The annual flu vaccination campaign will start in September 2021. In this article, we will answer the main questions related to the seasonal epidemic of respiratory diseases and talk about the vaccines that are available to children and their parents this season.
Available: Ultrix quadri, Grippol Plus, Sovigripp and Flu-M.
How the vaccine works
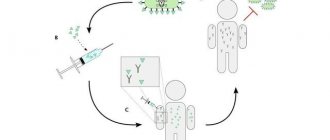
Vaccination ensures that a small amount of the virus enters the body; the immune system must recognize and respond by multiplying protective cells. The point of the flu shot is that the body, once it has overcome a small attack, must remember how to repel it in the future. The infection from outside will be repeated: it will be easier for the person to cope with it.
Is it worth undergoing immunoprophylaxis?
No doctor can guarantee that getting a flu vaccine will definitely eliminate the risk of getting sick or will definitely reduce the chance of complications. Individual characteristics of immunity and a temporary weakening of the body’s defenses can play a role. The measure is preventative, not curative.
The nuance is that every year in certain geographical areas there are outbreaks of certain strains. They may differ in different regions. The task of doctors is to suggest which strains should be used to create the correct vaccine. Also, if you were vaccinated against one species last year, the antibodies may not work against the current variety.
Medical statistics show that after vaccination against influenza a person:
- less susceptible to viruses from the outside;
- it is easier to bear the disease if it overtakes;
- Treatment is easier and takes less time.
State institution "Minsk City Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology"
What vaccines are being used this season?
- "Grippol Plus" (country of origin - Russia);
- "Influvac" (country of origin - the Netherlands);
- "Vaxigrip" (country of origin - France);
- "Vaxigrip Tetra" (country of origin - France).
Which of these vaccines are used free of charge and which are paid for?
For immunization using budget funds, the Grippol Plus vaccine .
Grippol Plus, Influvac, Vaxigrip, Vaxigrip Tetra are available for a fee
- All vaccines are registered on the territory of the Republic of Belarus, are comparable in effectiveness and have experience of use in our country and abroad.
- All vaccines are identical in the strain composition of influenza viruses. Those. All vaccines contain 3 epidemically relevant strains of the influenza virus (two variants of the A virus (H1N1 and H2N3) and a variant of the B virus), which will cause the disease this year and are recommended by WHO. This season, the strain composition of the vaccine has been updated by 2/3 compared to last year.
* “Vaxigrip Tetra” contains an additional 4th strain of influenza B virus (2 strains of influenza A virus and 2 strains of influenza B virus).
- “Grippol Plus” and “Influvac” are subunit vaccines (i.e. they contain only external antigens (influenza virus subunit - hemagglutinin and neuraminidase);
- “Vaxigrip” and “Vaxigrip Tetra” are split vaccines, i.e. split vaccines containing external (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase) and internal antigens of the influenza virus.
- The vaccines used are highly effective and safe. Recommended for use in children from 6 months and pregnant women.
Is the Grippol Plus vaccine different from other vaccines?
It differs in that the Grippol Plus vaccine includes the immunomodulator polyoxidonium , due to which the antigenic load is reduced (i.e. the vaccine contains 5 mcg of each strain of the influenza virus). In all other vaccines, the amount of antigen is 15 μg of each strain.
A distinctive feature of the composition of the Grippol Plus vaccine is the presence of the immunomodulator Polyoxidonium, which has a wide spectrum of immunopharmacological effects, increases the immunogenicity of the vaccine and increases the immunological memory of the vaccinated person.
What are the contraindications to getting vaccinated against influenza?
Temporary contraindications. Vaccination is temporarily postponed during an acute illness or exacerbation of a chronic disease. After the temperature has normalized (at the end of the acute illness) and the chronic disease has entered the remission stage, the vaccine can be administered.
Absolute contraindications (i.e. vaccination is never carried out). Allergic reaction to chicken egg whites. This allergy includes immediate swelling of the lower lip and throat when trying to eat a chicken egg in any form (boiled egg, scrambled egg, etc.). If there are no such reactions, and a person calmly and without consequences eats chicken eggs, then there is no allergy to chicken egg whites.
An allergic reaction to previously administered influenza vaccines.
Is it possible to get the flu after vaccination and infect others?
You cannot get the flu if you are vaccinated with any vaccine. Since during the production process, vaccine viruses lose their ability to cause disease, but retain the ability to form protection.
When will immunity be formed?
Between the second and third weeks after vaccination, specific immunity develops, providing prevention of influenza for a period of up to 12 months.
What adverse reactions may occur after vaccination?
