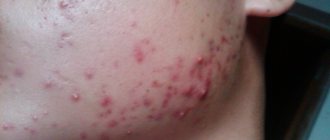
Skin diseases are accompanied not only by pain and severe discomfort, but also by the risk of unaesthetic scars or scars appearing on the skin. Therefore, it is extremely important to promptly contact a dermatologist who can diagnose the disease at an early stage and prescribe effective therapy. Our medical center provides the opportunity to receive qualified medical care, as a result of which it is possible to accurately diagnose and eliminate signs of skin damage. One of the most common problems with which patients come in this direction is demodicosis. This is a rather dangerous and problematic pathology, which is almost impossible to cope with on your own.
What is this?
Demodicosis in humans develops as a result of reproduction in the hair follicles, sebaceous glands of the skin and meibomian glands of the iron mite (Demodex). The breeding ground for the development of this parasite is sebum, so its main habitat is the skin of the face and external ears. But with a complicated course and lack of timely treatment, the skin of the chest and back is involved in the pathological process.
It is important to understand that healthy people can also be carriers of such a tick, since it is a representative of normal microflora. According to official statistics, about 60% of people are infected with Demodex, but not everyone develops this parasitic disease. Demodicosis of the body develops with the slightest disturbance of the biocenosis and a drop in immune defense.
Pathogenesis
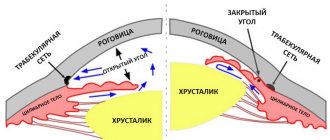
Demodectic blepharitis can be divided anatomically into anterior and posterior blepharitis. The first refers to invasion of eyelashes and follicles by D. folliculorum, clustering at the root of the eyelash, while the second involves infection of the meibomian glands. The following mechanisms of action have been proposed to explain the pathogenetic role of ocular demodicosis in blepharitis and other ocular disorders.
Direct damage
Demodex mites, especially folliculorum mites, consume the epithelial cells of hair follicles, which can contribute to the formation of lost or misdirected eyelashes. Micro-abrasions caused by mite claws can cause hyperplasia, epithelial and reactive hyperkeratosis around the base of the eyelashes, forming cylindrical dandruff. On the other hand, D. Brevis can mechanically block the openings of the meibomian glands, leading to meibomian gland dysfunction with tear lipid deficiency disorders. D. brevis usually burrows deep into the meibomian glands and its chitinous exoskeleton can act as a foreign body, causing a granulomatous reaction. D. brevis is observed in the center of the meibomian granuloma, surrounded by epithelioid cells, histiocytes, fibroblasts, lymphocytes and plasma cells. Thus, Demodex ocular mite may be a potential cause of recurrent and persistent chalazion.
Vector for bacteria
The demodex mite can cause blepharitis by carrying bacteria to the surface, including streptococci and staphylococci. Superantigens produced by these bacteria are also involved in the induction of demodicosis. Additionally, bacteria inside Demodex mites have been found to trigger an immune response. Bacillus oleronius, recently identified within Demodex mites, may stimulate the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with demodicosis. Our collaborative and prospective study further uncovered a strong association between positive serum immunoreactivity (83-kDa and 62-kDa bacillus proteins) and ocular Demodex infection, rosacea, facial acne, and blepharitis. Even dying mites in follicles or glands can increase the release of these two bacterial antigens. At a critical level of mite numbers, they cause a cascade of host inflammatory reactions.
Hypersensitivity reaction
Protein inside demodex mites, their remains or waste can cause inflammatory responses through delayed-type hypersensitivity or innate immune responses. Studying 92 consecutive cases of papular-pustular demodicosis, we found that infection of hair follicles was associated predominantly with an intense perifollicular CD4 infiltrate or T-cell inducer. In patients who tested positive for D. folliculorum, an increase in the number of macrophages and Langerhans cells was observed.
