What's happened
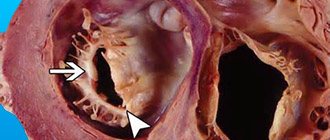
First, it’s worth understanding what a carotid artery is: in the human body there are two carotid arteries, running from the chest through the sides of the neck to the head. Their main task is to nourish the brain. Like any artery, they are confirmed by atherosclerosis - a serious disease, the nature of which is not fully understood, as well as the causes. This disease manifests itself in the deformation of the walls of blood vessels, when the tissues lining the vessel grow, cholesterol deposits appear between them, and the lumen of the vessel becomes smaller and smaller until it becomes completely blocked (obstruction). Oxygen-enriched blood flows through the carotid arteries for brain cells, so narrowing the lumen of the vessel is very dangerous - it can cause a stroke.
About prevention
To prevent carotid artery stenosis from being taken by surprise, attention should be paid to the prevention of vascular diseases. Since the symptoms of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries are often associated with bad habits (smoking, eating fatty foods, lack of physical activity), preventive measures are directly related to the normalization of lifestyle. Often the causes of a stroke lie in the fact that a person ignores the body’s alarm signals and seeks medical help too late. It is better to contact a specialized vascular center in Moscow in time and undergo an examination than to subsequently pay heavily for your negligence.
Causes and prevention
The causes of vasoconstriction are being actively studied, but there is still no clear understanding. A hereditary cause is identified, and everything else can be attributed to risk factors. Among them:
- arterial injuries,
- obesity,
- smoking,
- diabetes,
- sedentary lifestyle,
- older age,
- high level of “bad cholesterol” in the blood (low-density lipoproteins are a combination of cholesterol and protein that do not take excess cholesterol from the vessels, but, on the contrary, attach them to the walls, forming cholesterol plaques).
Prevention of carotid artery stenosis, like any other arteries, consists of maintaining a healthy active lifestyle and a balanced diet to prevent an imbalance in the ratio of low- and high-density lipoproteins, and therefore the development of atherosclerosis.
Causes
In most cases, vascular stenosis is caused by the presence of atherosclerotic plaques on their walls. A chronic vascular disease such as atherosclerosis gradually affects large arteries. Cholesterol is an element present in the blood of every person. Any of us is susceptible to a disease such as atherosclerosis, and vascular stenosis as its consequence. Provoking factors in this case are bad habits (smoking, alcohol), poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and old age. Diabetes mellitus can also aggravate arterial stenosis.
Cholesterol deposited on the vascular walls hardens and turns into dense plaques. If they block the lumen of the vessel, we are talking about stenosing atherosclerosis. Fragments of atheromatous plaques can separate and form blood clots, which leads to complete blockage of blood vessels. In addition, atherosclerosis weakens the walls, as a result of which they delaminate and aneurysms form on them - a vascular pathology, which you can learn about in detail here.
Symptoms of carotid artery stenosis
The disease is dangerous because the symptoms are practically invisible, and only when stenosis becomes the cause of other pathological conditions does a person consult a doctor. Among such conditions, ischemic attacks (mini-stroke, small stroke) are primarily distinguished, when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted for a short period of time. This condition manifests itself as follows:
- numbness of hands/arms,
- speech distortion,
- temporary loss of vision, visual acuity,
- temporary disorientation,
- numbness of the face.
And more general symptoms
- headache,
- nausea,
- weakness.
Carotid artery stenosis develops slowly, often asymptomatically, and people attribute general fatigue and increased fatigue to excessive stress or the weather. Therefore, doctors recommend carefully monitoring your condition, and, if you experience prolonged general weakness without obvious reasons, contact a specialist. Some diseases are so dangerous if not diagnosed promptly that the risk of their presence justifies an unplanned trip to the doctor, who will reassure you if there is no cause for concern, or carry out the necessary diagnostics if suspicions arise.
Clinical picture or symptoms of atherosclerosis
Symptoms of atherosclerosis depend on the organ that feeds the vessels affected by atherosclerotic plaques. Thus, when the coronary arteries are damaged, the heart muscle (myocardium) suffers, and coronary heart disease (CHD) develops. Signs of angina appear - chest pain and shortness of breath during exercise or at rest.
Among the vessels supplying the brain, the internal carotid and vertebral arteries are most often affected by atherosclerosis. In this case, patients may experience dizziness, impaired memory and vision, episodes of loss of sensitivity or movements in the face and limbs, and speech disorders. With the long-term existence of an atherosclerotic plaque in the lumen of the carotid artery, ulcerations may occur on its surface, as well as blood clots, which can be carried with the bloodstream into the vessels of the brain, causing clinical manifestations such as paresis/paralysis, sudden loss of sensation in the limbs or in the face, as well as temporary blindness.
