New means of treatment and prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections
Influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) are the most widespread diseases that occur throughout the year, but most often in autumn and winter. According to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, acute respiratory viral infections occupy first place in the structure of infectious diseases and account for 80-90% of all cases of infectious pathology.
Influenza is an acute infectious disease of viral etiology, which is accompanied by damage to the upper respiratory tract. Influenza reduces the body's defenses, as a result of which it can cause various diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract, central nervous system, heart, kidneys and other organs. Given the ability of influenza to cause annual epidemics and pandemics throughout the globe, it can be argued that influenza is a problem of global concern. During the epidemic, from 5 to 20% of the population gets sick. During pandemics, when there is a sharp change in the properties of the virus, every second person gets sick. Typically, new strains of influenza first appear in China and Southeast Asia and then quickly spread throughout the world.
The economic damage from influenza, both for each sick person (lost work days, expenses for medicines) and for society as a whole, is enormous. The seasonal outbreak of influenza in Russia brings direct and indirect losses of about 40 billion rubles.
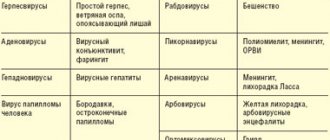
In addition to direct harm to human health, influenza can aggravate the course of other diseases, which poses a particular danger for people with chronic pathologies and a weakened immune system - the elderly, newborns, patients with cardiovascular diseases, etc. Many acute respiratory diseases are caused by parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial , adeno-, corona-, entero-, rhinoviruses and other pathogens.
You can reliably protect yourself against these diseases using specific (influenza vaccines) and nonspecific means of protection. Modern medications can significantly increase the body's defenses and create a barrier to the penetration of respiratory viruses, including influenza. This article is the result of two years of work by specialists from the Influenza Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences to study new means of treating and preventing influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. The studies included drugs for both preventive and therapeutic use. Some of them (algirem, rimantadine/no-shpa) are etiotropic agents and are recommended for use according to the treatment regimen; others (anaferon, influpferon) can be used both for the treatment and prevention of acute respiratory viral infections. For some drugs (arbidol, influenza, carmolis), their antiviral activity has also been proven in in vitro model experiments, and the spectrum of this activity has been expanded to include other human pathogens (bird flu H5N2 and coronavirus).
Algirem
For the first time in world practice, employees of the Influenza Research Institute, together with other organizations of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, developed a new antiviral drug based on the polymeric form of rimantadine - algirem.
The drug algirem is a complex of rimantadine fixed to a polymer (sodium alginate) in an optimal ratio of 1:1, and sugar syrup or 20-60% sorbitol syrup. Since algirem is a polymeric drug, its pharmacological properties are significantly changed compared to rimantadine. The low molecular weight modified sodium alginate included in its composition has adsorbent and detoxification properties, which helps to enhance the antitoxic activity of the drug. The circulation time of algirem in the blood plasma is tens of times higher than that of rimantadine, and the rate of diffusion into tissue is significantly reduced, which makes it possible to reduce the dosage of the drug, and therefore significantly reduce the risk of undesirable effects and ensure good tolerability of its use.
It has been shown that the use of the tested drug in the early stages of the disease (1-3 days) with influenza contributes to a faster recovery of children, which is manifested mainly by the accelerated elimination of elevated body temperature and manifestations of intoxication. The effect of algirem was especially pronounced in cases of absence of bronchial damage, when the duration of the acute period of the infectious process was significantly shorter than in patients in the control group (4.7 and 6.0 days, respectively), while there was a tendency to reduce the duration of some catarrhal symptoms in nasopharynx.
The therapeutic activity of the drug in influenza with symptoms of stenosing laryngotracheitis or bronchitis was less pronounced, but the effect on the duration of the febrile period and intoxication syndrome was also evident in these cases. The maximum reduction in the duration of the temperature reaction against the background of the tested drug was observed already on the 3rd day from the start of its administration.
The beneficial effect of the drug algirem on the humoral (sIgA) and cellular immunity, which plays a leading role in influenza infection, has also been shown. Its use contributed to the normalization of the subpopulation composition of immunocompetent cells and improvement of their functional activity (in terms of CD4, CD8, CD20, IFN-α, IFN-γ, IL-8 and TNF-α). The administration of the drug Algirema contributed to a significant reduction in the duration of detection of antigens of respiratory viruses, especially influenza pathogens, in the epithelial cells of the nasal mucosa.
