What it is?
Anogenital warts are growths protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes that appear on the genitals or in the anus.
They are formed after infection with the human papillomavirus. In total, more than a hundred types of the virus are known, and it can also cause ordinary warts. They differ from anogenital ones in location and form on the skin of the palms, knees, fingers, protrude above it, feel compacted to the touch, and can grow together. The types of virus that cause anogenital warts are not associated with cervical cancer. In 70% of cases it is caused by a number of other types of pathogens. However, such neoplasms require monitoring and treatment by a dermatologist or venereologist. Read more about it in our article “Human papillomavirus”.
Reasons for development
The appearance of anogenital warts in 90% of cases occurs after infection with HPV types 6 or 11. From the moment of infection to the growth of neoplasms on the skin, an average of 11-12 months passes in men, and 5-6 months in women. The rapid growth of genital warts is associated with immunity deficiency and pregnancy. Frequent maceration of the skin (its swelling, wrinkling due to prolonged contact with water) can accelerate the spread of neoplasms.
Figure 1. Human papillomaviruses. Photo: iLexx/Depositphotos
Where do condylomas appear?
Acute condylomas can be transmitted by any type of sexual contact - vaginal, oral, anal. Their location is closely related to the site of infection.
Genital condyloma
Changes usually develop 3–8 months after contact with the virus, that is, with an infected partner. In more than 75% of cases, people who have sex with a partner who has genital warts develop symptoms within three months.
In men, condylomas are most often found on the head of the penis, mainly under the foreskin, which can lead to complications in the form of phimosis, on the central part of the penis, and sometimes on the scrotum. The development of condylomas is promoted by heat and moisture, under their influence they grow quickly, become larger and take the shape of cauliflower.
In women, they grow even faster during pregnancy, probably under the influence of the pregnancy hormone progesterone. If the warts are very large and on the vaginal wall, it may become less elastic, which can make labor difficult.
In general, genital and anal warts tend to persist or enlarge and disappear for years. Self-excision occurs in 10-30% of infections. In most cases, tumors form again.
Transmission routes
Both adults and children can become infected with the human papillomavirus. In adults, the most common route of transmission is through sexual intercourse. Infection can occur through contact with an affected area of skin. The types of HPV that cause anogenital warts can also be transmitted through anal sex. Using condoms reduces the risk of infection, but does not completely eliminate it. People who frequently change sexual partners are at risk.
Important! Infection with the human papillomavirus is possible even from a person with an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Children become infected with HPV in several ways. If a pregnant woman is infected, the virus can be transmitted to the baby during childbirth. Prenatal transmission (before birth) is rare. Infection is also possible through contact with affected areas of the skin.
Dealing with warts is difficult
It is true that natural medicine has its own ways of treating genital warts. This is mainly an external influence - urine compresses, the use of white films of citrus fruits soaked in vinegar, compresses made from tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar. But these methods can, and only in consultation with the doctor, complement basic therapy, and in no case are they the main method of combating genital warts.
At the same time, you can use supplements that strengthen the immune system, for example, garlic capsules or echinacea extract. But even in such cases it will be necessary to inform the attending physician.
Garlic capsules
If the illness recurs and your own observations confirm that it occurs under stress, it is worth focusing on methods of dealing with stress.
Types of warts
HPV can cause several types of skin lesions.
Condylomas acuminata
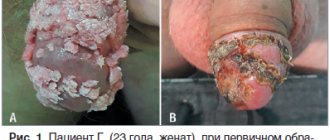
Neoplasms protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. They may consist of nodules with a loop-like structure, the surface may be variegated. Their appearance may be accompanied by discomfort and itching (not in all cases). Condylomas are localized in the groin, perineum, anus, and genitals;
Papular rash
They look like a rash, are flat, almost do not protrude above the surface of the skin, and are localized in the same way as genital warts;
Stains
Areas of discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals (grayish-white or red spots appear);
Bowenoid papulosis
A sexually transmitted disease, which is accompanied by the formation of many nodules of discolored color (brown, gray, red) on the mucous membrane and skin of the genital organs. Later, such nodules merge into large papules;
Giant condyloma
Papillomas merging with each other (look like small warts), forming a large lesion.
Figure 2. Condylomas and warts. Source: CC0 Public Domain
The appearance of warts and other growths due to HPV may be accompanied by discomfort and itching. In rare cases, the affected areas of the skin may crack, bleed, and become painful.
Outpatient treatment of warts on the genitals
The only effective way to combat genital warts, recognized throughout the world, is to remove them.
There are several methods that can help you get rid of unpleasant tumors in a matter of minutes:
- Laser therapy procedure. It is performed under local anesthesia using a colposcope, which makes it easier to view the intervention area. Laser therapy is very effective and leaves no possibility of relapse. For numerous condylomas, the procedure is repeated every other week.
