Possible causes of eye pain and their symptoms
Discomfort and pain in the eyes are common. This symptom can be encountered after working for a long time at the monitor, reading in poor lighting, or when foreign particles enter. The pain can be sharp or aching, appear on the front or back of the eyeball, occur spontaneously or at a certain time of the day. With more serious pathologies, it will be accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity and can lead to its complete loss.
Foreign body entry
Pain in the eye area can also occur in healthy people. The membranes of the eyeball are very sensitive, and the entry of a foreign body into the conjunctiva causes its damage. This can be determined by characteristic features:
- severe pain in one or both eyes;
- profuse lacrimation;
- redness of the conjunctiva.
When a foreign body enters, profuse lacrimation usually begins. This is a reflex defense mechanism - it is necessary to flush out small particles that cannot be removed mechanically. In this case, it is recommended to rinse the eye with plenty of liquid, being careful not to irritate the mucous membrane.
Dry eye syndrome
Another cause of eye pain is a decrease in the secretion of the lacrimal glands. Normally, fluid is constantly formed and protects the mucous membrane from drying out. Dry eye syndrome is manifested by redness of the conjunctiva, a feeling of pain and stinging, discomfort and decreased visual acuity. This phenomenon can occur in any person, but several categories are at risk:
- office employees who spend working hours behind a monitor;
- aged people;
- those who work with welding machines;
- persons who live in hot climates, high dust or air pollution.
To treat dry eye syndrome, medications are prescribed that are analogues of natural tears. They have a similar chemical composition and are available in the form of eye drops. They can be used as needed throughout the day. Additionally, gymnastics will be useful.
Corneal erosion
The cornea is the outer layer of the eye's outer layer. It is a thin transparent film in which the primary refraction of rays occurs. It can be injured by irritation by mechanical or chemical means, as well as due to inflammatory processes. Other factors that can cause this symptom are improper eyelash growth and ill-fitting contact lenses.
Corneal erosion is a damaged area of the cornea. It can be identified by characteristic redness, severe pain in the eyes, lacrimation and photophobia. The healing rate of erosion depends on its depth and size. In most cases, it passes without consequences, but can also lead to loss of vision.
Barley
Barley (hordeolum) is an inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash, sometimes the sebaceous or meibomian glands. A painful lump appears on the eyelid, the skin turns red, and swelling may occur. The main cause of this disease is a pathogenic infection in combination with other factors (weakened immune defense, cold eyes). In most cases, the causative agent is staphylococcus.
A chalazion is a type of stye that is caused by inflammation of the meibomian gland duct. It is also called an internal or cold stye, as well as a meibomian cyst. The disease is characterized by a slow course (1-2 months), occurs with inflammation of the eye cartilage and the appearance of dense swelling. It may disappear on its own, but in some cases (if it is pressing on the eyeball) it is recommended to remove it during a simple operation.
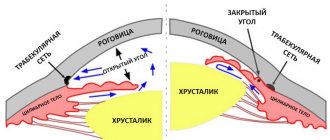
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is increased intraocular pressure. It occurs when the circulation of fluid in the chambers of the eye is disrupted and its accumulation occurs. As a result, there is a risk of damage to the optic nerve, loss of elasticity of the membranes and gradual loss of vision. This disease is accompanied by pressing pain in the eye area and visual field defects. Over time, it can lead to complete blindness. An acute attack of glaucoma is a hard eyeball with a pupil that does not respond to light stimuli. There is also a headache that presses on the eyes.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. The process may be associated with mechanical damage to tissues, as well as with the action of fungal or bacterial microflora. Depending on the cause, there are several types of blepharitis:
- simple (aseptic, non-purulent);
- seborrheic - develops under the influence of a fungus, while the eyelid becomes covered with scales, crusts, and ulcers;
- staphylococcal - ulcerative blepharitis;
- demodicosis - its causative agent is a subcutaneous mite, the inflammation is accompanied by severe itching;
- allergic - most often occurs symmetrically (if the allergy is caused by eye drops or detergent, a one-sided reaction is possible);
- Rosacea-blepharitis (acne) - the skin of the eyelids becomes covered with a rash. filled with purulent contents.