Causes of demodicosis
As mentioned above, the main reason for the development of this disease is the active reproduction of the iron mite. There are several possible reasons that can lead to increased activity of these opportunistic microorganisms. These are internal and external factors. The first category includes:
- A significant drop in immune defense and exhaustion of the body caused by poor nutrition, autoimmune pathologies, previous diseases, constant stress, etc.;
- Viral and microbial diseases that occur in chronic forms (hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc.);
- Helminthiases. The vital activity of helminths contributes to the weakening of the immune system;
- Malignant neoplasms. With many types of oncology, the body becomes exhausted, making it more difficult for it to cope with infections;
- Damage to the gastrointestinal tract. There is a proven relationship between the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and demodicosis;
- Other skin diseases. These are seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, acne, etc. In the presence of inflammatory processes or integrity disorders on the skin, the risk of pathogenic activation of opportunistic flora increases significantly;
- Hormonal imbalance associated with illness or natural condition (for example, pregnancy or breastfeeding).
Skin demodicosis can also develop as a result of exposure to unfavorable external factors. As a rule, they are combined with internal ones, but in some cases (for example, choosing the wrong skincare products) they can be the main etiology. Among them:
- Temperature effect. This parasite multiplies especially actively in warm conditions;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. This includes poor nutrition, frequent stress and bad habits;
- Use of low-quality cosmetics for care. This is especially true for cosmetics that do not have quality certificates and do not meet legal requirements;
- Poor environmental conditions. High levels of environmental pollution lead to a weakening of the barrier function of the skin.
Introduction
Demodex mites are the most common microscopic ectoparasites found in human skin. The rate of spread of Demodex pests increases with age, affecting 84% of the population over 60 years of age and 100% of those over 70 years of age. In addition to high densities in patients with demodicosis, demodex mites are also implicated as a cause of other skin diseases such as pityriasis folliculitis, eyelid dermatitis, exacerbation of scabies-like symptoms, facial pigmentation, alopecia, demodicosis myasthenia gravis, and even basal cell carcinoma. Since the eye is surrounded by prominent parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks, the eyelid is not as accessible to daily hygienic cleansing as the face. Therefore, once a Demodex infestation affects the face, it is likely to spread and develop on the eyelids, which can lead to blepharitis. Despite this, the clinical significance of Demodex infection remains controversial, in part because it can be found in asymptomatic patients. As a result, in case of demodicosis, the differential diagnosis of the cornea and external diseases is often forgotten, not to mention the consideration of therapeutic options. In the study, we summarized the key literature and our research experience regarding the pathogenic potential of Demodex mites in causing inflammation of the ocular surface.
Demodectic mange symptoms
Due to the fact that this disease can affect different areas of the skin, the clinical picture differs. In the cutaneous form, the following signs of demodicosis appear:
- Acne of varying severity: from small nodules and ulcers to rosacea;
- A strong tooth that causes discomfort. In most cases, it intensifies in the evening and night;
- Excessive sebum production. It is the greasy environment that is most nutritious for ticks of this genus;
- Red spots that are a symptom of high blood pressure in the blood vessels. This indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- Nose enlargement. If you contact a dermatologist late or in the absence of adequate treatment, it is possible to replace the functioning tissue with connective tissue.
Demodicosis of the eyelids and eyes, in turn, manifests itself as follows:
- Clumping of eyelashes. Along their growth line, a thin layer of film is formed that has adhesive properties;
- Redness of the eyelids as a result of the inflammatory process;
- Tired eyes. This symptom occurs due to inflammation and due to the fact that the patient is forced to strain his vision;
- Eyelash loss caused by damage to hair follicles.
A person perceives the world using five senses: sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. And although it is very difficult to single out one of the senses and call it the main one, vision is always named first on this list. And folk art testifies that the eyes have always been considered a very important human organ. “His eyes are behind him” people say about people who do not see obvious things; not only poets, but also psychologists call the eyes the mirror of the soul, and many such examples can be given. The world fades when something happens to the eyes. And there can be a lot of troubles here - from a speck that accidentally gets on the mucous membrane, to serious injuries and diseases.
Symptoms of the presence of demodex and demodicosis caused by it
If the eyelids begin to itch intensely and it is almost impossible to relieve this itching, if the eyelids swell and their edges turn red, if eyelashes fall out, and dry crusty scales form along the edges of the eyelids, then there is reason to suspect the presence of demodex.
What does a Demodex mite look like?
Often the disease also affects the mucous membrane of the eyes - the eyes become red, the mucous membrane becomes dry and irritated, and eye fatigue appears very quickly. In addition, mucous and sticky discharge appears, which accumulates along the edges of the eyelids, and yellowish crusts appear after sleep. Cream and any cosmetics, as well as ultraviolet rays (either in the sun or in a solarium) only aggravate and worsen the condition and increase both swelling and itching.
