Specialist: Gastroenterologist
TO GET A CONSULTATION
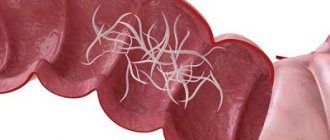
Description of the disease Symptoms Causes Diagnostics Treatment Prevention Pinworms are protocavity worms ranging in size from 2 to 12 mm, often living in the intestines of a child and causing significant harm to the child’s body. The diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by a pediatrician, gastroenterologist and infectious disease specialist.
How can you become infected with pinworms?
Most often, pinworm infection occurs due to non-compliance with hygiene rules in everyday life. Washing your hands too often or carelessly is the first step to infection.
Pinworm eggs can be found literally anywhere. Females live in the human intestine. However, to lay eggs, they crawl into the anus in the evening and at night, which causes severe itching. Scratching, often unknowingly, causes parasite eggs to be transferred to the hands and under the nails, and from there to anything the infected person touches or directly into the mouth.
Itching in the anus
The source of pinworm infection can also be contact with the underwear or towel of a sick person, although it is no less likely that pinworm eggs will also end up on bed linen, a toilet seat, or a bathtub. Food products can also be contaminated with pinworm eggs.
Direct contact with eggs is not the only way to become infected. Infection is possible through airborne droplets. The eggs are very small and light, so they float in the air. Then they settle, for example, on dust that a person inhales. Adult worms live up to 2 months, but self-medication can cause the problem to persist much longer.
How to avoid infection
The main measures to prevent enterobiasis are to comply with hygiene requirements:
- mandatory hand washing after visiting the toilet, walking, visiting public places, contacting animals, etc.;
- nail care, getting rid of the habit of biting nails;
- frequent replacement of bed linen, towels, hygiene items;
- washing underwear and bed linen in hot water, followed by ironing and steaming;
- wet cleaning with disinfectants every two to three days.
Cause of pinworm infection
Pinworm infection in humans occurs for the following reasons:
- poor sanitary and hygienic conditions;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- pinworms in family members.
The only source of pinworm infection is humans. The infection spreads very easily through the mouth, for example through contaminated hands or food. This problem especially affects children, who often do not follow basic hygiene rules and put various objects, toys or school supplies, such as pens and pencils, in their mouths, which facilitates the penetration of pinworms into the body.
Pinworm infection through contaminated hands
This is why it is so important that adults teach children basic hand hygiene rules and set an example of proper behavior themselves.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of enterobiasis is based on the examination of scrapings from the surface of the skin of the perianal zone to detect pinworm eggs. The material for research is collected with a spatula from the surface of the skin or an imprint is made on adhesive transparent tape (Graham method). Previously, a smear was taken with a cotton swab attached to a stick, but now the use of a spatula or adhesive tape is considered more effective. In severe cases of the disease, not only eggs, but also large numbers of adult pinworms are found in stool samples taken for analysis. To confirm the diagnosis, samples are taken three times at intervals of one to two days.
The doctor may order a clinical blood test to detect eosinophils, which is necessary in cases where not too much time has passed since the infection.
Symptoms of pinworms
Among the symptoms of pinworms that may indicate an infection, the most common is persistent itching around the anus.
Patients are often irritable and have trouble concentrating. They often complain of abdominal pain and headaches. Teeth grinding is also a characteristic symptom that many parents pay attention to.
Pinworms may also be accompanied by:
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- pale skin;
- dark circles under the eyes.
Dark circles under the eyes
Weight loss
It is worth noting that women may experience itching around the vagina. Pinworms can penetrate the female genitals and cause inflammation. There are also known cases of appendicitis caused by pinworms. In adults, the symptoms of pinworms are not very different from those in children. However, they are often much less serious.
A modern view of the problem of helminthiasis in children and effective ways to solve it
According to the World Health Organization, of the 50 million people who die annually in the world, more than 16 million are caused by infectious and parasitic diseases. In the structure of infectious diseases, intestinal helminthiases are in third place. The World Bank estimates that the economic cost of intestinal helminthiases ranks fourth among all diseases and injuries. Given the importance of the control of parasitic diseases for many countries, the 54th World Health Assembly in 2001 approved a strategy for the control of soil helminthiasis until 2010 [5].