An analysis of morbidity during outbreaks of acute respiratory viral infections in orphanages showed that the use of algirem for the purpose of emergency disease prevention was effective in outbreaks of any etiology, and the differences in the frequency of registration of acute respiratory infections among children who received the tested drug and in the control groups were always significant. Algirem's tolerability was assessed as generally excellent.
The results obtained indicate the possibility of using algirem for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes against influenza and acute respiratory viral infections of other etiologies in young children.
Anaferon
The drug anaferon for children (homeopathic tablets) is an affinity-purified and potentiated antibody to human γ-interferon in a mixture of homeopathic dilutions C12, C30. According to the instructions, the drug can be used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes for influenza and ARVI (rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheobronchitis) in children.
As a result of clinical studies, it was shown that the tested drug has pronounced therapeutic efficacy and can be used for this purpose in these diseases.
Preventive use of this drug (in orphanages) contributes to a milder course of the disease, reduces the severity and duration of symptoms by 2-3 times, and also reduces the frequency of complications. The use of anaferon for children in the early stages of influenza helps to reduce the duration of the manifestation of all clinical symptoms, especially the febrile period, intoxication and, accordingly, the entire disease as a whole. Data were obtained indicating that anaferon has children's immunomodulatory properties, which was manifested in stimulating the activity of T-helper cells, normalizing the CD4/CD8 relationship, and its participation in the creation of specific immunity, helping to sanitize the body from infection.
It has been shown that under the influence of the drug the functional activity of lymphocytes increases, which is expressed in an increase in their ability to produce under the influence of IFN-α inducers. The use of the tested drug promotes faster elimination of pathogen antigens in the nasal passages of the examined children and a significant reduction in the frequency of nosocomial infections. There were no side effects of the drug Anaferon for children on the child’s body, which was confirmed by the absence of pathological changes in hematological parameters and an increase in IgE in the blood serum, and in some cases even a decrease in this indicator in children receiving the tested drug.
Conducted over a 3-month period, placebo-controlled clinical and epidemiological trials of the preventive effectiveness of the interferon-inducing drug anaferon for children among children of the first years of life, including those under the age of 1 year, from orphanages who received it according to a preventive regimen and according to a therapeutic regimen - with development of acute respiratory infections in these children with a temperature reaction and other clinical symptoms, showed that the drug has reliably proven preventive effectiveness, increases the number of children who have never developed acute respiratory infections by 8 times, and also facilitates the clinical course in case of its development.
The results obtained indicate the possibility of using the homeopathic drug Anaferon for children for preventive purposes in children of the first years of life, including the first year. The drug can be used for this purpose both in individual children and in organized children's groups.
Arbidol
Indications for the use of arbidol are influenza, ARVI (including those complicated by bronchitis and pneumonia), chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, recurrent herpes infection, postoperative period (normalization of immune status and prevention of complications). The drug has interferon-inducing and antioxidant activity. Prevents the development of post-influenza complications, reduces the frequency of exacerbations of chronic diseases, and normalizes immunological parameters.
Considering the lack of drugs against human coronavirus infection in clinical practice, studies were conducted aimed at expanding the spectrum of action of arbidol. The studies demonstrated the ability of arbidol to suppress the reproduction of human coronavirus 229E in cell culture. This activity was manifested both in a dose-dependent decrease in viral replication in the presence of the drug and in a decrease in the infectious titer of viral progeny. The ratio of 50% toxic dose to 50% effective dose (chemotherapeutic index) for arbidol was 25, which is a relatively high indicator for chemotherapy drugs.
The results obtained did not allow us to determine the nature of the antiviral effect of the drugs (virusstatic or virucidal), but they gave reason to consider arbidol as a potential agent used for the prevention and treatment of human coronavirus infection.
Grippferon
The drug Gripferon, nasal drops, is a new dosage form of recombinant IFN-α2, available in 10 ml bottles with a dropper. 1 ml of the drug contains at least 10,000 IU of IFN (100 times more than in domestic leukocyte interferon preparations for intranasal use) and a filler consisting of a mixture of polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene oxide and Trilon B.
At the Influenza Research Institute in 2003-2004. Model experiments demonstrated the antiviral activity of influenzaferon against human adenovirus type 6 and influenza A virus.