- Cryotherapy is the freezing of lesions with liquid nitrogen. Used at weekly intervals. Hyperpigmentation or scarring develops after cryotherapy. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the experience of the doctor.
- Trichloroacetic acid. This is a strong caustic substance that causes tissue necrosis as soon as the composition is applied to the affected areas. This method of combating condylomas is effective with small changes, and its effectiveness is estimated at 51-81%. Relapses occur in 36% of patients. Side effects - excessive use of the drug leaves deep wounds and scars.
- Surgical methods. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. The highest level of cure is provided by curettage and electrosurgery methods. Condylomas after such treatment recur in less than 19% of cases.
- Photodynamic therapy – 5-aminolevulinic acid. The method can be used alone or in combination with laser therapy, cryotherapy or curettage. The advantage is a low percentage of side effects and a high percentage of successful procedures.
Cryotherapy
Laser therapy
Photodynamic therapy
Risks during pregnancy
In women infected with the human papillomavirus, pregnancy can provoke the appearance of anogenital warts and their growth. The virus can cause abortion. The mother can transmit the virus to the child during pregnancy (rarely), during childbirth (more often), and during subsequent contacts. For a newborn, HPV is dangerous due to damage to the respiratory tract (development of respiratory papillomatosis, breathing problems, voice formation).
To reduce the risks associated with HPV when planning pregnancy, it is advisable to undergo preventive examination and treatment when the virus is detected. If pregnancy has already occurred, treatment is performed before 36 weeks, using laser or cryodestruction, electrocoagulation to remove tumors. If there are extensive lesions, operative delivery is recommended to reduce the risk of infection to the baby.
Diagnostics
You should consult a doctor if neoplasms, nodules, compactions, or areas of discoloration appear on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs or anus.
During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the clinical manifestations and examine the affected areas.
To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests may be performed:
- PCR diagnostics with determination of the genotype of the virus; it is additionally possible to determine the degree of viral load. Biomaterial – vaginal smear, scraping from the urethra, cervical canal.
- Morphological, cytological examination to assess the risk of oncological pathology.
Photo: freepik.com
The severity of the condition is assessed by the number of tumors, the volume of affected tissue during examination and laboratory testing (the number of copies of HPV DNA in the test samples is determined).
Important ! Anogenital warts are treated using destructive methods (cryodestruction, laser destruction, electrocoagulation). In this regard, before treatment, tests for HIV, hepatitis, and syphilis are required.
Diagnosis is carried out by specialists from dermatovenerology departments. Additionally, consultations with specialized doctors may be required:
- a urologist if the tumors are localized inside the urethra;
- a proctologist if warts grow extensively in the anal area;
- obstetrician-gynecologist when planning and managing pregnancy;
- immunologist (for relapses of the disease or immunodeficiency states).
Treatment
The main direction of treatment is the destruction of anogenital warts. In 70-80% of cases, after removal of tumors they do not reappear. Several methods are used for destruction.
Photo: zhykova / Depositphotos
Electrocoagulation
Destruction of neoplasm tissue under the influence of high frequency current. Around the area of the neoplasm, extensive thermal damage to tissue occurs (formation of a dry crust). After it heals, there are no traces of exposure left on the skin.
Laser destruction
Laser exposure at a controlled depth to remove tumors within clear boundaries. Once the wart tissue is destroyed, there is no bleeding and there is no need to close the wound.
Cryodestruction
Destruction and removal of tumors using liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of ultra-low temperature, instant tissue necrosis occurs, followed by rejection and wound healing.
Radiosurgery
It involves the generation of a high-power radio wave that passes through the tumor tissue, destroying it.
If the area of damage to the mucous membranes or skin is extensive, it is possible to remove the tumors surgically. With any method of destruction, the affected area is disinfected and anesthetized before the procedure.
It is also possible to use chemical and cytotoxic methods for the destruction of anogenital warts. For this purpose, local drugs are used that gradually destroy the tumor tissue. Such treatment requires caution and can only be carried out as prescribed by the attending physician.
Important! Attempts to remove anogenital warts on your own can be dangerous: you can injure healthy tissue, cause infection, and provoke the growth of tumors. If the wart was torn off by accident, you need to treat the affected area with an antiseptic, stop the bleeding, and consult a doctor.
Figure 3. Structure of a wart. Source: CC0 Public Domain
In addition to methods of destruction of anogenital warts, local immunomodulators and nonspecific antiviral drugs can be used.