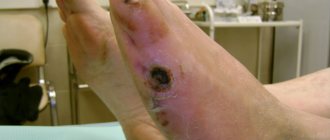
When the vessels of the legs are damaged, symptoms of intermittent claudication appear - pain in the calf (less often in the gluteal and thigh) muscles that occurs when walking. With the progression of obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, trophic ulcers and gangrene of the extremity ultimately occur. With atherosclerosis of the iliac arteries, potency disorders (erectile dysfunction) may also occur.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing a narrowed blood vessel may require one or more types of tests because the location of the narrowing is not always easy to find. For this purpose, our center uses:
- ultrasound - as the main method - since modern equipment provides maximum information not only about the presence of stenosis, but also the degree of deformation of the vessel, while being a non-invasive safe diagnostic method;
- MRI or CT;
- angiography - thanks to the introduction of a contrast agent, a complex diagnostic device monitors blood flow throughout the body, noting even minor deviations from the norm).
To diagnose atherosclerosis (which is the cause of narrowing), a laboratory method is also used - a blood test.
Prevention of vascular atherosclerosis
The best treatment for atherosclerosis is its prevention. It is necessary in order to prevent the occurrence of the first signs and symptoms of the disease, which will help overcome atherosclerosis already in the initial stages. Prevention consists primarily of diet: do not abuse fatty foods, as well as mandatory smoking cessation. If you have hypertension (hypertension), it is necessary to maintain normal blood pressure values by monitoring it, as well as taking medications, after consulting with a therapist or cardiologist. In the presence of diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to maintain normal blood glucose levels by taking glucose-lowering drugs prescribed by an endocrinologist, daily monitoring of blood glucose levels, and regular monitoring by an endocrinologist.
Treatment of carotid artery stenosis
The most common treatment for stenosis is artery stenting. Stenting is a surgical treatment method, therefore, like any other surgical intervention, it requires a highly qualified doctor in diagnosis, deciding on the need/possibility of surgery and direct insertion of the stent. A stent is a metal frame inserted directly into an artery. At the point of narrowing, it unfolds and expands the walls of the vessel as necessary. The stent remains in the artery. Only in the first days its presence can be inconvenient due to changes in blood flow, but over time the patient stops feeling it and returns to normal life without the risk of a stroke. But of course, the doctor will give certain recommendations for further lifestyle in order to prevent re-stenosis.
Our doctors understand the importance of high-quality patient management and postoperative monitoring, so by contacting us, you can count on an integrated approach to diagnosis, treatment and the postoperative period. To implement this approach, the neurology department of the Federal Scientific Research Center has a powerful diagnostic base and a strong team of specialists with extensive experience in the treatment of stenosis, who additionally undergo advanced training courses on a regular basis. The department closely cooperates with the cardiac surgery service and the department of vascular surgery, which is separated into a separate unit.
The advantage of our center is the provision of a full range of services to our patients in one place, starting with an initial consultation, which you can sign up for by phone or through a special form on the website.
How to treat vascular atherosclerosis: drug treatment of atherosclerosis
Vascular atherosclerosis can be combated conservatively and surgically. Conservative treatment of atherosclerosis is used for mild and non-stenotic forms of atherosclerosis. It includes the fight against risk factors for atherosclerosis, as well as taking medications such as statins (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, etc.) and antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, etc.), which prevent further growth of atherosclerotic plaques and the formation of blood clots on them. surfaces. Medications are prescribed for permanent or long-term use.
Treatment
The method of treating narrowing of blood vessels in the cervical spine is prescribed depending on the degree of progression of the disease. The earlier the condition is detected, the easier it is to get rid of it; in the later stages, only surgery is indicated.
Drug treatment
It is prescribed if the manifestations of stenosis are not yet very pronounced. In such a situation, the patient will have to take a large number of medications, among which will be:
- antioxidants;
- vasodilators;
- statins;
- fibrates;
- antidepressants.
Treatment with medications for vasoconstriction of the cervical spine involves quickly relieving pain and stopping the progression of the disease.
Operation
If the doctor determines vascular spasm and their occlusion by more than 70%, only surgical intervention will be indicated. There are several options to solve the problem:
- Carotid endarterectomy - the vessels are “cleaned” of plaques by scraping them out.
- Angioplasty - the lumen of the vessel is increased thanks to a special catheter.
- Stenting - a special frame is installed, which leads to straightening of the narrowed section of the vessel.
The possibility of performing each type of operation is determined by the doctor individually, since each type has its own indications and contraindications. Everything will depend on the diagnostic results.
Diagnostic methods
Neurologist
It is not enough to interview and examine the patient to identify narrowing of the blood vessels of the spine; in any case, additional examinations will be prescribed. These include:
- Duplex scanning
- despite the fact that this is a rather dangerous diagnostic method in this situation, it is informative and accessible, it allows you to determine the degree of narrowing and its nature. - Angiography - the process uses a contrast agent to examine the vessels.
- and MRI
- allow you to obtain layer-by-layer 3D images, with which you can make a diagnosis.
All this will allow the doctor to determine not only the patient’s health status, but also the reasons that led to the occurrence of stenosis.