In the Russian Federation, more than 10 million people are examined annually for helminth infections, most of them are children. In 2002, 813 thousand infected were identified, of which 681 thousand (83.8%) were children under the age of 14 [4]. More than 15 types of helminths are found in children, of which the most common are enterobiasis, ascariasis, opisthorchiasis, diphyllobothriasis, trichocephalosis, and hymenolepiasis. In recent years, toxocariasis has been increasingly recorded, which is associated with the widespread introduction into practice of a diagnostic test system for its detection.
In the structure of helminthiasis, the leading place is occupied by enterobiasis (91%) and ascariasis (8%). Among all infected children, 92.3% of cases of enterobiasis, 71.1% of ascariasis, 61.5% of trichuriasis and 66.2% of toxocariasis occur.
The incidence of enterobiasis and ascariasis in children in rural areas is significantly higher than in cities, which is apparently due to different sanitary and hygienic conditions in child care institutions in the city and village, as well as the degree of contamination of the environment with helminth eggs (Fig. 5).
Ascariasis is one of the most common helminthiasis, in the formation of foci of which soil contamination with ascaris eggs is of primary importance. In 2002, 74,196 cases of ascariasis were identified, including 52,801 in children under 14 years of age; compared to 2001, the incidence increased by 3.5% and amounted to 217.7 per 100 thousand children.
The incidence of trichuriasis, with a clear downward trend over the last decade, in 2002 increased by 2.8% and amounted to 7.4 per 100 thousand children. Trichocephalosis is registered mainly in the Southern Federal District (Republic of Dagestan, Chechen Republic).
Enterobiasis still ranks first in terms of prevalence among other helminthiases. In 2002, 614,955 cases of the disease were registered among children, which amounted to 2535.5 per 100 thousand patients.
The maximum number of people infected with enterobiasis in 2002 was identified in the Siberian, Northwestern, Ural, Far Eastern, and Volga federal districts.
A feature of most helminthiasis is the chronic course of the disease, associated with the long-term presence of the pathogen in the body and repeated repeated infections. Helminth infections in children, as a rule, are accompanied by a variety of nonspecific clinical manifestations: weakness, fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, dyspeptic symptoms, slower growth and weight gain, and decreased immune status. The most important component of the pathology of helminth infections is the sensitizing effect of metabolic products and excretion of helminths, leading to the development of allergic reactions in the form of atopic dermatitis, asthmatic bronchitis, rhinitis, blepharitis, etc.
A selective analysis of the results of clinical examination of 520 children, carried out in the Sverdlovsk region of Perm in 2002, showed that ascariasis was detected in 1.35%, and enterobiasis in 5.8% of those examined. At the same time, on average, the number of health problems per child in children with enterobiasis in the group of preschoolers was 2.5, and in schoolchildren - 2.9. More often than others, diseases of the genitourinary system (in girls), allergic dermatitis, anemia, vegetative dystonia syndrome, neuropathic conditions and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract were noted. Of the diseases diagnosed in children with ascariasis, the most common were vegetative dystonia syndrome, functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, pneumonia, and allergic dermatitis. Among children with ascariasis, the incidence rate per child averaged 2.0. In the control group, which included children without parasitic diseases (37 people), the average number of health problems was significantly lower than among those infected with ascariasis and enterobiasis, and amounted to 0.2. Thus, the presence of ascariasis and enterobiasis leads to a deterioration in the general health of children. At the same time, children with various underlying diseases that lead to weakening of the body are more often infected with them.
Let us dwell in more detail on the importance of the most common helminthiasis in the development of pathology in children - ascariasis and enterobiasis [1, 3].