Symptoms that may lead one to suspect demodicosis include blurred vision, a feeling that the eyes are covered with sand, photophobia (the desire to hide from light sources or at least close the eyes), and the frequent formation of styes. Symptoms may appear at different times and with varying intensities.
Demodicosis of the eyes (and this is what we were talking about) can begin in any person (it is known that demodicosis has “blessed” 97% of people on the planet with its presence), but people with a weakened (for example, colds) immune system are at particular risk, with metabolic disorders, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as pregnant women and elderly people whose immune status is reduced due to physiological reasons.
Factors that can provoke the disease can be the use of corticosteroids (especially in the form of ointments), climate change, and severe stress, that is, any life situation that in one way or another can affect the state of the immune system. Also, provoking factors include increased oily skin and seborrhea, many cosmetic procedures (including manual facial cleansing, solarium, and peeling), high temperatures (and it doesn’t matter at all whether it’s a hot shop or a sauna).
Among other things, it is necessary to note the importance of hygiene procedures, because insufficiently careful adherence to hygiene rules can also provoke this disease. As a rule, demodicosis becomes a chronic disease with periods of remission (when the condition becomes significantly better) and exacerbation (in most cases this is spring and autumn).
Causes of demodicosis
Demodicosis of the eyelids or eyes is a chronic eye disease that is caused by small parasites - Demodex eyelash mites (Demodex folliculorum or Demodex brevis). These mites are not just small, but literally microscopic (the largest specimens do not exceed 0.5 mm in size), and they can only be seen with sufficient magnification.
Demodex mites are opportunistic microorganisms, that is, for the time being they do not cause any concern or inconvenience to the person on whose skin they live. But when the immune system suffers (the reason does not matter), microscopic mites begin to actively reproduce, their population increases many times and this becomes a serious problem. Moreover, it should be understood that demodex mites (eyelash mites) feed on dead skin cells and therefore are completely harmless in themselves.
And all the inconveniences and problems are caused by the waste products of these microscopic parasites, because these are the strongest allergens that provoke the appearance of seborrhea, rosacea, blepharitis (demodex of the eyelids) and blepharoconjunctivitis (demodex of the eyes).
Attention! Demodicosis is a contagious disease that is transmitted through personal contact, including handshakes, and through cosmetics and care products.
Treatment of demodicosis
Treatment of demodicosis is a long and quite troublesome process, because it is not limited only to the use of medications.
Attention! The diagnosis must be made by a doctor after laboratory tests.
Since demodicosis is contagious, every effort must be made not to infect others and to prevent repeated self-infection. Thorough sanitization and disinfection of bed linen, towels, personal hygiene items and clothing is necessary. Naturally, it is not permissible to use shared towels - everything must be individual.
During treatment, it is recommended to change the pillowcase on the pillow daily, wash it and steam it with an iron.
All cosmetic products should have dispensers; it is better not to use mascara at all during this period, because changing the brush every day is very problematic. It is better to avoid contact lenses during treatment for demodicosis, and glasses must be disinfected daily (by the way, do not forget about the need to disinfect the glasses case). The same goes for shaving accessories. When washing, it is better to use only disposable wipes. And, unfortunately, you will have to limit close contact with your pets. Visits to the bathhouse, sauna, and swimming pool will also have to be postponed for now.
When treating demodicosis, nutrition is very important: spicy, salty, fatty, sweet and any irritating foods should be excluded from the menu. Alcohol is completely contraindicated.
It is very important to understand that demodicosis is a chronic disease with remissions and exacerbations, so it is very difficult to treat. It is almost impossible to cope with demodicosis on your own, so contacting an ophthalmologist will be the best solution in this situation.
Any medications are prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis has been established. In any case, cleansing of the eyelashes and eyelid skin with an alcohol-containing solution (for example, calendula tincture) will be prescribed, using only disposable cotton swabs or swabs. Some time after this procedure (about 15 minutes), it is necessary to apply a cream or ointment prescribed by the doctor to the edges of the eyelids.
The names of these medicines may be different, but only a doctor can determine which medicine should be used in a particular case. Using the “wrong” drug will only complicate further treatment and make it even longer.
