Back pain
- a common complaint. Usually we talk about back pain when pain is felt in the lumbar region. Sometimes in such cases they say that “the back is pinched.” According to recent studies, out of every five people, four have experienced such pain at least once in their lives. Read more about lower back pain>>>
Another typical location of back pain is under the right or left shoulder blade or between the shoulder blades. Read more about pain under the shoulder blade>>>
With age, back pain is more common - among older people, every second person experiences such pain from time to time.
Back pain can have a different character: it can be sharp, stabbing, burning, aching, pulling, and can radiate to other parts of the body (for example, to the chest, legs, abdomen, genitals). The pain may be occasional or constant.
When listening to pain, a person usually asks himself two questions: should he see a doctor, and which doctor should he go to for back pain? Let's try to answer these questions.
Cause 1. Spinal infections
Another name is spinal infections. These are viral lesions that affect the internal structures of the vertebrae or the interdisc space. Viruses can enter the body from the outside (wound infections - due to injuries, operations) or be complications of viral diseases (often various types of myelitis, coccal infections, etc.).
Symptoms of spinal column infection depend on the type of infection. This may be unexpressed aching pain in the back and chest area, or sudden intense pain. The focus is quite difficult to determine. The patient usually says “everything hurts.” The condition is accompanied by limited mobility, chills, fever, weakness, and body aches.
If you have these signs, we recommend calling an ambulance immediately. Spinal infections are fraught with paralysis and other irreversible (!) restrictions on mobility. But they are quite rare.
Types of myositis
Often, a disease associated with inflammation of muscles and tissues is considered one problem. Myositis of the back muscles is of two types:
- Acute myositis. Appears as a result of hypothermia or serious injury, which in the future, without careful treatment, leads to complications in muscle function.
- Chronic myositis. The main reasons for the deterioration of the patient’s condition are lack of desire for treatment or infection with a virus. Associated with exacerbation of symptoms at certain times of the year. Sometimes the lack of required treatment leads to disease not only of muscles and tissues, but also worsens the general condition of human organs. In rare cases, skeletal muscle myositis may develop, which can be fatal.
Reason 2. Degenerative-dystrophic diseases
Caused by wear and tear of the intervertebral discs, brittle bones, and loss of elasticity of spinal tissue. Moreover, such changes are not necessarily age-related. Today, young people also suffer from arthritis, spondylosis, and osteochondrosis.
Over time, pathological processes in the spine become degenerative, i.e. irreversible. In this case, it is necessary to use surgical treatment methods - joint replacement, surgical restoration of vertebrae and other structures. Arthrosis, osteoporosis, and radiculitis often develop into a degenerative form.
Of course, such changes do not occur without symptoms. Often patients note lumbago, acute pain in the affected area, limited mobility, stabbing pain, crunching, pain with certain movements (for example, in the lower back when bending forward). As a rule, a person can clearly determine exactly where it hurts.
Treatment of degenerative-dystrophic diseases is carried out by a rheumatologist, osteopath, chiropractor, traumatologist, neurologist and a number of other specialists. Don't know who to contact? Make an appointment with a general practitioner first.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system that cause lower back pain:
Why does your lower back hurt?
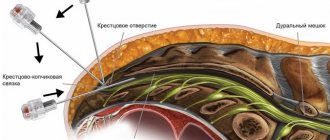
- pinched sciatic nerve. The nerve roots extending from the spinal cord are compressed by neighboring vertebrae. In this case, a sharp, shooting pain occurs. As a rule, pinched roots become possible due to degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis): the intervertebral discs separating the vertebrae from each other are destroyed, the gap between the vertebrae narrows and sudden movement (tilting, turning) can lead to pinching of the nerve branch;
- sciatica (lumbosacral radiculitis). Pinched nerve roots can become inflamed. Inflammation of the nerve roots is called radiculitis (from the Latin radicula - “root”); To indicate inflammation of the sciatic nerve, a special name is sometimes used - sciatica. If the sciatic nerve is damaged, lumbar ischialgia may be observed - pain in the lower back, also spreading to the buttock and leg along the sciatic nerve;
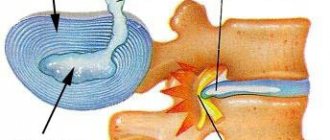
- intervertebral disc herniation – protrusion of a fragment of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. Occurs as a result of injury or degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis);
- myositis of the lumbar muscles. Myositis is an inflammation of skeletal muscles. The cause of myositis of the lumbar muscles can be hypothermia or sudden tension.
Also, lower back pain can be caused by diseases such as multiple sclerosis, degenerative sacroiliitis, osteoporosis.
Reason 3. Intervertebral hernia
Intervertebral hernia is the “squeezing out” of the nucleus pulposus by neighboring vertebrae. The nucleus pulposus is a kind of hinge that is located in the center between the vertebrae and ensures their mobility. Therefore we can bend in all directions. But this structure is semi-liquid, and with increased or sudden physical activity it can “crawl” beyond the intervertebral space, forming a hernia.