Ascariasis. The development of the causative agent of ascariasis (Fig. 2, 3) in the human body occurs with the migration of larvae emerging from the eggs along the bloodstream through the lungs; the larvae are then swallowed with sputum and develop into adults in the intestine. The lifespan of roundworm in the human body is several months. Ascariasis has a significant impact on the quality of nutrition and immunological mechanisms in children. Ascaris allergen is the most powerful of allergens of parasitic origin. It can cause reactions in the lungs, skin, conjunctiva, and gastrointestinal tract. Allergic reactions can be so severe that they often pose a threat to the child’s life.
The immunosuppressive effect of roundworms is due to the lack of effect of vaccination and revaccination against measles, diphtheria, tetanus, and polioviruses in children.
The leading mechanisms of pathogenesis of the migratory stage of ascariasis are the traumatic effect of larvae and sensitization by parasitic antigens. In this case, 2 main types of lesions occur in different organs and tissues.
- The traumatic effect of migrating larvae in organs and tissues along the migration route. At the beginning of migration, the larvae are still small (no more than 0.5 mm long) and cause limited hemorrhages in the wall of the small intestine and in the liver. By the end of migration, the larvae reach 2 mm in size and, penetrating into the alveoli and bronchioles, and then into the bronchi, cause more significant hemorrhages.
- Eosinophilic inflammation of the tissues in which the larvae develop. The tissue phase of ascariasis occurs during the migration of ascaris larvae to the liver and lungs. The metabolites released in this process cause serious immunological changes and inflammatory reactions. In the migration phase, ascariasis can cause hepatomegaly and asthmatic syndrome. In this case, the clinical picture resembles respiratory allergosis.
In the intestinal phase of ascariasis, important pathogenetic factors are the ability of roundworms, reaching a length of 20–40 cm, to spiral forward movements and the desire to penetrate small openings (Vater's nipple, drainage tubes, etc.). The presence of invasion leads to hypertrophy of the muscular layers of the intestinal wall, a decrease in the depth of the crypts, changes in the chemical composition of the intestinal contents, and disruption of the motor-secretory function of the stomach and intestines. Roundworms secrete inhibitors of trypsin and chemotrypsin, as a result of which the absorption of nutrients, proteins, and fats worsens. With ascariasis, functional deficiency of pyridoxine develops, the level of retinol and ascorbic acid decreases, and lactase tolerance decreases. Ascariasis is usually accompanied by intestinal dysbiosis.
Often symptoms of the intestinal phase of ascariasis are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, dizziness, poor sleep, and abdominal pain. An increased level of eosinophils in the peripheral bloodstream is characteristic of the migratory phase of ascariasis.
Complications of the intestinal phase of ascariasis: intestinal obstruction caused by a ball of adult roundworms; peritonitis due to perforation of the intestinal wall or penetration of roundworms into the abdominal cavity through a surgical suture; obstructive jaundice during migration of helminths into the common bile duct; blockage of the pancreatic ducts; asphyxia due to the migration of roundworms into the upper respiratory tract.
Enterobiasis. The development of the enterobiasis pathogen (Fig. 1) in the human body occurs within the gastrointestinal tract. The larvae emerge from the eggs (Fig. 4) and, on average, develop into adults within 2 weeks, which parasitize the lower parts of the small intestine and the upper parts of the large intestine. The lifespan of pinworms can reach 100 days, and the state of infestation in children due to repeated infections can last much longer.
| Figure 1. Life cycle of the enterobiasis pathogen (according to HC Jeffrey, RM Leach, 1975) |
Inflammatory reactions during enterobiasis develop under the influence of larvae, which produce hyaluronidase, proteolytic enzymes, lectin-like substances that promote the activation of the complement system, the release of prostaglandins by the cells of the host tissues surrounding the helminth [1, 2, 3].
With enterobiasis, the processes of absorption and digestion of food products are disrupted. In 30–40% of infected people, the acidity of gastric juice decreases, up to anacidosis and inhibition of pepsin-forming function. In most children, the intestinal microbiocenosis changes. Impaired absorption and digestion of nutrients in the intestines lead to weight loss and delay the growth and development of the child.
