The blood pressure value is expressed in two numbers. The first indicator is systolic pressure, which is popularly called upper, the second is diastolic, or lower. Systolic shows the level of blood pressure when the heart contracts, diastolic - at the moment of its relaxation.
Normally, blood pressure should not exceed 120/80 mm Hg. pillar If it is between 120/80 and 139/89, we are talking about prehypertension, higher values indicate hypertension, or hypertension. Most often, with elevated blood pressure, both indicators exceed the norm. A more rare occurrence is high lower blood pressure with normal upper blood pressure.
What is diastolic pressure?
It means the degree of blood pressure on the vascular walls at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle, when there is little blood in it. This indicator gives an idea of the tone of the vascular walls, since diastolic pressure is a reaction to their resistance. Lower blood pressure is considered normal if it is below 80 mm Hg. pillar
A sustained increase in diastolic blood pressure indicates a high resistance of the vascular walls, which means their constant spasm. If the vessels are always narrowed, blood flows poorly to the organs and tissues and they do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This leads to disruption of organ function.
There are three stages of isolated increase in lower blood pressure:
- 1st – 90-100 mm Hg. Art.;
- 2nd – 100-110;
- 3rd - above 110.
What is isolated diastolic hypertension?
Blood pressure is determined by two indicators - the upper
and
lower
. Upper pressure is measured at the moment the left ventricle ejects arterial blood into the aorta. An increase or decrease in the indicator indicates the contractility of the heart and the condition of the coronary vessels.
In everyday life, high lower (diastolic) pressure is called “renal”. It quickly leads to overload of the entire body, wear and tear of blood vessels and the development of atherosclerosis.
Lower pressure is an indicator of the condition of the peripheral vessels at the moment when the heart muscle relaxes and the aortic valve closes.
If their resistance is high, then the lower pressure will be high. The normal limits for it are 60-80 mmHg. An increase in only the lower pressure with normal or reduced upper pressure is called isolated diastolic hypertension.
Causes of increased diastolic pressure
Hypertension can be primary, that is, it is unknown why blood pressure has risen, and secondary (symptomatic), if it develops against the background of other diseases. Why does diastolic blood pressure increase?
Causes of isolated increase in lower blood pressure
If lower pressure is elevated for a long time, the reasons may be the following:
- Kidney disorders. The kidneys are one of the main organs involved in regulating blood pressure. The cause of increased diastolic blood pressure may be a narrowing of the renal artery, in which the volume of blood entering the kidneys decreases. An increase in blood pressure with a predominant increase in diastolic is observed in chronic glomerulonephritis, congenital anomalies in the structure of the renal vessels, and renal failure.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Cardiac pathologies: heart defects, tumor processes.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland.
- Spinal hernias.
- Changes in hormonal balance, for example in women during pregnancy.
The kidneys are directly involved in regulating blood pressure. If their work is disrupted, the pressure deviates from the norm
Reasons for increasing lower blood pressure simultaneously with upper blood pressure
- Increased lower pressure is usually observed in essential hypertension, which is also called essential hypertension (HD) or primary hypertension. The reasons for the increase in pressure in this case have not been established and it is in no way related to other pathologies. Hypertension with high diastolic pressure is more often observed in young people and can progress and take a malignant course. With this disease there is a high probability of developing complications, and the higher the pressure, the greater the risk.
- Lower pressure can change throughout the day in healthy people, for example, it can increase during emotional or physical stress. As a rule, it quickly decreases on its own, and this is considered normal.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
Why is isolated diastolic hypertension dangerous?
Stably high diastolic pressure over time leads to “full-fledged” arterial hypertension, that is, to an increase in upper pressure with all the ensuing consequences in the form of heart attacks and strokes.
High numbers of lower pressure mean that the heart is working hard, as it cannot relax.
At the same time, the heart muscle uses up its resources at an accelerated rate. Without blood pressure control and treatment, even death cannot be ruled out.
An increase in lower pressure is an SOS signal from the body about serious health problems. It cannot be ignored; an urgent medical examination is necessary.