The ointment or cream is applied to the eyelids twice a day after the skin of the eyelids has been thoroughly cleansed. It is likely that the treatment will not be limited to the use of ointment or cream, but eye instillation with antibacterial drops will be prescribed, which will be prescribed by the attending ophthalmologist. Self-prescription of any medications is unacceptable.
In addition to medications, physical therapy may be prescribed, possibly the use of drugs that can correct the functioning of the immune system and normalize metabolic processes in the body. It is possible to prescribe vitamin complexes. But any prescriptions for the treatment of demodicosis can only be made by the attending ophthalmologist.
It is very important not to postpone a visit to the doctor if alarming symptoms appear, because treatment of demodicosis in the early stages of the disease is disproportionately simpler and faster (but still long and difficult) than treatment of advanced forms.
Prevention of demodicosis of the eyelids (eyes)
- Firstly, you should not neglect the rules of hygiene and always use only individual hygiene items. Especially if any symptoms of the disease appear.
- Secondly, a healthy diet is very important, which will allow the body to maintain an excellent (or at least as good as possible) immune system.
- Thirdly, it is necessary to protect your eyes from sunlight and use sunglasses.
- Fourth, during periods of active sun exposure to the skin (especially in summer), you should use sunscreen with SPF of at least 15.
If demodicosis has been diagnosed at least once, the likelihood of its reappearance is very high, so you should constantly carefully monitor the condition of the eyelids and eyes.
It is necessary to understand, although you don’t want to believe it, that it is almost impossible to cure demodicosis without the help of a doctor. Therefore, only timely seeking qualified ophthalmological help can help, and such treatment is simply necessary.
Similar
Diagnostics
Demodicosis on the face and skin is diagnosed by a dermatologist. If the disease is secondary and has developed against the background of the underlying disease, then doctors of other specialties (gastroenterologist, gynecologist, trichologist, endocrinologist, etc.) may be involved for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. For diagnosis, first of all, visual inspection is used. The doctor evaluates the condition of the skin, eyes and affected areas of the body. In addition, eye biomicroscopy and laboratory examination methods are practiced. The most informative of them are:
- Slit lamp biomicroscopy of the eye is a non-invasive examination aimed at looking for active inflammation. This is an absolutely painless manipulation that does not require special preparation;
- Eyelash test - involves taking freshly removed eyelashes (4 from each eyelid) for further examination under a microscope. Using this method, it is possible to determine the number of parasites (the presence of more than 1 mite on 2-4 eyelashes is pathogenic). This is also a painless procedure, but before it is carried out it is necessary to abandon decorative and skincare cosmetics for several days;
- Biopsy. This is the most informative diagnostic method, but the most traumatic. Diagnosis is carried out under local anesthesia using a tubular knife or scalpel. The taken biomaterial is fixed in a formaldehyde solution for a day and treated with dyes. This makes it possible to fully visualize the gland and adjacent tissues with the pathogenic mite.
Non-drug therapy
Treatment of blepharitis can be carried out not only with the help of medications. Non-drug therapy can also be carried out. So, it is useful to wipe your eyelids with decoctions of calendula or chamomile, or make lotions from green or black tea. To enhance the effect, you should resort to physiotherapy. It is worth taking medications to strengthen the immune system: vitamins and vitamin-mineral complexes. During treatment, it is recommended to avoid spicy, sour and salty foods. It is necessary to seek the help of specialists such as a dermatologist, nutritionist, gastroenterologist and allergist. To cleanse the skin, you can use soap with added tar and rinse it off thoroughly, avoiding contact with the cornea. Additionally, tansy can be used as an antiparasitic agent, a strong decoction of which should be rubbed into the surface of the head. Another effective remedy is propolis. It is necessary to dissolve 5 grams in 100 ml of water and instill this solution into the eyes. This will help relieve irritation, dryness and itching.
Kalanchoe juice will help get rid of skin ulcers: the product should be applied to the edges of the eyelids with a cotton swab. If the crust does not come off the eyelids and pus forms, it is worth treating the area with brilliant green diluted with vegetable oil. Tinctures of ginseng root, eleutherococcus, and echinacea are also indicated for the treatment of blepharitis. An integrated approach will help get rid of this complex eye disease.