Inhibition of viral reproduction was shown on the chorionic-allantoic membrane and when taking into account cytopathic doses in cell culture and was confirmed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data have been obtained indicating that influenzaferon has direct inhibitory activity against human coronavirus. This activity was manifested both in a dose-dependent decrease in viral replication in the presence of the drug and in a decrease in the infectivity of viral progeny. The chemotherapeutic index of influenzaferon (the ratio of its maximum tolerated concentration to the minimum effective concentration) was 10. In addition, in vitro experiments showed that influenzaferon slightly but consistently suppressed the replication of the avian influenza virus (H5N2) in MDCK cells. Based on the data obtained, the chemotherapy index of the drug in cell culture is at least 133, which is a high indicator for chemotherapy drugs.
Considering the resistance of the avian influenza virus isolated from sick people to the action of interferon, the ability of influenza to suppress the reproduction of the avian influenza virus is an advantage of the drug and can serve as the basis for a more detailed study of its preventive and therapeutic activity in diseases caused by the avian influenza virus.
Clinical and laboratory observations of young children, including those under the age of one year, who received influenzaferon both as a therapeutic regimen (when included in complex therapy for influenza and other acute respiratory infections) and as a preventive regimen - in an organized children's group - showed that the drug has pronounced therapeutic and prophylactic effectiveness.
The use of this drug in the early stages of ARI helps to reduce the duration of manifestation of all symptoms of the disease, especially the febrile period, intoxication and, accordingly, the entire disease as a whole. The preventive effectiveness of the drug is manifested by a decrease in the number of sick people in children's groups, as well as the frequency of development of nosocomial infections while taking it.
The observations did not reveal any adverse effects of influenza nasal drops on the children's body, which was confirmed by the absence of pathological changes in hematological parameters in the dynamics of observation, as well as the absence of an increase in IgE, and in some cases even a decrease in this indicator in children who received the tested drug a drug.
The results obtained indicate the possibility of using influenza for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes in young children, including those in the first year of life, with influenza and other acute respiratory infections.
Immunal
Immunal is a herbal preparation and is juice from rudbeckia (Echinacea purpurea, aster family). The biologically active substances it contains are nonspecific stimulants of the immune system. The main active components of Immunal include chicorienic acid and its esters, alkylamides, and hydrophilic polysaccharides. The mechanisms of the immunostimulating effect of the drug are associated with the activation of bone marrow hematopoiesis, with an increase in the mitotic index and the phagocytic ability of granulo- and monocytes.
As a result of clinical trials conducted in children's groups, it was shown that the preventive course of taking Immunal, carried out during the epidemic season of influenza and ARVI of 2003-2004, helped reduce the incidence of these diseases in children 7-15 years old by 3.3 times compared to with the control group. Against the background of preventive administration of Immunal, a decrease in the duration of diseases by 1.4 days and a decrease in the number of complications by 3.2 times were noted.
Immunal was well tolerated and had no side effects. The pronounced effectiveness and good tolerability of Immunal make it possible to recommend the drug for the prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections during periods of epidemic outbreaks and seasonal surges in organized groups of school-age children.
Carmolis, drops
Carmolis is a herbal preparation based on essential oils obtained from 10 plants: anise, cloves, Indian mint, lavender, nutmeg, rosemary, pine, thyme, sage, eucalyptus. According to available data, carmolis, as a complex of biologically active substances extracted from the listed plants, has antiseptic, virus-inhibiting, as well as general strengthening, immunocorrective effects.
As a result of in vitro studies, it was shown that the drug has pronounced virucidal and virostatic effects, manifested equally against different serotypes of influenza virus, reducing the infectious titer of the virus down to a concentration of 0.08% and 1.25%, respectively.
An electron microscopy study demonstrated that the use of the drug Carmolis, drops, led to a persistent dose-dependent increase in the percentage of morphologically defective virions in the viral population.
In the course of clinical studies, it was possible to prove that a preventive course of the drug Carmolis, drops, carried out during the period of an epidemic rise in the incidence of influenza, contributed to a reduction in the incidence of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections by 2.9 times.
A significant reduction in the incidence of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections was observed after 4 weeks of taking Carmolis. The efficiency index was 3.7, and the protection index was 73%, indicating a stable effect of the drug with a positive aftereffect. The length of hospital stay of ARVI patients from the main group was 1.9 days shorter than that of patients in the control group.
In addition, in ARVI patients who received Carmolis prophylactically, there was a 1.9-fold decrease in the incidence of complicated forms of the disease compared to the incidence rates in the control group.