Malignant hypertension poses a particular danger
when the lower pressure readings go off scale beyond 130 mm. It is always symptomatic. In this case, the patient needs urgent treatment of the underlying disease.
Women of reproductive age who are prone to obesity should pay maximum attention to their blood pressure. According to statistics, they are the ones who most often suffer from isolated diastolic hypertension.
Danger
An increase in lower pressure often has no symptoms, and a person does not even know about it. They may be discovered during a routine examination or when visiting a doctor for other reasons. There is a misconception that only elevated upper blood pressure threatens health and life, but in fact, an increase in lower blood pressure is no less dangerous. The heart in this state is constantly tense and practically does not relax. The blood flow in it is disrupted, the disease progresses, structural changes begin to occur, which ultimately become irreversible.
It is important to know that high lower blood pressure cannot be ignored. It leads to organ dysfunction and, without treatment, can result in death within six months. There is a high risk of developing thrombosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
Symptoms and diagnosis of high blood pressure
How do you know if your kidney pressure is high? If it grows to 90-100 mm, there may be no symptoms. Pathology is detected during preventive examinations or medical examinations. At higher rates, characteristic features are:
- difficulty breathing - shortness of breath and inability to take a deep breath;
- excessive cold sweat;
- rapid pulse;
- dizziness;
- pain under the shoulder blade or in the chest.
In addition, there may be a headache, swelling of the face and limbs. With a prolonged increase in pressure, morning swelling, periodic ringing in the ears, a constant desire to drink, and tachycardia are characteristic.
In addition to subjective symptoms (according to the patient), there are diagnostic methods - ECG, blood tests (general and biochemistry). The doctor first finds out why diastolic pressure rises. He recommends that the patient keep a diary - regular self-monitoring of blood pressure (at least two measurements per day). Daily changes in indicators also have diagnostic value
[media=
https://youtu.be/I7E1RJSbYXE
]
Treatment
Treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor. You should not do this yourself. First of all, you need to find out the reasons for the increase in lower blood pressure. If hypertension is secondary, treatment of the primary pathology is required. In any case, it is necessary to reduce the pressure, for which a set of measures is used, including:
- proper nutrition;
- loss of excess weight (if any);
- compliance with the daily routine (work and rest);
- physical activity (sports, physical therapy, walking);
- staying in the fresh air;
- taking medications;
- folk remedies.
Diet
Proper nutrition is of great importance for normalizing blood pressure. The diet should consist of:
- Fresh vegetables, herbs, berries and fruits.
- Lean meats.
- Dairy and fermented milk products.
- Lean fish.
- Bread made from wholemeal flour.
- Replace sugar with honey.
The following foods should be limited or avoided:
- salty (salt retains fluid in the body, which increases blood pressure);
- fatty and fried;
- sweet and buttery;
- alcoholic drinks.
All people with hypertension should limit salt in their diet
Medicines
You should only take medications prescribed by your doctor. Typically, medications from several groups are used to normalize blood pressure, including:
- Beta blockers are drugs that reduce the heart's need for oxygen, regulate its functioning and lower blood pressure.
- Calcium antagonists - increase the activity of renin, which is poorly produced in renal pathologies. Prescribed in severe stages of hypertension, for example, in renal failure, after heart attacks to prevent death.
- Diuretics (diuretics).
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers many remedies to lower diastolic blood pressure, but they should only be taken with the permission of a doctor. As a rule, these are decoctions and infusions that reduce nervous tension, help you relax and calm down.
Hawthorn
An infusion of the fruits of this plant relaxes vascular walls and relieves nervous excitability. A glass of water will require 20 grams of dry fruits. Boil for 30 minutes, then strain and add water to the original volume. Take a tablespoon three times a day.
Traditional medicine suggests treating hypertension with a decoction of hawthorn fruits
Motherwort
The infusion increases the strength of heart contractions, calms the nerves, and eliminates overexcitation. Two tables. Pour a spoonful of herbs into a glass of hot water and leave for an hour. Drink two per table. spoons every day before bed.