Out of 100 people vaccinated against influenza, 4-8 people may have local reactions in the form of redness, hardness or soreness at the site of vaccination, and 1-8 people out of 100 vaccinated may have general reactions in the form of a short-term increase in body temperature (up to 37.5 ° C ), general malaise. All these symptoms are short-lived and disappear spontaneously, usually after 1–2 days.
Does the flu shot guarantee 100% protection against the disease?
How reliable protection will be developed after vaccination depends on many factors, including. the patient’s age and health status, individual characteristics, etc. On average, out of 100 vaccinated people, 65-90 people will not get the flu. If a vaccinated person does get sick, his illness will be mild and without complications. Thus, vaccination guarantees protection against severe and complicated forms of influenza that end in unfavorable outcomes. The influenza vaccine has additional, to some extent immunomodulatory properties. Thanks to this, the immune system of approximately 15-20 people out of 100 vaccinated acquires additional protection from other respiratory viral infections.
Do I need to be vaccinated this year if I was vaccinated in the past?
Protective antibodies produced after vaccination are usually destroyed within 6-12 months after vaccination or their quantity becomes insufficient to protect against influenza in the new season. In addition, the variants of influenza viruses that are included in vaccines are updated annually. Therefore, it is necessary to be vaccinated annually.
Features of vaccinations
There is no way to predict which flu strain will be active in a particular region at the beginning of the season, so vaccines mix up to three varieties. Which ones are determined by WHO (World Health Organization) professors, based on statistics and probability. Experts give their recommendations by the end of spring; laboratories producing vaccines are guided by them.
Statistics from ongoing studies show that with the use of good vaccines, the likelihood of contracting the flu during the season is reduced to 20%. Other people, even if they get sick, tolerate the disease quite easily.
Effect duration
How long antibodies last in the body depends on the type of vaccine: drugs with live agents are more persistent (up to a year) than inactivated ones (about six months). However, the former have a larger list of contraindications and the likelihood of adverse reactions.
When to get vaccinated
The most “favorite” time of year for the flu is autumn. It gets colder, the body adjusts to a new rhythm, and the immune system reduces its defenses. Against this background, the mucous membranes easily accept harmful bacteria. Epidemic outbreaks can be recorded regionally from September to March. Especially often - in December and January.
The vaccination should be done at the very beginning of autumn, until about November; later this may no longer be relevant. The fact is that immunity will not develop immediately, and for about two weeks a person will be very vulnerable to the disease, which can have the opposite effect at the height of the disease.
Indications for use Prevention of influenza in adults and children over 6 months. (especially for people who are at increased risk of developing post-influenza complications or who, by the nature of their work, have extensive public contacts - medical personnel, teachers, etc.).
Contraindications : Hypersensitivity (including to neomycin and chicken protein), history of severe allergic reactions to vaccines. Diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature (including acute manifestations of an infectious disease). In these cases, vaccination should be postponed.
Side effects General reactions: increased body temperature, malaise, chills, feeling tired, headache, sweating, myalgia, arthralgia. Local reactions: hyperemia, swelling, pain, bruising, compaction at the injection site. These reactions usually resolve within 1-2 days without special treatment. In rare cases, neuralgia (pain along the nerve), paresthesia, convulsions, short-term thrombocytopenia, allergic reactions with the development of shock, vasculitis with short-term involvement of the kidneys (in extremely rare cases), and neurological disorders may occur.
The interaction of GCS and immunosuppressants reduces the immune response to the vaccine.
Overdose No data available.
Method of administration and dosage IM or SC (deep), adults and children over 3 years old - 0.5 ml, children: from 6 months. up to 3 years - 0.25 ml. Before use, the vaccine must be warmed to room temperature and shaken until homogeneous.
Special instructions Intravascular administration is not allowed. Can be administered simultaneously with other vaccines (in different parts of the body). In case of acute manifestations of the disease and exacerbation of chronic diseases, vaccination is postponed until recovery. Against the background of mild ARVI, acute intestinal diseases, etc., vaccination is carried out after normalization of body temperature. In patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, the immune response to the vaccine may be insufficient. The doctor should be informed about any treatment that coincides with vaccination, or about the recent use of any drugs (including over-the-counter ones), as well as about the patient’s immunodeficiency, allergies, or unusual reaction to a previous vaccination. The vaccine can be used during lactation. There is currently no data indicating a possible risk to the fetus or fertility problems when using the vaccine in the first 8 weeks. pregnancy, however, the advisability of vaccination during this period should be assessed by a doctor (taking into account the risk of contracting influenza). The vaccine should not be used if coloring or foreign particles are present. Due to the fact that influenza is seasonal, it is recommended to vaccinate annually in early autumn in temperate countries or at the beginning of the period of greatest risk of an epidemic in tropical countries.