An additional factor in the pathogenesis of enterobiasis is the mechanical effect of pinworms in the intestines, leading to pinpoint hemorrhages, erosions, and penetration of bacterial flora, in particular pathogens of intestinal infections.
A striking symptom of enterobiasis is perianal itching, which occurs when the female moves during oviposition (Fig. 6). Severe itching occurs, as a rule, during sleep, more often at night, from 23.00 to 1.00 am. It is at this time that helminths can, remaining unnoticed, lay eggs that will mature to the invasive, contagious stage by the morning. Despite its apparent harmlessness, perianal itching is difficult for children to tolerate and can persist for quite a long time after enterobiasis is cured as a result of the formation of a persistent focus of excitation in the cerebral cortex. Complications that arise as a result of perianal itching are skin damage when scratching, perianal pruritis, eczema, weeping dermatitis. The etiological agent of the inflammatory process is most often streptococci.
| Figure 2. Roundworm egg (70 microns) |
| Figure 3. Adult roundworms |
| Figure 4. Pinworm egg (50–60 µm) |
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of enterobiasis. Pain of a transient nature is observed in the majority of infected people. Sometimes acute abdominal pain may be the reason to seek surgical help. In such cases, it is often not possible to detect a specific pathology; only the accumulation of gases is detected.
In recent years, the number of cases of the formation of perianal granulomas or abscesses in children, inside which female pinworms or helminth eggs were found, has increased. In this regard, it is advisable to screen all children with these conditions for enterobiasis.
In many cases, enterobiasis occurs over a long period of time and is repeated many times. As a result, the intestinal biocenosis is disrupted and the antagonistic properties of the intestinal microflora in relation to pathogens of acute intestinal infections are reduced. In the majority of infected children, the number of E. coli decreases and the proportion of lactonegative intestinal flora increases. The activity of enterokinase and alkaline phosphatase in feces increases. Since the intestinal microflora is one of the factors that supports the activity of intestinal enzymes, disturbances in the processes of digestion and absorption of nutrients that develop as a result of enterobiasis lead to loss of body weight and retard the growth and development of the child. Pinworms have a mechanical effect on the intestinal mucosa, which leads to pinpoint hemorrhages, erosions, and penetration of bacterial flora, in particular pathogens of intestinal infections. The antagonistic properties of the flora in relation to the causative agents of typhoid fever and other intestinal infections are reduced [1, 3].
If pinworms migrate into the abdominal cavity, urinary and genital tracts, inflammatory and allergic reactions outside the intestine may develop.
| Figure 5. Incidence of enterobiasis and ascariasis in urban and rural children in 2002. |
One of the common complications of enterobiasis is vulvovaginitis due to the penetration of pinworms into the genital tract and the addition of bacterial infections. If vulvovaginitis develops in a girl, a parasitological examination for enterobiasis should be prescribed and, if the result is positive, this invasion should be treated with simultaneous bacteriological examination and, if necessary, antibacterial therapy.
Against the background of enterobiasis, children often develop urinary tract infections, especially girls, since enterobiasis is a factor predisposing to the development of this complication.
Parasitism by pinworms in children leads to suppression of nonspecific immunity, manifested by a decrease in the level of interferon a in the blood serum. A decrease in the nonspecific resistance of the child’s body leads to an increase in the incidence of viral and bacterial infections.
| Figure 6. Tail end of a female pinworm |
The presence of enterobiasis leads to a decrease in the effectiveness of preventive vaccinations. The immune layer against diphtheria was initially lower among children infected with pinworms. Protective immunity does not develop during primary vaccination against this dangerous infection, and during revaccination in many cases there is no immune response. It is difficult to develop immunity when vaccinated against measles and tetanus, so to increase the effectiveness of vaccinations, you first need to make sure that the child’s body is free from helminthiasis pathogens.
In children with allergic diseases, enterobiasis develops much more often. Due to the relatively high probability of detecting enterobiasis in children with allergic diseases, patients in this group should be recommended to be examined for enterobiasis and deworming if infestation is detected.