With blepharitis, the skin of the eyelid is inflamed, swollen, and pain appears, radiating to the eye. In the acute form of the disease, it can occur in the form of barley or with the formation of subcutaneous cysts. In some patients, prolonged blepharitis can lead to decreased visual acuity. Treatment is prescribed individually, depending on the cause of inflammation.
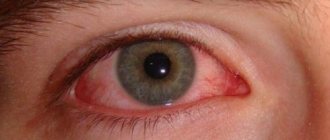
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva). It can develop from fungal, viral, bacterial diseases or have a non-infectious origin. There are several main types of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial - most often caused by streptococcus aureus, accompanied by redness of the eyes, excessive flow of tears and photophobia, small hemorrhages appear on the mucous membrane;
- adenoviral - occurs with the release of pus and the formation of small follicles;
- hemorrhagic - in addition to eye pain, hemorrhages (bleedings) on the conjunctiva and on the eyelid become a symptom;
- fungal;
- allergic - may be accompanied by additional clinical signs and inflammation of varying severity.
According to the form of the course, acute and chronic conjunctivitis are distinguished. In the first case, it develops suddenly and begins with severe pain in the eye area. The acute stage lasts no more than a week. The chronic course is protracted, accompanied by discomfort, redness of the mucous membranes, and a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
Keratitis
Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea of the eye. The process can be of bacterial, fungal, viral origin, or develop due to injuries and mechanical damage to the shell. If the cornea is normally transparent and can transmit light rays, when it becomes inflamed, it becomes cloudy. The most dangerous is the protracted course of keratitis - it can lead to vascularization of the cornea, that is, the growth of blood vessels through it. This pathology is accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity. Keratitis causes acute pain in the front of the eye, photophobia, and lacrimation.
Pain in the eyes due to inflammation of the optic nerve
Inflammation of the optic nerve is a dangerous pathology that leads to rapid loss of vision. The process is accompanied by demyelination of nerve fibers, that is, destruction of the myelin sheath and loss of the nerve’s ability to conduct impulses. As a result, visual objects cannot be analyzed in the brain.
The causes of optic neuritis can be:
- inflammatory diseases of the meninges;
- acute intoxication;
- diseases of the inner membranes of the eye;
- systemic infectious diseases (influenza, tonsillitis, smallpox, malaria and others);
- systemic non-infectious diseases (hematopoietic pathologies, diabetes, gout and others);
- multiple sclerosis;
- injuries.
With optic neuritis, acute pressing pain appears in the eyes, the main focus of which is located behind the eyeball. The sensations intensify when pressing on it. There is also a narrowing of the field of view. Treatment takes place in a hospital and is aimed at eliminating the cause of neuritis and restoring nerve conduction. Its effectiveness depends on the timeliness of medical care.
Migraine
Migraine is an attack of headache. It begins abruptly and can last from several hours to several days. Painful sensations are often localized in the frontotemporal part of the head, but can spread to its entire surface. The exact cause of this phenomenon is unknown, but there is a relationship between migraine and traumatic brain injuries, nervous and endocrine disorders, and a genetic predisposition is also determined.
Classic migraine begins with additional symptoms (aura). Before the headache appears, discomfort also occurs in the eye area. Photophobia and deterioration of visual acuity may be observed.
If it's unpleasant to blink
You should immediately examine your eye thoroughly. Perhaps there will be some foreign body there. This reason is most common if there is pain under the eye, as if there is a bruise there. In addition, certain infections manifest themselves in a similar way.
Pain when blinking can occur quite quickly. During this, a person is able to feel unobtrusive, unpleasant feelings, but in some cases the sensations are so powerful that it is not even possible to fall asleep.