Storage conditions Store in a place protected from light, at a temperature of 2-8 degrees. C, (do not freeze).
Literature Typical clinical and pharmacological article.
Why does a vaccinated person get sick?
The question often arises as to why a person gets the flu despite being vaccinated. First of all, the idea that the vaccine is a panacea is wrong - it is not. There is a significant likelihood of exposure to the disease. There are several reasons:
- Delayed immune response. The person has already been vaccinated, antibodies have not yet been developed, but infection has occurred.
- Wrong vaccine strain. This is acceptable, since there are only three of them in the drug, but in nature there are more.
- The vaccination was done incorrectly: it is necessary to give an injection into the shoulder or thigh intramuscularly.
- Too much attack by viruses: many agents entered the body at the same time, the immune system could not cope with all of them at once.
- The vaccine was expired or not of good quality.
Even more often, doctors discover that a vaccinated person presents with flu-like symptoms, but in fact he has an acute viral infection - a common ARVI, of which there are many varieties. In this case, the disease is treated symptomatically, and the vaccine aimed at influenza infection does not affect the virus.
How to further protect yourself
The immune system benefits from healthy eating, adherence to a routine, mobility, and walks. Autumn in Russia is a time when many fruits and vegetables are available in fresh, natural form and at reasonable prices. It is important to nourish the body well with useful substances and minerals to invigorate the immune system. At home, it is necessary to regularly carry out wet cleaning and humidification of the premises; adding drops of essential oils helps in creating a healthy microclimate: eucalyptus, rosemary, pine. A normalized day, good sleep, sufficient mobility - these factors help to gain strength and resist not only colds, but also stress.
Also, taking care of your health allows you to prepare for a flu shot: vaccination is not carried out if the patient has at least mild signs of acute respiratory viral infection or other diseases. In order to get vaccinated on time and help yourself develop antibodies, you need to be healthy.
You should know that other vaccinations should not be given along with a flu shot or at short intervals. In this case, it is always better to consult with your doctor: which drug is more important to receive earlier, how long to wait between vaccinations.
Rospotrebnadzor recommendations for flu vaccination
Rospotrebnadzor reminds that a flu vaccination campaign opened at the beginning of September.
Why is it important to do this and why now? Epidemiologists and infectious disease specialists are unanimous: a flu shot is needed. The autumn period is the most suitable time for vaccination against influenza, since you need to be vaccinated two to three weeks before the rise in incidence in order for the necessary immunity to form.
The main goal is to use a vaccine to protect the population from the uncontrolled spread of infection, from an epidemic. Otherwise, massive outbreaks of the disease will inevitably occur. It is not just vaccination that is important, but mass vaccination. It is carried out over a short period of time, when a large pool of protected people is created in the population and human-to-human transmission of the virus is stopped.
Annual vaccinations are due to the constant variability (mutation) of influenza viruses. In this regard, the composition of vaccines is updated as necessary.
Risk groups include young children whose immunity is in the process of developing, pregnant women, elderly citizens, those who suffer from chronic diseases, and people with immunodeficiency conditions. It is especially indicated for those in high-risk professions—medical workers, teachers, students, service and transport workers.
Symptoms of influenza are sudden onset, fever up to 40 degrees, chills, severe fatigue, headache, nasal congestion in the absence of discharge from the nasal passages, cough (pain or sore throat), pain in muscles and joints, possible nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
It is important to distinguish the symptoms of influenza from the symptoms of ARVI and the new coronavirus infection, so it is necessary to remember that self-medication is unacceptable; a doctor must make a diagnosis and prescribe an examination and the necessary treatment. It is extremely dangerous to carry the flu on your feet - this can lead to serious complications.
For prevention, experts recommend, first of all, getting vaccinated, leading a healthy lifestyle, washing your hands regularly, using masks, limiting your stay in crowded places and avoiding contact with sick people.
If you do become infected with influenza , it is necessary to limit contact to a minimum, allocate a separate room for the patient if possible or maintain a distance of at least 1 meter from him, allocate separate utensils for eating, and subsequently disinfect them. It is important to keep the room clean; it should be ventilated every two hours. When caring for a patient, you need to wash your hands frequently and correctly with soap and use masks and gloves.
You can get vaccinated at city clinics at your place of residence or at mobile points that are open daily. On weekdays they are open from 08:00 to 20:00, on Saturdays - from 09:00 to 18:00, on Sundays - from 09:00 to 16:00. You can find out where they are and study in detail information about flu vaccination on the website of the Moscow Department of Health.
By getting vaccinated against the flu, you are making not only a personal choice, but also showing responsibility towards your loved ones, your family, and making sure that the infection does not spread.
Press service of the Department of Labor and Social Protection of the Population of Moscow