Enterobiasis negatively affects the neuropsychic development of children. This invasion leads to a lag behind the corresponding age norms. Among those infected with enterobiasis, there is a high percentage of irritable children, with a disruption in the process of falling asleep, and with negative habits (biting nails, sucking fingers, etc.).
With enterobiasis in children, the level of copper, zinc and magnesium in the blood decreases significantly. Since the lack of these microelements can negatively affect the physical and mental development of children, their loss should be compensated by introducing certain foods into the child’s diet, prescribing medications (or nutritional supplements) until these indicators are normalized after enterobiasis is cured.
Main indications for examination for helminth infections:
- stomach ache;
- frequent nausea, vomiting;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- fatigue, irritability, restless sleep, grinding teeth in sleep;
- allergic conditions;
- perianal itching (enterobiasis);
- vulvovaginitis (enterobiasis);
- urinary tract infections (enterobiasis);
- increased level of eosinophils in the blood;
- retardation in height, weight;
- untidiness.
The diagnosis of enterobiasis and ascariasis is made only upon receipt of positive results from a laboratory parasitological examination of the patient. If enterobiasis is suspected, a perianal scraping (imprint) is examined, and fecal samples are examined for ascariasis. On the laboratory referral form, you should indicate what kind of helminthiasis the doctor suspects in the child. The choice of the most effective research method by laboratory specialists will depend on this.
Treatment of ascariasis and enterobiasis
The search for remedies for the treatment of helminthiases, including enterobiasis and ascariasis, began many centuries ago. To expel pinworms, Ibn Sina recommended taking elecampane and celandine with sugar, washing them down with water. The medicine for expelling worms (“killing worms”), indicated in the Ebers Papyrus, contains, among other components, date seeds and the plant disart, sweet beer. The Salerno Health Code, which dates back to the early 16th century, recommends another remedy: mint [3].
The modern arsenal of drugs used to treat intestinal helminthiases includes a significant number of drugs of various chemical classes. They are used both in clinical practice for the treatment of identified patients or parasite carriers, and for the purpose of mass prevention.
The Russian pharmaceutical market currently offers several anthelmintic drugs that act on the causative agents of ascariasis and enterobiasis (Table 1).
The most effective drugs for the treatment of enterobiasis and ascariasis are derivatives of carbamate benzimidazole (mebendazole, medamine) and tetrahydropyrimidine (pyrantel). In addition to the ability to influence mature forms of helminths, they are distinguished by high ovicidal and larvicidal activity. Drugs of these pharmacotherapeutic groups disrupt oxidative processes, inhibit glucose transport in helminths, act on the muscles of intestinal nematodes by depolarizing their neuromuscular junctions and block the action of cholinesterase.
The effectiveness of medicines used to treat enterobiasis and ascariasis is very high, the method of administration is very simple and is designed primarily for children. It is very important that as a result of their intake, the process of releasing the pathogen into the environment is not activated. Thus, during treatment the person does not become more dangerous to others. However, pinworm eggs that have already entered the environment, in particular indoors, persist for a long time - more than 2 weeks. Therefore, it is recommended to repeat the treatment of enterobiasis after 2-3 weeks at the same dose in case hygienic measures were not effective enough. For the same reason, simultaneously with the treatment of infested people, everything possible must be done to clear the premises of pathogens.
For many years, pyrantel has been used throughout the world to treat ascariasis and enterobiasis, and has gained popularity among pediatricians and patients. According to recommendations developed in the USA (Medical Letter, 2002), pyrantel is considered a first-line drug for the treatment of enterobiasis in children and adults.
The anthelmintic effect of pyrantel pamoate is associated with a stimulating effect on the H-cholinergic receptors of the ganglion synapses of helminths, leading to spastic paralysis and their subsequent expulsion from the human body. Clinical trials of the effectiveness and tolerability of pyrantel showed its high medicinal activity against enterobiasis and ascariasis - 94-100%, as well as good tolerability [1, 3].