The pain is acute, pronounced, and sharply intensifies with exercise. May be accompanied by impaired sensitivity in the arms and legs, numbness and pain in the extremities, and radiate to the buttock.
An intervertebral hernia can be diagnosed by an orthopedist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, or vertebrologist.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
For whatever reason your back hurts, the doctors at the Health Energy clinic will come to the rescue. We conduct detailed diagnostics to identify the cause of pain, and also prescribe comprehensive treatment to eliminate it. It includes:
- the most effective and safe drugs;
- physiotherapeutic techniques;
- physical therapy under the guidance of an experienced instructor;
- massage;
- services of an acupuncturist, chiropractor;
- blockades for quick pain relief.
If necessary, we will organize sanatorium-resort treatment or send the patient to another hospital for immediate care.
Reason 5. Diseases of internal organs
In some cases, “bones and joints” specialists will not help, since they will not detect any abnormalities. But do not rush to complain about their incompetence, because the source of back pain can be internal organs.
First of all, these are gynecological (uterus, appendages) and andrological (prostate) diseases. Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs and menstruation radiate to the lower back. The pain is nagging, aching, dull. For diagnosis, consult a gynecologist or andrologist, respectively.
Kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, renal colic) cause pain. It is quite strong, spreads throughout the lower back, and intensifies with light tapping in the lumbar region. If this applies to you, a nephrologist will help.
In general, almost all inflammatory diseases can cause back pain. With lung diseases, pain occurs between the shoulder blades; problems with the liver and stomach are reflected in the lower back at waist level.
What can low back pain look like?
Lower back pain
Most often, lower back pain occurs suddenly, sharply and is acute. In this case they talk about lumbago
(outdated popular name -
lumbago
). The pain is described as sharp, “shooting.” Movements are constrained, sometimes it is even impossible to straighten your back. With any movement the pain intensifies.
An attack of pain can last a couple of minutes, or it can last for a longer period of time (up to several days). It may be that the attack will pass and the pain will no longer remind itself, but often the pain returns and the person gets used to the fact that his lower back can hurt.
Lower back pain can not only be acute (sharp), it can be nagging and chronic. Mild but constant pain in the lower back, sometimes worsening, for example, during physical activity, an infectious disease, hypothermia, etc., is called lumbodynia
. Sometimes there is no direct pain, but stiffness remains in the lower back, and the patient experiences discomfort.
Reason 6. Poor posture
These include scoliosis, stoop, and abnormal deflection in the lumbar region. Poor posture is often accompanied by a protruding abdomen, retracted buttocks, and problems with gait (heavy gait, limping). The basis of such external changes is the curvature of the spine, which disrupts blood circulation and leads to muscle overstrain in some areas of the back and weakening in others. Incorrect position of the vertebrae, their friction against each other, rotation around their own axis (with scoliosis) - all this causes severe back pain.
The pain can be either acute, if the vertebrae are damaged, or aching, dull, spreading throughout the back.
Back problems associated with incorrect posture will be treated by an orthopedist or vertebrologist.
What to do to prevent back pain? Prevention of back pain
In order to reduce the risk of diseases that can cause back pain, Family Doctor doctors recommend:
- sleep on a comfortable bed with an elastic and hard mattress;
- try to maintain correct posture;
- do not stay in one position for a long time. When working at a computer or driving a car, you need to take breaks that give you the opportunity to stretch, warm up, and move around;
- When working while sitting, organize your workplace correctly. The chair should have a back, preferably with armrests and a headrest, so that you can lean back and relax the muscles of your back and neck. The forearms should not be suspended; it is necessary to ensure that they lie completely on the table;
- do not walk in high-heeled shoes for more than two hours at a time;
- Avoid sudden turns and bends of the body. If you need to pick something up from the floor, it is advisable to sit down and not bend over;
- when standing for a long time (when traveling on public transport or waiting in a public place), find a point of support (lean on something with your hand or lean your back);
- do not gain excess weight;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- engage in physical therapy, swimming or fitness.
Reason 7. Spinal tumors
These are cystic formations and cancerous tumors.
A cyst is a bubble with blood. It appears as a result of various types of hemorrhages in the spine. The cyst is characterized by constant severe pain, which can only be relieved with the help of painkillers. Numbness and tingling in the extremities can also be symptoms of a cyst.
Cancer can be primary or secondary. Primary is cancer that has formed in the spinal column, secondary is metastases, that is, secondary tumors that form in late stages in all organs. With malignant tumors, pain may be accompanied by muscle weakness and loss of sensitivity in certain areas.
Neoplasms in the spine are studied by a vertebrologist, oncologist, and neurosurgeon.
How does the disease manifest?