Classification
Demodicosis (photo can be found below) is classified into 2 main clinical forms - primary and secondary. The first diagnosis is made in the event of a sharp surge in parasitic reproduction and effective treatment with the use of antiparasitic drugs. In most cases, it occurs in people over 40 years of age. The secondary form is diagnosed by identifying concomitant skin lesions and systemic diseases (usually associated with immunodeficiency). In some cases, this diagnosis is found in people taking epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and in those who have been exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
Based on the symptoms manifested on the skin, the following types of demodicosis are distinguished:
- Acneiform - the presence of papules and pustules similar to acne;
- Rosacea-like - papules appear due to diffuse erythema;
- Seborrheic - skin rash combined with peeling;
- Ophthalmic - inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by discomfort in the affected eye.
Complications of the disease
Treatment of demodicosis on the face should be carried out exclusively with the assistance of a doctor. Self-medication or ignoring this problem may not only not bring the desired result, but also worsen the course of the pathology. Skin scratching and regular trauma to the skin (due to severe itching and the patient’s desire to remove the rash mechanically) lead to disruption of the barrier function. As a result, the risk of developing a pustular infection significantly increases, which can be diffuse and affect large areas of the body.
In addition, this disease (especially demodicosis on the face in women) leads to psychological problems. As a result of the appearance of visible defects, the patient becomes withdrawn, begins to feel embarrassed about his appearance and stops leading a full-fledged lifestyle (closes himself off from the outside world, stops communicating with people, prefers to be alone). As this problem worsens, the developed complexes can develop into psychoses, neuroses and prolonged depression.
A large number of people with this diagnosis have concomitant pathologies (gastrointestinal tract, endocrine glands, etc.) and chronic infectious foci. Demodicosis damage to the body contributes to the aggravation of these conditions and, accordingly, deterioration of well-being.
Skin demodicosis
The transmission route is contact or contact-household. Can be transmitted through contaminated clothing, bedding, contaminated hands and more. Demodex is distinguished by its survivability under comfortable conditions that correspond to the daily life of most people. The parasite remains viable at a temperature of 17-20°C for 10 days or more, and in an aquatic environment at a temperature of 12-18°C for 3 days. When water is heated to 50° C, the microorganism dies within one minute, and at low temperatures it dies immediately.
To date, there is no single theory explaining the etiology of the development of the inflammatory process and the active reproduction of mites. But there are several predisposing factors that can provoke these processes:
- Excessive sebum production;
- Improper skin care, abuse of cosmetics (especially low quality);
- Long-term use of external corticosteroids;
- Poor nutrition (abuse of sugar, soda, spicy foods, coffee, alcoholic drinks);
- Concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- Reduced immunity;
- Hormonal imbalance, excess weight;
- Psychological problems, frequent stress.
Demodectic mange of the eyelids
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids requires a comprehensive approach and qualified medical intervention. Demodectic blepharitis is a chronic disease that occurs with periodic exacerbation and remission. It has the following clinical picture:
- Severe eye fatigue associated with the need to strain to better focus on an object or letters;
- Intense itching in the eyelashes and eyebrows. Often this symptom intensifies with external exposure to heat, in the evening and at night;
- Foreign body sensation, burning and tingling that does not go away after washing or scratching;
- Sticky discharge from the eyes after waking up;
- Accumulation of foamy contents in the eye corners;
- Hyperemia, swelling and thickening of the eyelids (especially at the edges).
- The chronic form of demodectic blepharitis can be complicated by keratoconjunctivitis, keratitis and dry eye syndrome. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to consult with an ophthalmologist at our clinic, who will be able to prescribe preventative and therapeutic therapy aimed at maintaining eye health.
The main symptoms of demodectic blepharitis
With this eye disease, pronounced symptoms are observed. Signs of the disease are usually noticed by the patient himself, but this does not eliminate the need to consult an ophthalmologist
to make a final diagnosis.
The most characteristic symptoms of this disorder include:
- Swelling and itching of the eyes and eyelids;
- Sticky eyelashes;
- A specific plaque, as well as small, but noticeable upon close examination, scales located along the edges of the eyelids and at the roots of the eyelashes.
If you have any of these signs, you should contact a specialist! This is necessary not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to alleviate your condition.