Pyrantel for the treatment of enterobiasis is prescribed at a rate of 10 mg/kg per day once during or after meals. For the treatment of ascariasis, pyrantel is prescribed at a dose of 5 mg/kg once. The drug is well tolerated by children; in some cases, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain may develop; very rarely, a transient increase in the activity of liver transaminases, headache, dizziness, and sleep disturbances may occur. Pyrantel is contraindicated in children with liver disease.
We have extensive experience in treating enterobiasis in children with the drug Pyrantel (tablets, suspension). Pyrantel is well known on the world market of anthelmintic drugs and is widely used for the treatment of enterobiasis in Russia by many generations of doctors. In our opinion, this drug has a number of advantages compared to other anthelmintic drugs. Firstly, the drug in the form of a suspension is easy to give to children, secondly, Pyrantel has a pleasant peach taste, as a result of which the child does not experience negative emotions during treatment, and, finally, thirdly, Pyrantel has a reasonable price and is widely sold in pharmacies. The bottle is equipped with a measuring spoon with a division scale of 2.5 and 5.0 ml, which makes it easy to dose the drug depending on the body weight of the infected child (or adult). Pyrantel suspension can be used in children from 6 months of age.
Along with pyrantel, mebendazole and medamine have a good anthelmintic effect against enterobiasis and ascariasis.
Mebendazole (Vermox) for the treatment of enterobiasis is prescribed to children 2–5 years old at the rate of 5 mg/kg per day, over 5 years old - 100 mg per day. For the treatment of ascariasis in children 2–5 years of age, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 5 mg/kg in 2 doses per day for 3 days; for children over 5 years of age, mebendazole is prescribed at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day in 2 doses for 3 days.
Mebendazole is not recommended for use in the first trimester of pregnancy. It must be remembered that the drug is contraindicated in children under 2 years of age. Side effects of mebendazole include abdominal pain and loose stools.
Medamine (2-medoxycarbanylamino-benzimidazole) is close in chemical structure and spectrum of anthelmintic action to mebendazole. For the treatment of enterobiasis, it is prescribed at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day in 2-3 doses (simultaneous administration is also possible) after eating a small amount of food; it is recommended to chew the tablets and wash them down with water. For the treatment of ascariasis, medamine is prescribed in the same doses for 3 days.
Side effects of medamine include nausea and weakness. In case of allergic manifestations, the drug is discontinued. Medamin is contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy.
To restore the microbiocenosis of the colon in patients with intestinal nematodes, including enterobiasis and ascariasis, and to increase the effectiveness of specific therapy, it is recommended to prescribe bificol, milk bifidum-bacterin. Food products and medicinal plants that can be used for the treatment and prevention of enterobiasis have long been known. Carrots and carrot juice have a good anthelmintic effect. You can also use the anthelmintic activity of walnuts, wild strawberries, pomegranate (especially pomegranate juice), garlic and lovage.
Among the medicinal plants, St. John's wort is used in the form of decoctions and infusions, tea, as well as elecampane (Inula helenicum). The effectiveness of herbal medicine for enterobiasis is low, but the introduction of foods with anthelmintic effects into the diet is a good measure for the prevention of enterobiasis and enhances the effect of medications prescribed by a doctor.
The criteria for the effectiveness of treatment of helminthiases are a negative result of a control parasitological study of fecal samples (for ascariasis) and a perianal scraping or print (for enterobiasis), as well as the disappearance of clinical symptoms of invasion.
Prevention of helminthiases
Features of the prevention of helminthiases depend on the characteristics of their epidemiology. With enterobiasis and ascariasis, the only source of infection is humans. Infection occurs when mature infective helminth eggs are ingested. However, the epidemiology of these helminthiases is otherwise very different. Pinworm eggs mature indoors and on the human body within a few hours and last on average up to 1 month on various household items. Ascaris eggs mature when dropped into the soil within several months and remain there for up to 10 years or more. Enterobiasis is transmitted indoors from one person to another mainly through dirty hands, bed and underwear, toys, dishes and other household items contaminated with pinworm eggs.