Diuretic collection
Pour a mixture of herbs (a tablespoon each of St. John's wort, oregano, motherwort and sage) with boiling water (two glasses) and leave for half an hour. Drink half a glass a day for a month.
Valerian
It has a relaxing effect on the central nervous system and helps lower blood pressure.
Peony
Pharmacy tincture from herbs and peony roots eliminates muscle spasms and has a calming effect.
Cedar cones
Tincture of pine cones helps lower blood pressure. To prepare, you need to take three whole cones, put them in a glass jar and fill them with vodka (1/2 liter), add ten pieces of sugar, a tablespoon of valerian tincture purchased at the pharmacy and leave for 10 days in a dark place. Strain and drink a tablespoon before bed. You can fill the cones two more times.
Beet
Freshly squeezed beet juice strengthens vascular walls and is used to lower blood pressure. You need to take two teaspoons of juice daily half an hour before meals.
Increased upper pressure: causes, symptoms
Upper (systolic) pressure reflects the contractile activity of the myocardium during systole. Its increase may be due to various reasons:
- congenital defects and acquired cardiac pathology - coarctation of the aorta, PDA, blockade of the atrioventricular node, insufficiency of the valves at the entrance to the aorta;
- ion deviations - accumulation of sodium and calcium in the blood;
- atherosclerosis of large and small vessels;
- renal pathologies of an inflammatory, autoimmune nature;
- diabetes;
- dehydration of the body.
Over time, increased upper pressure first leads to hypertrophy, and then to wear and tear of the myocardium and the formation of heart failure. The aortic wall becomes rigid due to constant trauma by increasing blood pressure. Hemodynamic disturbances of internal organs are also noted due to inadequate distribution of blood through the vessels.
This type of hypertension is more often recorded in women. It manifests itself as regular headaches, discomfort in the heart, fatigue, memory impairment, tinnitus, and decreased vision.
Features of treatment
Any symptom of hypertension is considered dangerous because its consequences are unpredictable. Therefore, if it occurs:
- prolonged dizziness;
- disorientation in space;
- migraine with nausea;
- syncope (fainting);
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- unruly legs and arms;
- facial asymmetry;
- chest pain of varying intensity;
- neurological symptoms - you need to call an ambulance.
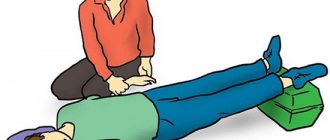
Before the doctors arrive, there is very little that can be done at home.
First aid
{banner_banstat4}
First of all, you need to calm the patient down. Then:
- help him take a comfortable position;
- open the window, loosen tight clothing;
- measure blood pressure.
You can take medications only if you already have a proven regimen for stopping the attack. You can reduce lower pressure without affecting the upper if:
- take a quarter of a Captopril tablet;
- Verapamil tablet or another calcium antagonist;
- No unnecessary movements, basins of hot water, cold douches are allowed.
Upon arrival of doctors, you should agree to hospitalization.
Medicines
The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor depending on the individual characteristics of the person; the following drugs are most likely to be used:
| Group of drugs | Mechanism of action |
| Diuretics (Veroshpiron, Spironolactone, Triampur) | Remove excess fluid from the body, reduce tension in the vascular bed, lower blood pressure |
| Adrenergic blockers (alpha: Doxazosin, Yohimbine, Nicergoline, beta: Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Norvasc) | Reduce arterial tone, affecting endothelial receptors, reduce heart rate, leading to a drop in lower blood pressure |
| ACE inhibitors (Losartan, Telmisartan, Rasilez) | Block the production of biologically active substances that stimulate vasospasm, reducing DBP |
| Calcium antagonists (Amlodipine, Verapamil, Felodipine) | They stop the flow of ions that potentiate vasospasm, cause dilatation of the arteries and a fall in the lower marker |
Isolated arterial diastolic hypertension is insidious, it is difficult to find effective therapy, therefore they use a combination of drugs from different groups and folk recipes, among which the most effective are herbal decoctions:
- bearberry;
- lingonberry leaves;
- rowan.
In addition, tincture of horsetail and pine cones is used. Only regular use of these medications can lower your lower blood pressure.