Pain in the back, chest or other part of the body where there are muscles are the first signs of the disease, which are not immediately felt. It can be triggered by various irritants, which lead to back myositis, but the symptoms and treatment are very similar. However, there are also advanced cases when the disease can develop into purulent muscle myositis, and surgical intervention cannot be avoided. There are two types of disease that differ from ordinary inflammation, in such cases a complete diagnosis is needed:
- Dermatomyositis is a female disease caused by age-related infection in the body or constant stress. Leads to the appearance of red spots on the body, swelling of the limbs and increased temperature.
- Polymyositis - affects several muscles in the body at once after suffering a serious illness: influenza, bronchitis, inflammation. May lead to muscle atrophy.
Other reasons
Bruises, pregnancy and childbirth, sedentary work, physical activity, and gardening activities also often cause back pain. If it does not go away or gets worse within 3-4 days after exercise, make an appointment with a specialist.
To determine the exact cause of back pain, often requires not only the experience of a specialist, but also precise diagnostic equipment. Doctors at Best Clinic work with equipment that allows you to see even minor changes in the structure of the spine. Computed tomography, MRI, radiography - you will find modern diagnostic methods and get help with us. Call us or leave a request on the website!
Treatment
There are no universal treatments for back pain. Treatment of back pain in each individual case depends both on the genesis of pain manifestations and on the individual characteristics of the person, since people’s perception varies significantly.
Drug treatment includes the use of various drugs, both conventional analgesics or NSAIDs, and muscle relaxants or antibiotics when it comes to infections. For chronic pain syndrome, it is possible to use antidepressants, tranquilizers or antipsychotics.
Non-drug treatment methods such as physiotherapy, massage, manual therapy, acupuncture and exercise therapy are widely used in the treatment of back pain. These treatment methods are effective for both acute and chronic pain associated with spinal diseases.
We have accumulated extensive experience in diagnosing and treating back pain using the most modern methods of both diagnosis and treatment.
Features and causes of pain syndrome
Doctors distinguish between acute and chronic manifestations of ailments. The pathological condition is considered acute if pain appears for the first time. If a person experiences discomfort constantly, with a periodic increase and decrease in the intensity of unpleasant symptoms, the pain is chronic. Painful sensations may be:
- pulsating;
- sharp, sharp;
- piercing or cutting;
- pulling.
Sometimes the pain is accompanied by swelling or numbness of the back, arms, legs, and face.
The reasons for back pain in the thoracic spine may be associated with problems in different body systems. Most often they are caused by diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Referred pain is less common in pathologies of internal organs. In some cases, both factors occur: diseases of the spine, which is the “axis” of the entire body, often lead to prolapse, displacement or compression of internal organs.
Pain with increased stress
After intense physical work, a nagging pain often appears. Most often it is caused by muscle tension and fatigue. Such sensations may occur after carrying heavy objects, sitting for long periods of time (static load) or sports training. Women sometimes experience nagging pain during pregnancy. Spinal diseases
If the soreness is accompanied by tingling, burning or burning sensations in the spine, then it is most likely not due to muscle fatigue. These symptoms usually indicate spinal diseases:
- arthrosis;
- retrolisthesis;
- osteochondrosis;
- deformations;
- protrusion or hernia.
These pathologies are characterized by chronic pain, which sharply intensifies after emotional stress, physical exertion or hypothermia.
The following signs indicate that the spine hurts in the middle of the back:
- crunching or clicking noises when moving;
- increasing stiffness;
- increased pain when changing body position, turning the head and other movements;
- coldness of hands and feet;
- periodic numbness of the hands, face, back, legs, neck;
- feeling of “current” in the body;
- frequent dizziness, migraines.
If the spine in the middle of the back becomes numb, this indicates compression or damage to the nerve roots. Without treatment, this problem can lead to spinal cord damage, sensory loss, and loss of mobility. If your spine hurts in the middle of your back when pressed, the pain is most likely caused by myositis or another inflammatory disease of the muscle tissue.
Pain due to stress
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are not always the cause of pain. Often, pain in the collar area, thoracic region and lower back is caused by a stressful condition. Due to strong emotional stress, a person constantly tenses his muscles, slouches, raises his shoulders - all this leads to uncomfortable sensations. To get rid of pain, you must first cope with stress. Sanatorium-resort treatment, manual therapy, massage and physiotherapy, including medicinal baths, are highly effective. Referred pain If the malaise is caused by diseases of the internal organs, the pain may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- cough;
- dyspnea;
- temperature increase;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- constipation, diarrhea;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- the appearance of a yellowish tint to the eyes and skin;
- coating on the tongue.
With tuberculosis, the back hurts in the area of the lungs at the back. With inflammation of the gallbladder or liver disease, pain occurs in the back and on the right under the ribs, nausea appears, and sometimes the temperature rises. When the kidneys are inflamed, pain is accompanied by difficulty or frequent urination.