general description
Congenital heart defects (heart defects) are an abnormal structure of the heart chambers, large vessels or valves (combinations are not uncommon) due to genetic predisposition, intrauterine development disorders, infectious, autoimmune, metabolic and other diseases, injuries received by the mother during pregnancy.
Valve lesions can be congenital (due to disorders of intrauterine development) or acquired, that is, occurring during life under the influence of diseases, infections or injuries.
In most cases, complex congenital defects require surgical correction in both children and adults.
Folk remedies
Photo: serdcemed.ru
When choosing folk recipes, three aspects should be taken into account. First, such methods are often contraindicated for children; the recommendations below are more suitable for adults. Second, no folk remedies can replace official methods of treatment. Any drops, infusions and decoctions are used only in addition to the prescribed therapy. Refusal of specialized care can cause serious complications and even death of the patient.
Third, such prescriptions can only be used in consultation with a doctor, since they may not be suitable for treating a particular defect, cannot be combined with prescribed medications, cause allergic reactions, or worsen the course of the disease. In folk medicine, the following remedies are known to be used for congenital heart defects:
- Lily of the valley drops . To prepare them, you will need a jar with a small neck in which you need to place fresh buds or flowers of lily of the valley. The contents of the jar are almost completely filled with alcohol and allowed to brew.
- Lily of the valley infusion . It is made by steaming flowers with boiling water. The resulting solution is infused for about an hour and then applied every 2 hours.
- Drops of motherwort with the addition of tincture of lily of the valley . They have a number of positive properties that are useful for patients with heart disease. To make these drops, you will need to mix the herbal infusion with drops of lily of the valley tincture.
- Nettle leaves and honey . If the defect is accompanied by shortness of breath, make a paste from the listed ingredients. The resulting mixture is infused, stirring the contents from time to time. Then heated over steam and filtered through a bandage or gauze. To achieve positive results, the composition is taken for a month.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
SEARCH FOR TREATMENT AROUND THE WORLD WITH YELLMED
What are the types of congenital heart defects?
- pulmonary valve stenosis
- stenosis of the aortic valve, aortic orifice, subvalvular stenosis;
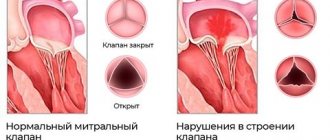
- mitral stenosis - narrowing of the bicuspid atrioventricular valve;
- Mitral valve insufficiency - incomplete closure of the bicuspid atrioventricular valve;
- Mitral valve prolapse - excessive length of one or two valve leaflets;
- aortic valve insufficiency;
- tricuspid stenosis;
- triscupidal insufficiency;
- defects of the interatrial and interventricular septum;
- anomalies in the development of heart cavities: Ebstein's anomaly, single atrium, single ventricle;
- transposition of large vessels - aorta and pulmonary artery;
- tetralogy of Fallot;
- open arterial (Botallov) duct;
- coarctation of the aorta;
- The most common congenital heart defect is an abnormal communication between the atria—atrial septal defect.
Symptoms of congenital heart disease
They are divided into two large groups according to the color of the child’s skin: “white” and “blue”. A changed skin tone is the first reason for parents and pediatricians to be wary.
"Blue" vices
They usually appear either immediately at birth or a little later. In this case, the ears, lips and body skin are susceptible to cyanosis. Blue discoloration can occur during exertion (screaming, crying of a newborn), during breastfeeding. The “blue” appearance is usually manifested by a mirror arrangement of the great vessels, atresia of the pulmonary artery, and tetralogy of Fallot.
CHD of the “white” variety
Accompanied by pallor and coldness of the extremities. When listening with a stethoscope, noises are heard. They are not direct symptoms, but a heart examination is still required. With “white” pathologies, heart failure is often detected. Changes are detected on x-rays, ECG, ECHO-CG. This type of congenital heart disease is most often a pathology of the interatrial septum and interventricular septum.
Unfortunately, not all types of congenital heart disease occur in newborns. A child can feel well even up to 10 years of age. But sooner or later the vice will appear:
- delay in physiological development;
- pallor or cyanosis;
- shortness of breath during exercise.
Diagnosis and treatment of heart disease
Cardiac surgeons can recognize and eliminate the defect in a timely manner. In most cases, x-ray surgeons close the defect using catheter technology without resorting to an incision.
- A defect may appear between the ventricles of the heart - a ventricular septal defect.
- Often the defects are combined with anomalies of the valvular apparatus of the heart or large vessels.
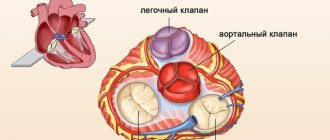
The valvular apparatus of the heart consists of four valves: mitral (bicuspid), tricuspid (three-cuspid), aortic and pulmonary valve. The functioning of the heart depends on the coordinated and correct functioning of these structures.There are two main types of valve disease: valve insufficiency and stenosis.
When there is insufficiency, the valve leaflets do not close completely, leaving a gap through which blood is thrown in the opposite direction to the normal direction. And with stenosis, the valves do not open completely, preventing normal blood flow. Isolated lesions of the heart valves are relatively rare; they are very often observed in other congenital heart defects. For example, a bicuspid acortical valve is often found in people with a patent ductus arteriosus. With this defect, part of the blood (rich in oxygen) from the aorta, which is not closed after the birth of the child, enters the pulmonary artery, causing an overload of the right side of the heart. In children and adolescents, such an abnormal message is most often eliminated without surgery, by installing a “plug” through the catheter.
- Another congenital malformation is stenosis of the descending aorta.