Pinosol
Pinosol is a medicinal product based on herbal raw materials. Available in two forms. Pinosol, 2% cream for children from 1 to 3 years old, contains: eucalyptus oil - 0.1000 g; Scots pine oil - 0.3800 g; thymol - 0.0032 g; tocopherol acetate - 0.1770 g. Pinosol, ointment for children over 3 years old, contains: eucalyptus oil - 0.4325 g; Scots pine oil - 0.685 g; menthol - 0.7225 g; thymol - 0.02175 g; tocopherol acetate - 0.2885 g.
Conducted in 2003-2004. Clinical and laboratory observations have shown that pinosol significantly helps to alleviate the course of ARVI in children, especially if it is used in combination with an etiotropic drug (rimantadine or algirem).
If rimantadine drugs in our observations had an effect mainly on the symptoms of intoxication, then pinosol was effective against catarrhal symptoms, which was accompanied by a significant increase in sIgA in nasal secretions. The treatment regimen used contributed to a faster recovery of children compared to the control group.
It should be noted that the observations did not reveal any side effects exerted by pinosol on the children's body, which was confirmed by the absence of pathological changes in hematological parameters in the dynamics of observation, as well as the absence of an increase in IgE, and in some cases even a decrease in this indicator in children receiving tested drugs, as well as a decrease in the level of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-8 in patients of the observed groups.
Reaferon
The oral form of the liposomal preparation of recombinant interferon-α2 - reaferon-EC liposomal lipint, easily dosed and easy to use, ensures long-term circulation of interferon in the blood and, in addition, causes the induction of endogenous interferon. Currently, the drug is used as part of complex therapy for patients with acute hepatitis B in active and inactive replicative forms, as well as for chronic hepatitis B complicated by glomerulonephritis.
In 2003-2004 At the Influenza Research Institute, studies were conducted to determine the preventive activity of the drug against influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. The studies showed that during a 4-week course of prophylactic administration of the drug Reaferon-EC Lipint liposomal, its tolerability was good, there were no side effects or allergic reactions. Taking the drug Reaferon-EC Lipint liposomal for 4 weeks, 500,000 units 2 times a week, 30 minutes before meals, helped reduce the incidence of acute respiratory infections by 2.2 times. In patients with acute respiratory infections who received Reaferon-ES Lipint liposomal prophylactically, complications occurred 1.6 times less frequently, and febrile reactions were stopped more quickly.
The tested drug, used according to the proposed scheme, was well tolerated and expressed effectiveness, which made it possible to recommend it for the prevention of influenza and acute respiratory infections during epidemic or seasonal increases in morbidity.
Remantadine/No-spa
As was established during preliminary studies, the vasodilator no-shpa, which is widely used in clinical practice and normalizes the tone of blood and lymphatic vessels, has the ability to inhibit the reproduction of the influenza virus in vitro and in vivo. The antiviral activity of this drug is manifested against two types of influenza virus: A and B. It was found that the simultaneous use of no-shpa and rimantadine helps eliminate intoxication in all children within 2 days after the start of treatment, while when using rimantadine alone symptoms of intoxication in some cases persisted until the 6th day of observation. Similar results were obtained regarding the intensity of the decrease in the temperature response.
The introduction of the rimantadine-no-spa complex was most effective in the acute period of the disease, regardless of the premorbid background of the children. These drugs are prescribed in the early stages of the development of influenza to children suffering from various underlying diseases, such as dermato- and respiratory allergosis, with the presence of chronic foci of infection, with an impaired immune status, the manifestation of which is frequent infectious (respiratory and intestinal) diseases, congenital defects development, showed approximately the same effectiveness as in the group of children with an uncomplicated premorbid background.
The new etiotropic complex for the treatment of influenza “no-spa-remantadine” has antiviral activity that exceeds the effectiveness of using each of the tested drugs in isolation against both influenza viruses type A and influenza viruses type B. The advantage of the new complex drug is also manifested in the relief of disorders in hemostasis system, characteristic of influenza infection, due to the vasodilating properties of no-shpa.
The use of two complementary drugs in combination allows you to reduce the dose of rimantadine by 2-3 times. Reducing the dose, in turn, makes it possible not only to reduce the possibility of developing adverse symptoms, but also to significantly reduce the incidence of rimantadine-resistant strains of influenza A viruses.