Genital warts: effective treatment methods
M.A.GOMBERG , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, A.M. SOLOVIEV , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, N.I.CHERNOVA , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, S.G.ISAEVA , MGMSU, Moscow Infections caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) are very widespread. In the United States alone, the Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that up to 5.5 million people per year are infected with HPV (Armstrong GL, et al., 2001).
In Russia, anogenital warts, the etiology of which is associated with HPV, are registered as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The level of official registration of anogenital warts in Russia (about 35 per 100,000 population in recent years) differs significantly from the true prevalence of HPV infection.
Meanwhile, with the widespread introduction of molecular diagnostic methods into practice, doctors of various specialties are diagnosing HPV infection in a variety of clinical manifestations of papillomatosis outside the genital area. Often, HPV is detected without the presence of manifestations associated with this infection. This is a special case, and we discussed the tactics of managing such patients earlier (Gomberg M.A., Solovyov A.M. // Medical Council. - 2009. - No. 3. - P. 12-18).
The problem of HPV infection became especially relevant after the Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded to Harald zur Hausen (Germany) in 2008 for proving the connection of cervical cancer with this particular virus. Currently, not only doctors, but also patients are aware of this.
The purpose of this article is to give outpatient doctors an idea of modern approaches to the management of patients with HPV infection, so that when anogenital warts are detected in patients, they can solve this problem on their own, without referring the patient to specialized centers.
Principles of treatment of clinical manifestations of HPV
According to existing principles for the management of patients with genital clinical manifestations associated with HPV, treatment is aimed at either destroying papillomatous lesions that arise at the site of virus entry by one method or another, or stimulating an antiviral immune response, or a combination of these approaches. The most optimal is the following classification of methods for treating anogenital warts: I. Destructive methods: 1. Physical - surgical excision; — electrosurgical methods; — cryotherapy; - laser therapy. 2. Chemical: - nitric acid; - trichloroacetic acid; - solcoderm. II. Cytotoxic drugs: - podophyllin (PF); — podophyllotoxin (PFT); - 5-fluorouracil. III. Immune methods: - interferons; — interferon inducers; - immunotropic drugs. IV. Combined methods: - combined use of various methods, usually immune and destructive. When choosing the most optimal method in each specific case, the doctor must be guided by the following main characteristics: - effectiveness for a given pathology; — frequency of relapses after treatment; — tolerability (minimal side effects); — simplicity of procedures.
Treatment of genital clinical manifestations associated with HPV is aimed either at destroying, by one method or another, papillomatous lesions that arise at the site of virus introduction, or at stimulating an antiviral immune response, or at a combination of these approaches
The main difference between physical destructive methods is that when they are used, rapid, often instantaneous destruction of lesions occurs. When using other methods, the lesions are eliminated within a few hours or weeks. As a rule, this time is comparable to the healing time of lesions after exposure to physical methods. The frequency of relapses, according to the literature, does not depend on the choice of treatment method.
Thus, the obvious advantages of physical methods are neutralized. To use physical destructive methods, special premises, expensive equipment, and trained personnel with certificates for this type of medical activity are required. All this limits the use of these methods in widespread practice, especially in small medical centers or in areas where the clinic has only dermatovenerological, gynecological or urological offices. In this regard, conservative treatment methods that can be applied by any practitioner are of particular interest.
Chemical destructive methods
Concentrated solutions of acids, alkalis, salts, etc. are used, for example, feresol, hydrogen peroxide, solutions of quinine and hingamine, preparations based on salicylic and lactic acids, acetic and nitric acid, thuja and celandine juices. All these methods have low, poorly predictable effectiveness, and numerous side effects. There is little consistent data on the effectiveness of these drugs.
Feresol
Feresol is a solution containing 60% phenol and 40% tricresol. It is used 1-2 times with an interval of 3-4 minutes once a week. Can be repeated 3-4 times. Among the chemicals that have a destructive effect, about which there is sufficient data in the literature, it should be noted that the combined acid preparation is solcoderm.
Solcoderm
Solcoderm is an aqueous solution, the active component of which is the interaction products of organic acids (acetic, oxalic and lactic) and metal ions with nitric acid having a concentration of 6.6 N. The solution contains nitrites in an amount of 0.02 mg/ml. When applied topically to affected areas, solcoderm leads to intravital fixation (the structure of the neoplasm is preserved) followed by mummification of the pathologically altered tissue with which the drug comes into contact. Healing occurs under the scab, which eliminates the formation of an open wound surface. Complications of treatment, such as secondary infection or scarring, according to the literature, are extremely rare. Ease of use, effectiveness in removing diseased tissue with minimal negative impact on surrounding tissue, and the ability to control the extent of treatment make Solcoderm useful for treating a wide range of benign skin changes.