Demodicosis of the ear
This pathology does not always stop at the face. In advanced cases or in the absence of timely treatment, it spreads to neighboring areas of the body, including the ears. In such a situation, it will not be possible to quickly get rid of demodicosis, especially without medical help. Damage to the auricle is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- Intense itching and irritation of the skin. As a result of constant scratching, bruises and microtraumas appear;
- Hyperemia and swelling of the ear, indicating an inflammatory process;
- The presence of red rashes of varying sizes and quantities;
- Pain upon contact with the skin (often a consequence of a violation of the barrier function of the tissue).
Preventive measures to prevent demodicosis
During primary infection with this disease, prevention should be aimed at a general increase in immunity.
Maintaining hygiene, alternating visual stress with periods of rest, and regular visits to the ophthalmologist for preventive examinations are of great importance.
If the disease is chronic, prevention should be focused on eliminating self-infection:
- To wipe your eyes, you must use disposable wipes.
- Treat glasses with antiseptic solutions.
- Minimize contact with your face and avoid touching your eyes unnecessarily.
- Treat your face with lotions containing alcohol.
- Disinfect razors.
- After massaging the eyelids, wash your face.
- Change your bed linen as often as possible or place a disposable cloth napkin on your pillow before going to bed.
All cosmetics, tools for applying them, and lenses must be disinfected or disposed of. If these rules are followed, the cured pathology will not arise again and will not spread to other areas of the skin.
Demodicosis of the head
Ticks of the genus Demodex are representatives of opportunistic microflora of the skin on the body, including the head. They are present in almost all people on the planet. In everyday life, their activities do not cause visible discomfort; they exist in a mutually beneficial relationship with humans, fighting harmful microorganisms. But when the immune defense drops and unfavorable conditions set in, the parasites begin to multiply uncontrollably, as a result of which their numbers increase greatly, and the vital activity of these parasites becomes noticeable. This situation can result from:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Long-term use of antibacterial and hormonal medications;
- Poor nutrition;
- Abuse of saunas, steam baths and solariums;
- Using low-quality cosmetics to care for skin and hair (since demodicosis needs to be treated comprehensively, our clinic specialists help patients choose the right and safe care products);
- Failure to comply with simple hygiene rules.
Results
Demodicosis of the eyelids is a disease caused by skin mites of the Demodex species. This is a fairly common infection that affects people, regardless of gender and age. The tick itself is not life-threatening; many people are carriers. But with weakened immunity, hormonal, age-related changes in the body, or under the influence of other factors, parasites begin to actively multiply and develop, which can provoke demodicosis. The disease is usually diagnosed using laboratory tests of samples of biological material. The treatment is complex and includes both drug therapy and special procedures to cleanse the skin, relieve inflammation, itching and other symptoms of the disease.
Demodicosis treatment
The treatment regimen for demodicosis is a set of measures aimed at eliminating external symptoms and the cause that provoked them. The final stage of therapy is the use of preventive measures that help consolidate the therapeutic result and prevent relapse of the disease. It is important to understand that it is almost impossible to cope with this problem on your own. This problem requires qualified help and long-term drug treatment, since an infected person is dangerous to others. It is a source of infection and can therefore infect other people.
Standard therapy aimed at eliminating demodicosis infection consists of several parts:
- Diet for demodicosis. The patient will need to give up fatty, spicy and smoked foods. It is also recommended to reduce your consumption of sugar, sweets and dairy products. The diet should consist of low-fat fish, vegetables and fruits;
- Local treatment. For this purpose, sulfur ointment is used for demodicosis, creams and sprays that have antibacterial and antiparasitic properties;
- Systemic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing sebum production and eliminating existing imbalances (hormonal or metabolic). To do this, it is possible to involve specialized specialists, prescribe antibiotics in tablet or injection form;
- Symptomatic treatment. It is aimed at improving the patient’s well-being, eliminating active symptoms (inflammation, itching, soreness and redness). For this purpose, a special anti-demodetic mange may be prescribed;
- Physiotherapy. To improve the condition of the skin, electrophoresis, laser therapy and ozone therapy are prescribed.
Since it is practically impossible to cure demodicosis quickly but effectively, the average duration of the treatment course ranges from one to several months. The duration depends on the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the body (in some cases, treatment may take a year or more). The main criterion for cure is a repeat tape test with a negative result.