The pain most often increases over time. On the first day, the patient feels eye discomfort. There is a feeling of the presence of a foreign body for about a century.
In addition to pain, symptoms such as:
- swelling;
- discomfort when looking at the light;
- increased production of tears;
- swelling of the eyelid;
- the tissues of the eyelid become denser;
- redness;
- sverbezh.
Swelling of the eyelid may indicate an eye disease - consult a doctor.
In some cases, the feeling of a bruise is accompanied by a runny nose or migraines.
Most ophthalmic diseases are easy to treat. However, therapy can only be prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Minor unpleasant sensations appear from the ingress of dust, more dangerous ones from the ingress of foreign bodies or injury. In the case of other options, discomfort is a sign of illness.
Based on certain patient complaints, the doctor orders an in-depth examination in order to determine the presence or absence of glaucoma. In the presence of this anomaly, the pressure of the eyeball constantly increases, which is why the patient feels discomfort when blinking.
Diagnostic methods
In order to get rid of eye pain, you need to undergo an examination. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions for a full diagnosis of diseases of the visual apparatus. An ophthalmologist will examine the fundus of the eye and collect material for testing for infectious microflora.
There are several main methods for diagnosing eye pain:
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus and assessment of the transparency of eye structures using an ophthalmoscope;
- measurement of intraocular pressure - can be carried out by assessing the imprints of small weights on the retina or using tonometers;
- biomicroscopy - examination of the internal and external structures and membranes of the eye using light refraction at different angles;
- confocal microscopy of the cornea - hardware examination of this membrane;
- Vesta color test - used to study the patency of the lacrimal ducts;
- various methods for studying visual fields;
- Ultrasound of the eyeball;
- studying eyelid scrapings under a microscope to exclude demodicosis and others.
If a headache puts pressure on the eyes, the condition of the brain and its membranes is further examined. Diagnosis is carried out using MRI or CT - the most accurate methods of obtaining a three-dimensional image of internal structures. You may also need x-rays of your sinuses, blood tests, and other tests.
Optic neuritis
The pathology is an inflammation of the second cranial nerve. The general clinical picture is similar to the manifestation of papilloedema, but without the characteristic increase in intracranial pressure. The most common cause is pathology of the central nervous system (selective damage to the myelin sheath), less often - sinusitis, inflammation of the orbital contents.
Pain inside the eye is the main symptom of the pathology, intensifying with its movement. Additionally, the patient complains of changes in the perception of shades, deterioration of vision, and the appearance of pointless images before the eyes.
Diagnosis of the disease is quite difficult; instrumental research methods cannot always reveal characteristic changes in the fundus. The task is to determine the presence of multiple sclerosis, which is a provoking factor of the disease.
Treatment of eye pain
Treatment of eye diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Our clinic employs doctors of narrow and broad profiles, whose qualifications allow us to quickly make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. The course of therapy is selected individually and depends on the diagnostic results. It may include the following steps:
- taking medications (antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, symptomatic medications - analogues of tears and other medications according to indications);
- gymnastics to strengthen the muscles of the eyeball;
- surgical treatment, including modern methods of vision correction.
Pain in the eyes often develops when the visual organ is overworked. This is due to monotonous work at the monitor, lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet, and incorrect selection of vision correction products (glasses or lenses). To prevent diseases of the visual system, it is recommended to perform simple gymnastics and undergo regular examinations. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute will be able to identify dangerous pathologies in the early stages and help maintain visual acuity at any age.
Useful video
Pain in the left eye is caused by physiological and pathological reasons. To eliminate physiological disorders, it is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and prevent chronic diseases. Pathologies of the ocular apparatus require careful diagnosis and selection of individual therapy. To prevent the development of complications due to diseases, it is necessary to promptly consult an ophthalmologist, regardless of the presence of symptoms.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 5 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.