximately 1 mg per liter. What products contain this essential element? There is a lot of copper in nuts, raw egg yolk, liver, legumes, cereals, dairy products, vegetables, fruits and berries. Copper is found in fresh animal meat, fish, seafood, sprouted wheat, soybeans, rye bread, asparagus, potatoes and herbs: dill, cinquefoil, madder, cucumber, leaves of the tea bush, swollen lobelia. And the leaves and root of ginseng contain the highest percentage of copper of any plant.
Zinc affects all processes in the connective tissue - both synthesis and breakdown. It promotes rapid healing of wounds.
Zinc activates enzymes (matrix metalloproteases, MMPs), which disassemble molecules of intercellular substance; promotes the formation of phagocytes and enhances the activity of macrophages, which contributes to the cleansing of necrotic tissue elements; helps attract fibroblast cells to the affected area; replenishes the deficiency of hyaluronic acid (this acid belongs to glycosaminoglycans, which form the amorphous substance of connective tissue); activates enzymes responsible for collagen synthesis.
Sources of zinc: meat of geese, chicken, beans, corn, beef, pork, liver.
Zinc is less absorbed from grains and legumes than from meat and fish.
Fruits and vegetables are generally low in zinc. So vegetarians and people who eat insufficient amounts of foods containing this micronutrient may develop a deficiency.
Long-term consumption of foods that are too salty or too sweet can also reduce zinc levels in the body.
Magnesium. Magnesium deficiency reduces and slows down the rate of collagen synthesis.
Sources of magnesium: Wheat bran, soy flour, almonds, walnuts, peas, wheat, cabbage, cereals.
Antioxidants protect cells, including fibroblasts (which are responsible for rebuilding connective tissue) from the negative effects of free radicals in the cell's information center.
Antioxidants are substances that allow the human body to extract and bind oxidants. Like other antioxidants, the catechins found in green tea selectively inhibit specific enzyme activities that lead to cancer. They can also detect and repair DNA changes caused by oxidants. Currently, the following are used as antioxidants:
— antioxidant vitamins: beta-carotene (pro-vitamin) and other carotenoids (astaxanthin, lycopene, lutein, etc.), A, C, E. Each vitamin performs its own function. Therefore, it is necessary that each of them is present in your food products.
- Beta-carotene. Found in brightly colored green, orange, and yellow fruits and vegetables. For example, in carrots, pumpkin, apricots, mangoes, papaya, red peppers, spinach, cabbage, turnips, broccoli, melon.
— Vitamin C. Contained in red and green peppers, kiwi, oranges, grapefruits, tomatoes, potatoes, cabbage, strawberries, etc.
— Vitamin E. Also known as tocopherol, it is found in any plant food, but vegetable oils (naturally vegetable-pressed) are especially rich in it. For example, olive, corn, peanut, sesame, almond, wheat germ oil.
- antioxidant microelements: selenium, zinc, copper, chromium, manganese, etc. - natural (plant) antioxidants or bioflavonoids: extracts from the seeds or skins of red grapes, tree bark, blueberries, green tea, etc. — antioxidant amino acids: methionine, tyrosine, cysteine, taurine, etc.
Strong and popular antioxidants are also succinic and lipoic acids, coenzyme Q10, melatonin, etc.
Glucosamine is the main building material for connective tissue. Stimulates the production of the same collagen by cartilage cells, as well as such an important substance as chondroitin. At the same time, the produced chondroitin, after breakdown, will decompose into several components, one of which is glucosamine.
Glucosamine itself is produced by cartilage cells from glucose and an important amino acid - glutamine.
Glucosamine in food
Glucosamine is present in many foods, but tends to break down when exposed to extreme heat. The main source of glutamine can be cartilage, as well as foods high in glutamine – chicken, beef, hard cheese.
Chondroitin is the main component of the amorphous substance of cartilage. An important element of tendons, ligaments, cartilage, skin, blood vessels. It has anti-inflammatory properties and plays an important role in the restoration of cartilage tissue. Thanks to chondroitin, fluid is retained in cartilage tissue. Upon breakdown, it produces glucosamine as one of the components.
Chondroitin is produced by cartilage cells when using the same glucosamine.
Chondroitin in food
Contained in the skin, tendons and cartilage of animal origin and, to an even greater extent, in fish (especially salmon, salmon). It is for this reason that chondroitin supplements are made from salmon cartilage
Joint diseases
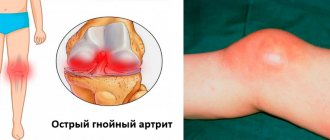
- Arthritis and its types - osteoarthritis, post-traumatic, reactive, rheumatoid, psoriatic. Arthritis manifests itself as acute pain in different parts of the body - feet, hands, elbow joints. Symptoms include swelling, redness, increased body temperature, limited joint mobility and deformation. Most often develops against the background of infectious diseases and injuries.
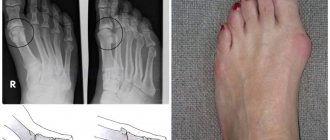
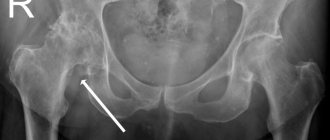
- Arthrosis. An age-related pathology that manifests itself as crunching, sharp pain in the hip, wrist and knee joints. The pain intensifies with exercise.
- Gout. A hereditary disease accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the heart and kidneys. Symptoms are acute pain, swelling, redness and peeling of the skin in the affected joints.
- Rheumatism. A disease of the joints and connective tissues, which in its symptoms resembles ARVI - the patient’s body temperature rises, aches, joint pain, and tissue swelling are observed. Often found in older people.
Causes of joint diseases
The causes of joint disease are varied and range from degenerative and destructive processes, such as osteoarthritis or sports injuries, to inflammation of the tissues surrounding the joints, such as bursitis. However, more often such pathologies arise due to:
- lack of normal physical activity, static lifestyle;
- increased and monotonous loads;
- joint injuries;
- untimely or poor-quality treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes.
Interesting fact! Arthritis (inflammation of the joints) is the leading cause of disability in people over 55 years of age. The most common form of arthritis is osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease).
Who treats joint pain?
A number of specialists—traumatologist, surgeon, and neurologist—are involved in the treatment of joint pain. In some cases, a cardiologist and a chiropractor are involved in the process.
It is impossible to cure joint pathologies on your own. Advertised ointments only relieve pain and improve blood supply to the joint, but do not help cope with the cause of the disease. Self-medication can result in chronic disease and aggravation of the existing problem, especially if it is a consequence of other diseases that occur in the background or are not fully treated at the time.
For diagnosis, modern methods are used: ultrasound, MRI, CT, radiography, endoscopy and arthroscopy, examination of blood and fluid obtained as a result of joint puncture. The attending physician decides which research methods the patient needs after examining and studying the patient’s medical history.
If you or your loved ones are concerned about joint pain, contact qualified specialists at a medical clinic in Moscow. Our surgeons and neurologists treat joint pain that occurs at any age and help patients overcome the disease. Don't wait, make an appointment and get examined by professionals with extensive experience.