Demodicosis - drugs for treatment
Today, finding effective remedies for demodicosis will not be a problem. The specialists of our medical center select medications in the optimal form on an individual basis, thereby speeding up the healing process. The most popular and effective remedies are described below.
Soap
- Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex demodex.by are especially popular among patients. For demodicosis of the eyelids, the treatment regimen often includes these drugs, as they show excellent results due to the presence in the composition:
- Glycerin - absorbs moisture, holding it on the skin. This helps prevent drying, promotes hydration and improves elasticity;
- Octopirox is an antimicrobial component that inhibits the activity of ticks. It gently exfoliates the top layer of the epidermis, normalizing the process of formation of new cells;
- Propylene glycol - helps normalize microflora, moisturizes the stratum corneum;
- Diazolidinyl urea - provides an antimicrobial effect.
Lotion
Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex lotions are prescribed for constant facial skin care and for cleansing damaged skin areas (even demodicosis on the back) before using the gel. They are often used for eyelid hygiene (for blepharitis), as they deeply cleanse the pores and facilitate the penetration of the active substances of subsequent medications. With their help, it is possible to soften the epidermis and normalize fat metabolism without resorting to tapping the skin. As a result of their regular use, mites are deprived of their nutrient medium, and the tissue is regenerated at an accelerated rate without the formation of scars.
Balm
Therapeutic and prophylactic balm Stop Demodex significantly increases the effectiveness of the main therapy. With its regular use, a visible therapeutic effect is observed after 2-3 days. It has the following properties:
- Anti-inflammatory and bactericidal;
- Moisturizing the skin;
- Promotes rapid tissue regeneration and healing;
- Improves local metabolism;
- Penetrates the cell membrane of the epidermis, replenishes the lack of microelements.
Eye gel
When diagnosing eye demodex, it is strongly recommended to use Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex gels. The presence of peppermint extract in the composition guarantees local anesthesia and inhibition of inflammation. They have a calming and refreshing effect, due to which the patient’s well-being noticeably improves. The presence of metronidazole provides effective antiprotozoal and antibacterial effects, while hyaluronic acid helps improve skin elasticity and firmness. These demodicosis preparations are perfectly absorbed, do not clog pores and do not disrupt cellular metabolism. They accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent the formation of scars.
Cream
An effective cream for demodicosis, Stop Demodex, with constant use, makes it possible to stabilize the normal secretion of the sebaceous glands, restore the skin microflora, eliminate the uncontrolled proliferation of parasites of the Demodex genus and noticeably cleanse the skin from foci of inflammation. It does not contain antibiotics, perfectly nourishes, increases tissue firmness and elasticity, and does not have a comedogenic effect.
Mask
For demodicosis infection, it is strongly recommended to buy a Stop Demodex treatment mask. It contains the active Cutipure complex and white clay, which promotes deep cleansing of pores and reduces the proliferation of pathogenic mites. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and keratolytic effects. Its use allows you to normalize sebum production, tone the skin, improve metabolic processes in cells and accelerate tissue regeneration. Moreover, with its help it is possible to remove toxic molecules.
Shampoo
Using Stop Demodex shampoo for demodicosis of the head, you can significantly reduce itching, eliminate dandruff and stop the active reproduction of parasites. It has a strong anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, fights mites and helps eliminate the consequences of the disease. Its effect is aimed at preventing ticks from sucking nutrients, disrupting their DNA replication and protein synthesis in the cell. The drug inhibits tissue respiration, which is vital for parasitic life.
Prevention
Demodicosis of eyelashes and other parts of the body can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to follow simple preventive rules. This:
- Maintaining personal hygiene (regular showering, thoroughly washing your face, washing your hair and hair);
- Eat a varied, rational and healthy diet (include fish, vegetables and fruits in your diet);
- Increased immune defense;
- Correct selection of decorative and skincare cosmetics;
- Do not use other people's cosmetics and personal hygiene products.
How is demodicosis of the eye transmitted?
Demodectic mange of the eyes can be contracted at home - by sharing hygiene items, towels, bed linen, and cosmetics with the patient.
To prevent re-infection, you need to change your pillowcase and towel (or use paper towels) daily, and throw away contaminated cosmetics.