The uniqueness of Solcoderm is that the acids included in its composition, having a low concentration and, therefore, a low probability of side effects, have a pronounced clinical effect due to redox reactions. The nitrogen oxidation products that are formed as a result of these reactions have some additional clinical benefits, characterized by more complete destruction of the affected area and reduced damage to surrounding healthy tissue (Weiner M., et al., 1983).
We observed 24 patients (14 men and 10 women) aged from 17 to 41 years (average age 25.8 years): 16 patients with genital warts on the genitals, 3 patients with vulgar warts on the hands, 2 patients with plantar warts and 3 with smooth skin nevi. Solcoderm was applied with a special plastic spatula or using a glass capillary onto the surface of the lesion, previously degreased with alcohol. The fastest way to saturate the lesion was achieved by applying the solution using capillary tubes, followed by mechanical action with a plastic spatula for deeper penetration of the solution.
Treatment of warts was carried out until yellow staining of lesions located on the skin or white staining of lesions located on the mucous membranes appeared. The appearance of a uniform yellow or white color indicates the sufficiency of processing and is a guarantee of subsequent mummification of the formation. A control examination of patients was carried out 3-5 days after primary treatment. If necessary, the lesions were re-treated with Solcoderm.
In patients with genital warts and nevi, in most cases, a single treatment with Solcoderm was sufficient. Complete rejection of the scab occurred within a period of 5 (usually with condylomas) to 14 (in the case of nevi) days, depending on the location and size of the lesions. For the treatment of vulgar warts, 2-3 therapy sessions were required, for the treatment of plantar warts - 3-4 sessions. In all cases, it was possible to achieve complete disappearance of the lesions. The treatment was well tolerated and no serious side effects were noted. During a 6-month follow-up, disease recurrence was noted in 3 patients with genital warts.
The data we obtained about the high effectiveness and good tolerability of Solcoderm therapy completely coincides with the data of large foreign studies. In the treatment of common and plantar warts, the drug was effective in 85-94% of patients (the recurrence rate was 6-10%) (Hettich R., Burri P., Binet O., 1984). In the treatment of genital warts in men and women, these figures were 80.1 and 7.0%, respectively, and in 64.7% of patients the effect was achieved after a single treatment (Brokalakis J., et al., 1984).
The short duration of treatment, the outpatient nature of the treatment and the precision with which the drug is applied to pathological tissues make Solcoderm a successful drug for the treatment of genital warts, as well as common and plantar warts.
Cytotoxic drugs. Podophyllin
Podophyllin is a resin obtained from the plants P. pelatum and P. emodi, native to North America and the Himalayas. To treat warts of the anogenital area, a 10-25% solution of podophyllin in ethanol or benzoin tincture is used. Podophyllin is the drug of choice in UK clinics (Reynolds M., et al., 1993). It binds to the microtubule apparatus of the cell and inhibits mitosis, and also suppresses the transport of nucleic acids, resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis and cell reproduction (Handley JM, et al., 1994). Podophyllin is not registered in Russia. Some researchers oppose the use of the drug, especially by patients themselves. In particular, Petersen, et al. (1995) consider podophyllin to be a poorly studied, crudely purified plant extract. Using liquid chromatography, these authors determined that approximately 10% of the dry matter of a 20% podophyllin solution consists of 2 mutagenic flavonoids - quercetin and kaemferol. In this regard, it is proposed to use only highly purified podophyllotoxins, but their independent use can be recommended to patients only after detailed instructions.
Podophyllotoxin
Podophyllotoxin is the most therapeutically active fraction of podophyllin. Available in the form of 0.25, 0.3 and 0.5% solutions, as well as in the form of 0.15, 0.3 and 0.5% cream.
Podophyllotoxin solution and cream are registered in Russia: - condiline - 0.5% solution. Apply 2 times/day for 3 days, then break for 4 days. The duration of treatment is no more than 5 weeks. — Vartek – 0.15% cream.
The undoubted advantage of podophyllotoxin is the possibility of safe self-administration of the drug by patients. Podophyllotoxin is used 2 times a day for 3 consecutive days a week for 4-5 weeks.
For podophyllotoxin, the effectiveness rate is 26-87% in men and 50-77% in women (Lassus A., 1987; Von Krogh G., 1987; Edwards A., et al., 1988; Kirby P., et al., 1990; Baker DA, et al., 1990; Handley JM, et al., 1991; Greenberg MD, et al., 1991). The wide range of effectiveness indicators is due to different periods of observation of patients, as well as the fact that in some studies the authors do not take relapses into account. The most common side effects of podophyllotoxin use according to Bonnez W., et al. (1994) are local inflammatory reactions (in 57% of patients), erythema, burning (in 48%), soreness (in 47%), itching (in 44%), slight weeping and erosion in the area of application (in 39%). Although systemic side effects have not been described, it is recommended to use podophyllotoxin in an amount of no more than 0.2 ml per procedure (Von Krogh G., 1982).