PhytoGOR
Among the small number of antiviral drugs used, the main place is occupied by chemically synthesized drugs. A significant disadvantage of the latter is its relatively high toxicity and the presence of a variety of undesirable side effects. Experience in the treatment and prevention of influenza with the help of such well-known antiviral chemotherapy drugs as amantadine, rimantadine, acyclovir has shown that there is a possibility of viruses developing resistance to the action of these substances. This makes the search for antiviral immunotropic agents among products of natural origin even more urgent. The therapeutic and prophylactic use of such drugs seems to be a more gentle procedure due to the evolutionarily established system of detoxification of xenobiotics in the human body.
To carry out preventive courses of taking immunotropic substances during seasonal or epidemic increases in the incidence of ARVI in adults and children, mainly preparations of eleutherococcus, echinacea, seaweed, pine needles and other plants are used, often in the form of herbal infusions. The most balanced in terms of the clinical effects of plant components is the new drug phytoGoR - a phytolectin complex extracted from wild and cultivated herbs. The composition of this herbal collection includes sage, polygonum, catnip, corn silk, calendula, lemon balm, peppermint, etc., traditionally used in folk medicine. According to available data, phytoGor is a general strengthening and tonic, has a positive effect on metabolism, promotes the elimination of heavy metals and radionuclides. In addition, phytoGoR suppresses the reproduction of viruses in cells and has direct virucidal activity. A test of the effectiveness of PhytoGor for the prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections was carried out at the Influenza Research Institute using a double-blind control method, that is, the formation of observation groups by random sampling and the use of the test substance and placebo in the form of encrypted preparations.
Based on the results of a controlled epidemiological observation conducted in placebo-randomized groups among children and adolescents of school age (9-18 years old), it was noted that preventive intake of herbal tea for a course of 3 weeks during the influenza epidemic provided a significant reduction in the incidence of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections 4.3 times compared to the control group.
Good tolerability and absence of unwanted side effects of the drug, pleasant taste were noted. At the end of the preventive course, no increase in morbidity was observed, which indicates a stable preventive effect of the drug. The favorable attitude of children and adolescents to the taste of the drug, the absence of side effects and the significantly high preventive effectiveness allow us to recommend phytoGoR tea for widespread use for the prevention of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections during epidemic and seasonal increases in incidence.
Thus, today medicine has a fairly wide range of drugs with a different spectrum of activity and mechanism of action that can be used for the treatment and prevention of ARVI. Their correct and timely use can significantly reduce the incidence of these infections.
O. I. Kiselev, V. P. Drinevsky, L. V. Osidak, O. I. Afanasyeva, V. V. Zarubaev, V. M. Guseva, M. K. Erofeeva, V. L. Maksakova, I. L. Kolyvanova, A. S. Shadrin, V. M. Guseva, P. M. Anfimov, A. K. Sirotkin
Research Institute of Influenza RAMS, St. Petersburg
How to recognize the disease
Flu symptoms
- high temperature from 38.5 °C to 40 °C;
- sudden onset of illness;
- severe intoxication of the body, which manifests itself in signs of general malaise: chills, severe weakness, drowsiness, increased sweating;
- pain in the eyes;
- pronounced painful sensations in the throat;
- runny nose, sneezing;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- severe headache, dizziness;
- muscle pain, chest pain;
- in rare cases, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort.
The incubation period lasts from 12 hours to 2 days.
ARVI symptoms
- temperature up to 38.0 – 38.5 °C;
- severe sore throat;
- runny nose, sneezing, cough, rhinorrhea;
- painful sensations when moving the eyes;
- pain in muscles, chest;
- general moderate weakness and drowsiness;
- lack of appetite;
- chills and mild headaches.
The incubation period ranges from several hours to 7 days.
Symptoms of some forms of influenza are similar to those of acute respiratory viral infections. For example, the temperature does not always rise sharply, and not in all cases there is severe intoxication of the body. Only a general practitioner can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent, effective treatment. Properly prescribed therapy helps to quickly get rid of the disease and alleviates symptoms in the first days of the disease.
Flu can lead to various complications, both mild (bronchitis, sinusitis, otitis) and severe (serous meningitis, neuritis, encephalitis, etc.).
Particularly susceptible to complications:
- elderly people;
- children under 2 years old;
- pregnant women;
- people with chronic kidney and lung diseases;
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- patients with cancer.