To treat each eyelid, you must use a separate (new each time) cotton swab.
1 Diagnosis and treatment of demodicosis
2 Diagnosis and treatment of demodicosis
3 Treatment of demodicosis
Demodicosis in children
- In childhood, this pathology rarely develops (due to the low activity of the sebaceous glands), but its course is much more complicated than in adults. As a rule, in children this disease is chronic, and relapses occur in the off-season. The main signs of the problem are:
- Swelling of the eyelids;
- Loss of eyelashes and hair;
- Severe eye fatigue;
- The appearance of spots on the skin;
- Itching, worse at night and on contact with water;
- Decreased appetite, moody behavior, decreased physical activity;
- Pain in the eyes.
The treatment regimen for democosis of the face and other parts of the body in children is practically the same as therapy for adults. It also includes diet, medication and rehabilitation aimed at healing the tissue and preventing scarring. The fundamental difference in the treatment method is only the dosage of medications, which will be lower in childhood.
Risk factors for developing blepharitis due to demodex
Recently, a close relationship between the severity of demodicosis and demodectic blepharitis has been confirmed. Demodicosis predisposes to blepharitis by creating an environment on the skin that compromises the health of the dermis and epidermis. There are other conditions for the spread of mites, for example, skin phototype, exposure to sunlight, alcohol consumption, smoking, stress, drinking hot drinks and spicy foods, and sudden changes in temperature. Due to the anatomical features of the face, the eyelids are not accessible for regular hygienic cleansing, which creates a favorable environment for the spread and development of demodex mites on the eyelids.
The susceptibility to demodex infection is high in patients whose local or systemic immune status is compromised by local or systemic administration of steroids or other immunosuppressive drugs or diseases such as leukemia and HIV.
Demodicosis in men
Demodectic mange infection occurs in both women and men, regardless of age or race. It has no distinctive features in its course, prognosis, symptoms and causes of development. Therapy is prescribed on an individual basis, but is usually the same for all genders. Differences may only relate to the dosage of medications.
According to statistics, women suffer from demodicosis 4 times more often than men. There is no scientific explanation for this information, but many are inclined to the hormonal theory. It is based on the fact that due to a regular surge of hormones (menstrual cycle, pregnancy), female representatives are more prone to stress and immunodeficiency states. The clinical picture of the disease is standard and includes:
- Skin rash of varying severity;
- Itching, pain and discomfort in the damaged area;
- Increased sebum production;
- Pain in the eyes, sensation of a foreign body.
The treatment regimen for demodicosis for women is standard. It consists of a diet, long-term medication and the use of special care products (oils, lotions, creams, etc.) to prevent relapse and consolidate the therapeutic result.
Questions and answers on the disease
Can a sick person infect others?
Yes, you can become infected with demodicosis through contact and household contact. Kissing, hugging, contact with contaminated things of a patient (towel, bed linen, clothes and much more) can be dangerous for a healthy person. But this does not guarantee the manifestation of symptoms of the disease. Ticks of the genus Demodex are representatives of the opportunistic microflora of the skin. They are found in almost all people, but most of them are simply carriers. For the development of a pathological process, the presence of certain factors is necessary (for example, reduced immune defense against the background of an active or past disease).
Can you get infected from animals?
Animals, like humans, suffer from the activity of Demodex mites. But pathogens come in different types - and each of them survives exclusively in the body of its host. When exposed to other conditions, the parasite immediately dies. Therefore, it is impossible to become infected with demodicosis from a pet or wild animal.
Causes of eyelid disease
Infection with tick-borne blepharitis occurs through contact and household contact. The infection is hidden in bedding (such as feather pillows) or dust. Ticks can also appear from the outside: they are able to live autonomously in humid conditions for up to three days.
The cause of the development of the disease can also be disturbances in the functioning of the nervous or endocrine systems, liver, and gastrointestinal tract. Also, the likelihood of infection increases due to heredity.
Other factors that provoke the occurrence of demodectic blepharitis:
- sunburn or prolonged exposure to high temperatures;
- non-compliance with sanitary standards;
- ophthalmological operations;
- acne-prone skin;
- frequent peelings and facial cleansing, solariums and an overabundance of other cosmetic procedures.