Handley JM, et al. (1994) considers podophyllotoxin to be the drug of choice for self-administration by patients with a small number of non-keratinizing condylomas located on the foreskin, glans penis, coronary sulcus and vulva. The drug is ineffective in the treatment of warts of the perianal area, vagina and urethra.
The disadvantages of podophyllotoxin are its high cost, long duration of treatment combined with not the highest efficiency.
5-Fluorouracil
5-fluorouracil is a pyrimidine antagonist and is capable of disrupting the synthesis of both cellular and viral DNA. For the treatment of warts of the anogenital area, it is prescribed in the form of a 5% cream (Krebs HB, 1987). According to Handley, et al. (1994), 5-fluorouracil is an effective treatment for intravaginal warts and condylomas of the terminal urethra. When treating intravaginal warts, the drug is prescribed once a night for a week or once a week for 10 weeks (Krebs HB, 1987). Although the drug with this treatment regimen has a fairly high effectiveness (85-90%), its use may cause weeping erosions on the vaginal mucosa, up to the development of severe weeping contact dermatitis.
When treating warts of the terminal part of the urethra, the cream is administered immediately after urination, at night for 3-8 days. Complete cure of intraurethral warts is observed in 90-95% of men (Dretler SP, et al., 1975; Von Krogh G., 1976). However, during treatment there are many side effects: stenosis and stricture of the urethra, dysuria, ulceration (Krebs HB, 1987).
Despite the fairly high effectiveness of 5-fluorouracil, availability and low cost, its use in widespread practice is limited due to the high frequency of side effects. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy.
There are no official preparations of fluorouracil for external use in Russia, but a cream of the required concentration can be prepared according to a prescription in the pharmacy production department from the substance.
Immune methods. Interferon
Since HPV persists in epithelial cells and the use of destructive methods does not guarantee against relapses, the use of interferons both as monotherapy and in combination with other treatment methods is promising in this regard.
It has been established that when interferon is used in patients, the amount of viral DNA in the lesions decreases (according to PCR data), which correlates with clinical improvement or disappearance of the lesions (Arany I., et al., 1995).
Interferon in the treatment of anogenital warts can be used locally, intralesional and systemically (subcutaneously, intramuscularly, intravenously or rectally).
Most studies have shown low effectiveness of external use of interferon (Keay S., et al. 1988). Gross G. (1996) believes that an important indication for external use of interferon is the presence of subclinical foci of HPV infection and CIN (especially caused by HPV types of high oncogenic risk).
According to various authors, with systemic use of interferon alpha in a dose of 1.5 to 3 million IU intramuscularly or subcutaneously every other day for 4 weeks, 11-100% of patients experience complete disappearance of warts (Gross G., et al., 1986; Zwiorek L., et al., 1989).
Flu-like symptoms may occur with systemic use of interferon, the severity of which depends on the dose received (Handley, et al., 1994). These side effects can be reduced by prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Considering that the effectiveness of systemic interferon monotherapy is low and not predictable enough, and also taking into account the high cost of treatment, this method is not widely used in clinical practice.
According to various authors, intralesional use of alpha and beta interferon is most effective. This method of therapy leads to the disappearance of 35-62.5% of warts, both treated and untreated (Corwin Vance J., et al., 1986; Reichman RC, et al., 1988; Welander CE, et al., 1990). The Russian market offers a wide selection of interferons from various manufacturers, both domestic and foreign - Viferon, Kipferon, Reaferon, Roferon-A, Intron A, Realdiron, etc.
It is preferable to use recombinant rather than human interferons. Drugs registered for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection include:
Viferon is a recombinant interferon alpha-2b. Available in the form of ointment, gel and suppositories. For papillomavirus infection, suppositories are used at a dose of 500,000 IU 2 times a day for 5-10 days;
Intron A – recombinant interferon alpha-2b. Apply systemically;
Roferon A is recombinant interferon alpha-2a. Apply subcutaneously at 1-3 million IU 3 times a week for 1-2 months;
Altevir is a recombinant interferon alpha-2b. Apply systemically;
Wellferon is purified interferon alpha-n1. Apply subcutaneously at 5 million IU daily for 14 days, then 3 times a week for 6-8 weeks.
There are reports of the effective use of interferon inducers as monotherapy. Of interest is the local use of a low molecular weight derivative of imihidazoquinolinamine - imiquimod, which is an inducer of cytokines and, in particular, alpha-interferon (Baker D., et al., 1995; Trofatter KE, 1997). It is used in the form of a 5% cream 3 times a week or daily at night until the rash completely disappears (but not more than 4 months). Complete disappearance of condylomas is observed in 56% of patients with the first dosage regimen and in 71% with daily use (placebo - 14%).