In the thoracic segment, the aorta is attached to the posterior wall, closer to the spine. At this point, the aorta is sometimes significantly narrowed, and the internal organs do not receive enough arterial blood. Previously, this condition, called coarctation of the aorta, could only be corrected with surgery. But today, in most cases, narrowing during coractation of the aorta is eliminated by balloon dilation and installation of a stent frame. It should be emphasized that if valve stenosis is an isolated lesion, it is often eliminated by balloon expansion, in a minimally traumatic way.
CONSENT TO THE PROCESSING OF PERSONAL DATA OF INDIVIDUAL CLIENTS
The user, by leaving a request or review on the website www.anadolutyumen.ru, accepts this Consent to the processing of personal data (hereinafter referred to as the Consent).
Acting freely, of his own will and in his own interest, as well as confirming his legal capacity, the User gives his consent to the individual entrepreneur Vladimir Aleksandrovich Butov (TIN 450130886311), which is located at the address: Russia, Tyumen st. Republic 61, office 713, for the processing of your personal data under the following conditions: 1. This Consent is given for the processing of personal data, both without the use of automation tools and with their use, by transmission via open Internet communication channels.
2. Consent is given to the processing of the following personal data:
1) Personal data that is not biometric: last name, first name, contact phone numbers; city of residence, email addresses; data on my state of health, diseases, cases of seeking medical help for medical and preventive purposes; user data (location information; OS type and version; Browser type and version; device type and screen resolution; source from where the user came to the site; from which site or from which advertisement; OS and Browser language; which pages opens and to which buttons pressed by the user; IP address.
3. Personal data is not publicly available.
4. Purpose of processing personal data: processing incoming requests from individuals for the purpose of consulting; preparing a commercial offer, receiving feedback, analyzing the actions of an individual on the website and the functioning of the website; Conducting advertising and newsletters.
5. The basis for the processing of personal data is: Art. 24 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation; Article 6 of Federal Law No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data”; agreement between the Anadolu Medical Center and individual entrepreneur Vladimir Aleksandrovich Butov; this consent to the processing of personal data
6. During the processing of personal data, the following actions will be performed: collection; record; systematization; accumulation; storage; clarification (update, change); extraction; usage; transmission (distribution, provision, access); blocking; deletion; destruction.
7. Personal data received through the preparation of an application or review on the website www.anadolutyumen.ru can be transferred to organizations or third parties related to the implementation of the goals specified in clause 4 via open (unsecured) Internet communication channels.
8. Processing of personal data may be terminated at the request of the subject of personal data. Storage of personal data recorded on paper is carried out in accordance with Federal Law No. 125-FZ “On Archival Affairs in the Russian Federation” and other regulatory legal acts in the field of archival affairs and archival storage.
9. Consent can be revoked by the subject of personal data or his representative by sending a written statement to individual entrepreneur Vladimir Aleksandrovich Butov or his representative at the address indicated at the beginning of this Consent.
10. If the subject of personal data or his representative withdraws consent to the processing of personal data, individual entrepreneur Vladimir Aleksandrovich Butov has the right to continue processing personal data without the consent of the subject of personal data if there are grounds specified in paragraphs 2 - 11 of part 1 of article 6, part 2 of article 10 and Part 2 of Article 11 of Federal Law No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data” dated July 27, 2006
11. This consent is valid all the time until the termination of the processing of personal data specified in clauses 8 and 9 of this Consent.
How do heart valve diseases manifest?
Most often, patient complaints are nonspecific: shortness of breath, rapid pulse, arrhythmia, fatigue, cyanosis, dizziness.
The severity and nature of symptoms depend on the location of the affected valve. With valve defects of the left half of the heart (mitral and aortic), the lungs are primarily affected, because Blood stagnates in their vessels, which manifests itself as shortness of breath. There are also signs of insufficient blood supply to all organs and systems, primarily the brain and the heart itself. Dizziness, fainting, and angina occur. If the functioning of the valves of the right half of the heart (tricuspid and pulmonary valves) is disrupted, blood stagnates in the vessels of the systemic circulation, i.e. all organs except the lungs are affected. Swelling of the legs and feet, ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity), enlargement of the liver, etc. develop (LIVER INCREASES, ETC.).
Heart valve defects are dangerous due to their complications and impact on the body, so the main prevention of pathological conditions is regular examinations and treatment of diseases leading to the formation of valve defects.
Medicines
Photo: heartsmatterllc.com
Drug therapy does not cure heart defects, but it helps improve blood circulation and alleviate the symptoms of the pathology during the period when the child has not yet reached the optimal age for surgery. It is used as part of preoperative preparation and treatment in the postoperative period. Used when surgical intervention is not possible. The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Diuretics . Remove excess fluid from the body in case of heart failure.
- Cardiac glycosides . Increases the energy of heart contractions.
- Vasodilators . They expand the lumen of blood vessels, thereby facilitating the work of the heart.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs . Necessary in the presence of rhythm disturbances.
- Antibiotics . Prescribed to prevent endocarditis and prevent complications in the postoperative period.
- Anticoagulants . More often required after surgery, when the risk of blood clots increases.
- Prostaglandin inhibitors . Increase blood flow to the lungs, improve blood supply to the whole body.
- Antihypertensive drugs . Helps normalize blood pressure in secondary arterial hypertension.
- Vitamins . Recommended as part of general strengthening therapy to provide the body with a sufficient amount of nutrients.
With heart defects that cannot be completely eliminated even by surgery, patients are forced to take medications for a long time, and sometimes for their entire lives. The dosage of drugs and the duration of the course are determined by a cardiologist. Self-medication can provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition and the development of complications.