A person becomes infected with ascariasis by ingesting soil particles containing invasive roundworm eggs (with unwashed vegetables, herbs, and fruits). The risk of infection (in the case of ascariasis) increases if a child has such a bad habit as geophagy (tasting or eating earth, sand, clay), which occurs quite often (in 3-10% of children under 7 years of age).
Prevention of enterobiasis and ascariasis is the most important task of medical and educational institutions and parents. It can be solved by simultaneously implementing a set of measures, the main components of which are the identification and treatment of infected people and sanitary and hygienic measures. Prevention of ascariasis, enterobiasis and other helminth infections in the Russian Federation is regulated by new sanitary standards and rules approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in 2003.
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
T. I. Avdyukhina, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor T. N. Konstantinova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor M. N. Prokosheva RMAPO, Moscow Children's Clinical Hospital named after. P. I. Pichugina, Perm
Complications due to the activity of worms
Warning symptoms should not be underestimated. Unfortunately, an untreated problem can cause many complications, the most common of which are:
- problems with concentration, which leads to problems with learning and remembering;
- sleep disorders;
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- colitis;
- appendicitis;
- dermatitis (caused by constant scratching around the anus);
- weight loss.
Human roundworm
Another prominent representative of roundworms is the roundworm. These helminths are large in size. Females can reach a length of 40 cm, males - up to 25 cm. Most often, parasites live in the small intestine. Roundworms are classified as geohelminths.
This means that their development cycle does not require intermediate hosts. A sick person excretes ascaris eggs along with feces, which then fall into the soil. This is where the larvae develop. The soil has optimal temperature and humidity for this.
It takes about 2 weeks for the eggs to become infective.
Human infection occurs through the fecal-oral mechanism (through food, water and dirty hands). In the stomach, the shells of the eggs are destroyed and the larvae emerge.
They live in the intestines, often leading to injury and obstruction. Sometimes the larvae are carried through the bloodstream to various organs (heart, lungs, brain, sinuses).
It is important that the development of larvae does not necessarily have to take place in the soil. Autoinvasion (self-infection) often occurs.
Analysis for pinworms
Testing for pinworms is recommended for people of any age every six months. The occurrence of severe itching around the anus, which worries mainly in the evenings and at night, is an immediate indication for testing.
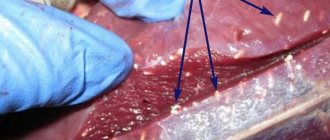
It also happens that pinworms are visible in the stool. This is possible with global pinworm infection. However, you should not wait until the disease becomes visible to the naked eye.
Pinworms are detected using a smear from the anal area, based on which it can be determined whether there are parasite eggs in the body. The material is collected using self-adhesive cellophane tape, which is glued to the skin around the anus in the morning before hygiene procedures and bowel movements. The tape is sent to the laboratory. The test may need to be repeated (only 3 tests performed in a row detect 90% of infections).
Analysis for pinworms
Doctors often decide to conduct a general stool examination, which can reveal possible infection not only with pinworms, but also with other parasites. This is a more accurate and effective test for worms.
What complications does the disease cause?
When the parasite attaches to the intestinal wall, it secretes a harmful secretion and damages the mucous membrane. In the latter case, poorly healing ulcers form and hemorrhages occur. If tissues are deeply damaged, inflamed granulomas appear. They consist of abnormally overgrown cells, lymph and blood. Due to the fact that pinworms injure the intestines, children experience abdominal pain. The microflora is disrupted and dysbacteriosis occurs.
When the female crawls out, she damages the soft tissue. The perianal area is irritated by the secretion of the worm - abrasions, cracks, eczematous rash, and neurodermatitis appear. If the helminth penetrates the genitals of girls, endometritis and other gynecological diseases may develop.
In the presence of pinworms the acidity of the stomach decreases , food is digested worse, and the course of intestinal diseases becomes more complicated . Parasites reduce immunity, because of them the effectiveness of vaccinations decreases and the number of side effects from them increases. Medicine knows of cases where pinworms pierced the rectum and entered the abdominal cavity, followed by peritonitis.