At follow-up examinations within 1 year, relapses were observed in only 13-19% (Baker D., et al., 1995; Trofatter KE, 1997). With daily use, local side effects more often developed: redness, swelling, erosion. The cream is especially effective in the treatment of subclinical HPV infection (Gross G., 1996). Imiquimod has been widely used in Europe, the USA, Japan and many other countries since the late 90s of the 20th century, but this drug has not yet been registered in Russia.
Relapse Prevention
To prevent relapses of HPV infection, it is more preferable to use interferon or its inducers, as well as other activators of antiviral immunity as adjuvant therapy in combination with various destructive methods. Immune drugs increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the frequency of relapses. Combination immunotherapy is of particular importance in the treatment of stubborn, difficult-to-treat warts.
Various methods have been proposed for treatment based on the use of immune drugs in combination with cryotherapy, laser therapy, electrocoagulation, solcoderm, etc. (Thin N., 1995). For example, it was found that the combination of interferon with laser therapy is more effective than laser therapy alone: complete disappearance of warts is observed in 52 (81.5%) and 19 (61%) patients, respectively (Corwin Vance J., et al., 1990; Hohenleuter U., et al., 1990; Petersen CS, et al., 1991).
Supplementing CO2 laser excision with low-dose alpha-interferon therapy (1-3 million IU per day for 5-7 days, then a break of 3-4 weeks, a course of 3-4 cycles) increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the percentage of relapses observed after the use of laser therapy only (Gross G., 1996). For small genital warts, the addition of laser therapy or electrocoagulation with local application of a gel containing interferon beta 0.1 million IU/g, 5 times a day for 4 weeks, effectively prevents relapses (Gross G., 1996).
However, according to The Condylomata International Collaborative Study Group (1993), the use of interferon alpha (3 times a week for 4 weeks) after removal of all visible condylomas with a CO2 laser does not give any positive results in comparison with placebo (complete cure occurred in 18%, relapses occurred in 35% of patients). According to Hopel MR, et al. (1992), the combination of the use of alpha interferon (3-6 five-day courses with an interval of 2 weeks) with destructive and/or surgical methods, despite increasing the effectiveness of treatment of persistent, treatment-resistant condylomas, does not prevent the development of relapses that occur in 50% of patients .
To prevent relapses of HPV infection, it is more preferable to use interferon or its inducers, as well as other activators of antiviral immunity as adjuvant therapy in combination with various destructive methods
Another group of conservative methods for treating HPV infection is of interest - these are immune drugs that can be used alone or in combination with destructive methods.
Immunotropic drugs
Antiviral immunity can be influenced by using inducers of endogenous interferon and other immune activators. There are many immunoactive drugs on the Russian pharmaceutical market, which, according to the manufacturer’s instructions or the recommendations of researchers, can be used in the combined treatment of anogenital warts in combination with various destructive methods.
Gepon
Gepon is a synthetic oligopeptide consisting of 14 amino acid residues. The drug belongs to the group of immunomodulators and is indicated to increase the effectiveness of immune defense against infections, treatment and prevention of opportunistic infections caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
The immunopharmacological and antiviral effects of the drug Gepon are due to the fact that it: - causes the production of alpha and beta interferons; — mobilizes and activates macrophages; - limits the production of inflammatory cytokines (interleukins 1, 6, 8 and tumor necrosis factor); - stimulates the production of antibodies to various antigens of an infectious nature; — suppresses viral replication; – increases the body’s resistance to viral and bacterial infections.
In patients with a weakened immune system, Gepon: - increases the reduced content of CD4+ T- and NK-cells; — increases the functional activity of neutrophils and CD8+ T cells, which are key parts of the body’s defense against bacteria, viruses and fungi; - enhances the production of antibodies specific to pathogens of opportunistic infections that are relevant for a given patient; - prevents the development of relapses of opportunistic infections.
Although the instructions for use of the drug do not directly indicate its use for papillomavirus infection (the drug is recommended to increase immune protection against infections, treatment and prevention of opportunistic infections caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi), the accumulated clinical experience of its use allows us to recommend Gepon for HPV. For example, applications of Gepon to the foci of HPV lesions after their removal by any destructive method (from 3 to 6 applications every other day) can speed up the healing process and reduce the level of recurrence (Soloviev A.M., 2003). Systemically, the drug is used at a dose of 2 mg orally 3 times a week. The course can be repeated at intervals of 1 week.
Immunomax
The use of an antiviral immunity activator, Immunomax, which is an acidic peptidoglycan with a molecular weight of 1000-40000 kDa, is promising. The drug is isolated from plants using a complex of biochemical methods, including ultrafiltration and chromatography. The sterile drug Immunomax is available in the form of a lyophilized powder of 200 units in vials for injection.
There is data on the use of the drug for clinical manifestations of HPV infection in combination with any of the destructive methods. Patients have genital warts removed and at the same time given intramuscular injections of Immunomax 200 units once a day on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 8th, 9th and 10th days of treatment (Perlamutrov Yu.N. et al., 2003). In 68% of patients, immediately after treatment, there is no recurrence of condylomas, and after additional destruction sessions, the effectiveness of treatment reaches 98% (with a follow-up of at least 3 months).
Epigen-intim
Epigen-intim is an aerosol preparation of plant origin for topical use, the main active ingredient of which is glycyrrhizic acid, obtained from licorice root. The drug activates local immunity due to interferonogenic action, while increasing the ability of tissues to protect against infections. Glycyrrhizic acid, by inhibiting DNA and RNA viruses, causes their inactivation, blocks the introduction of active viral particles through the membrane into the cell, and disrupts the synthesis of new structural components of viruses. The main mechanism of the antiviral activity of glycyrrhizic acid is inhibition of P kinase, which entails inhibition of phosphorylation of cellular and virus-encoded proteins in infected cells and those in the free state.
It has been shown that the use of epigen in combination therapy of anogenital warts can reduce the frequency of relapses (Chernova N.I., 2004). The drug also has an anti-inflammatory and healing effect, which is important when treating condylomas with destructive methods.
When used periodically for a long time in patients with asymptomatic HPV shedding, epigen has a preventive effect in relation to the clinical manifestation of infection - during observation for 1 year, condylomas appeared in 14.7%, while in the control group this occurred in 40% of patients (Chernova N.I., 2004).
Epigen-intim is used intravaginally, externally and intraurethrally. For external use, the drug is applied to the entire affected surface from a distance of 4–5 cm using 1–2 valve presses. The drug is injected intravaginally by 1-2 clicks on a special nozzle. The drug is used before removal of condylomas 3 times a day, against the background of destruction - 5 times a day for 10 or more days until healing; for the prevention of immediate relapses - 3 times a day for 1 month.
Immunotropic drugs with direct antiviral action
Immune drugs increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the frequency of relapses
Isoprinosine (inosine pranobex)
Isoprinosine (inosine pranobex) is an antiviral agent with immunomodulatory properties. The drug normalizes the deficiency or dysfunction of cellular immunity, inducing the maturation and differentiation of T lymphocytes and T1 helper cells, potentiating the induction of a lymphoproliferative response in mitogenic or antigen-active cells. Isoprinosine models the cytotoxicity of T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells, the function of T8 suppressors and T4 helpers, and also increases the amount of immunoglobulin G and surface complement markers. Isoprinosine increases the synthesis of interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-2 (IL-2), regulates the expression of IL-2 receptors, significantly increases the secretion of endogenous interferon-β and reduces the production of interleukin-4 in the body.
The drug enhances the effect of neutrophil granulocytes, chemotaxis and phagocytosis of monocytes and macrophages. Isoprinosine also has a direct antiviral effect, inhibiting the synthesis of viruses by incorporating inosine-orotic acid into the polyribosomes of the virus-affected cell and disrupting the attachment of adenylic acid to viral RNA.
One of the indications for the use of the drug is infections caused by the human papillomavirus: genital warts, human papillomavirus infection of the vulva, vagina and cervix (as part of complex therapy).
For infections caused by HPV, isoprinosine is prescribed 3 g/day (2 tablets 3 times/day) as an adjunct to local therapy or surgery for 14–28 days in low-risk patients or 5 days a week consecutively for 1–28 days. 2 weeks per month for 3 months in high-risk patients.
The literature describes various schemes and results of the use of isoprinosine for papillomavirus infection. There is known foreign experience in the use of inosine pranobex as a therapy that complements the destruction of anogenital warts (Mohanty KC, et al., 1986). The drug was used at a dose of 1 g 3 times a day for 28 days. The effectiveness of therapy increased from 41 to 94% when isoprinosine was added to traditional methods of treatment.
Similar results are shown in the works of V.N. Prilepskaya. et al. (2007). Adding isoprinosine to standard treatment at a dose of 1 g 3 times a day for 5 days before destruction increases the effectiveness of therapy from 65.6% to 87.5%, and reduces the frequency of relapses by 3 times. There is also a high frequency of HPV elimination from lesions - 65.6%.
In the work of Zabelev A.V. et al. (2005) showed the disappearance of atypical epithelium after courses of isoprinosine in women with HPV-associated low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Isoprinosine was prescribed 1 gram 3 times a day for 5 days, 3 courses with an interval of 1 month.
Similar results - an improvement in the morphological picture of the vulvar epithelium - were shown in a study by Sun Kuie Tay (1996). Inosine pranobex was prescribed 1 g 3 times a day for 6 weeks. A positive effect was achieved in 63.5% of patients, and in the group taking placebo – in 16.7%. To monitor and process research results from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine, the Astra program was developed and implemented in 2008 - an all-Russian multicenter program for monitoring, summarizing and generating statistical reporting on the features and results of the use of isoprinosine in the treatment of diseases associated with HPV in normal conditions. medical practice. The study involved 6191 patients (5896 women and 295 men) (Kostava M.N. et al., 2009).
Patients who took part in the study were treated in accordance with the identified diseases; the drug isoprinosine was included in the treatment complex. In the presence of only genital warts of the vulva and vagina, monotherapy with isoprinosine was performed. Treatment of CIN I-II, localized in a limited area of the exocervix, fully accessible for colposcopy, without damage to the cervical canal in 58 patients was also carried out with the drug isoprinosine. In the absence of a positive effect, adequate excision of the affected tissue was performed. Recommended therapeutic doses of isoprinosine corresponded to the severity of epithelial damage by the human papillomavirus. When genital warts were detected in the vulva and vagina, isoprinosine was prescribed at a dose of 50 mg/kg per day for 5 days in three courses with a break of a month. For cytological and histological data corresponding to CIN I–II, isoprinosine was used at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day, 10 days a month in 3 courses with a break of a month. For subclinical forms of HPV lesions of the epithelium, the drug was prescribed at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day, the course of treatment was from 10 to 21 days.
Before treatment, koilocytosis with a normal colposcopic picture was detected in 1367 patients, and after treatment - only in 71. Treatment of genital warts was effective in 91% of patients, combined treatment of CIN I - in 90%, combined treatment of CIN II - in 82%, treatment subclinical form of HPV infection - in 91% [Kostava M.N. et al., 2009].
Recently, a meta-analysis of the results of using isoprinosine was conducted (Eliseeva M.Yu. et al, 2009). Literature data based on 15 sources, which describe 2369 cases of the use of isoprinosine as monotherapy, 3369 in combination with other methods, compared with 71 observations of placebo control and 575 observations of traditional treatment, indicate the effectiveness of auxiliary immunotherapy with isoprinosine against the background of traditional methods for the treatment of genital lesions associated with HPV.
The main indicator of the effectiveness of any method of removing anogenital warts is the absence of relapses. Since the frequency of relapses of HPV infection does not depend on the method of destruction of lesions (physical, chemical or cytotoxic), destruction methods that can be used directly in the office are of particular interest to a doctor at an outpatient appointment. Therefore, in this work, we tried to focus on methods that allow us to quickly and effectively combat the manifestations of HPV infection and its relapses without the use of expensive methods of destruction, access to which is not available in every specialized clinic.
The advantage of this treatment is that there is no risk of infecting the doctor with viral particles, in contrast to laser destruction without the doctor using protective methods. To prevent relapses of HPV infection, it is recommended to prescribe immunotropic therapy. This approach will provide effective treatment of anogenital warts, which should significantly affect all aspects of the control of HPV infection in the population, including the level of its registration.
The main indicator of the effectiveness of any method of removing anogenital warts is the absence of relapses. Since the frequency of relapses of HPV infection does not depend on the method of destruction of lesions (physical, chemical or cytotoxic), in this work we tried to focus on methods that allow us to quickly and effectively combat the manifestations of HPV infection and its relapses. To prevent relapses of HPV infection, it is recommended to prescribe immunotropic therapy. This approach will provide effective treatment of anogenital warts, which should significantly affect all aspects of the control of HPV infection in the population, including the level of its registration.
It should be recognized that even modern advances in the research of human papillomavirus infection and the improvement of diagnostic and therapeutic methods leave a number of unresolved issues - the lack of standards for HPV therapy, the widespread dissemination of recommendations for patients on the prevention of HPV infection, and algorithms for the management of pregnant women with HPV.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of anogenital warts, you need to reduce the risk of HPV infection. To do this, they exclude casual sexual intercourse and use barrier methods of protection.
An obligatory part of prevention is vaccination:
- for women, a two-, four- or nine-valent vaccine is used with a single or double revaccination;
- For men, a quadrivalent or ninevalent vaccine is used.
Vaccination to protect against HPV infection is recommended to begin in childhood. Immunization for girls can be performed from 7 years of age, for boys - from 9 years of age. For girls, HPV vaccinations are especially important because of the risk of cervical cancer associated with the virus.