Being in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, parasites cause the following complications:
- inflammation of the pelvis and peritoneum;
- acute skin lesions in the perirectal area;
- stagnation of feces in the cecum;
- pyoderma;
- anemia;
- developmental delay of the child;
- disturbance of appetite and sleep; Source: R.A. Fayzullina, E.A. Samorodnova, V.M. Dobrokvashina Helminth infections in childhood // Practical Medicine, 3(42) May 2010.
- in girls – cystitis, vulvitis;
- in boys - enuresis;
- anal fissures.
Treatment of pinworms
Treatment for pinworms is generally not very complicated and consists mainly of taking appropriate medications and maintaining personal hygiene. Regardless of age, the drugs are usually taken immediately - a single dose of a prescription antiparasitic drug is determined by the doctor.
Treatment of pinworms
Treatment must be repeated after 2 weeks due to possible recurrence of helminth infestation. This repetition of the dose of the drug is aimed at completely eliminating all parasites. It should be emphasized that if pinworms were found in a child, then in order to avoid cross-infection, the whole family must undergo diagnostics and drug therapy. Often in adults, along with pinworms, a whole “bouquet” of parasites is detected.
Measures related to the removal of sources of re-infection from the environment are also of great importance in the treatment of pinworms. Therefore, on the day of treatment, it is necessary to very carefully clean the entire apartment, change and wash, or even boil linen, bed linen, towels, and then iron them with a hot iron.
These steps are necessary to get rid of parasite eggs. You also need to take care of your baby’s toys, which may contain pinworm eggs. If a child puts a toy contaminated with eggs into his mouth or hands that held the toy, reinfection may occur.
You should clean your apartment every day to remove dust that may contain pinworm eggs. In addition, you should change your underwear, bed linen and towels every day, shower every morning and wash the anal area with warm soapy water. Also don't forget to trim your nails.
Many people change their eating habits after learning about the infection. Because diet can help with drug treatment. A diet limited in carbohydrates (sugars) and rich in protein and fiber is recommended, sourced from vegetables, fruits, and whole grain breads and cereals.
Please note that home remedies cannot replace a visit to the doctor and appropriate diagnosis and pharmacotherapy. They can only support the healing process.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
How to get rid of helminths
When pinworms are detected in one family member, treatment of enterobiasis is necessary not only for him, but also for everyone who has close contact with him, i.e., all family members living in the same apartment. The basis of therapy is the use of specific anthelmintic drugs, which are carried out twice with a two-week interval. In addition, young children are prescribed cleansing enemas to remove parasites accumulated in the rectum from the body.
You can take medications against helminths only as directed by a doctor, after examination and an accurate diagnosis. Self-use of the medicine is strictly prohibited, since antiparasitic drugs are unsafe for health and are prescribed only after assessing the patient’s condition.
Along with drug treatment, it is necessary to take measures to prevent re-infestation:
- cut your nails short;
- carefully observe hygiene requirements;
- wear thick underwear at night;
- Before going to bed, place a cotton swab lubricated with Vaseline ointment in the anus;
- every morning, remove bed linen, wash and iron with a hot iron on both sides;
- Wash thoroughly in the morning and evening;
- Wet clean the apartment with soapy water twice a day.
At the end of the course of treatment, after two weeks, 25 and 30 days, samples of the contents of the perianal folds are taken from the patient for pinworm eggs.
How long do eggs live in the external environment?
Pinworm eggs can live outside the human body for about 30 days. But for their life to continue, certain conditions are needed: humidity should be 70%, and the temperature for convenience should be from 22 to 40 degrees.
Any violation of temperature and humidity can lead to the death of parasites. That is why it is advised to carefully iron bedding and underwear, and it is advisable to iron carpet paths along which infected pets and small children can run.
When identifying the disease, doctors strongly recommend disinfecting all toys or simply taking them out into the cold for a long time, where the offspring of helminths die.
Similarities
The main similarity between these parasites lies in their structure. Like pinworms, roundworms are also roundworms and nematodes. They have the same light color. There are also other similarities:
- Both types of parasites are localized in the intestines and affect other organs to a much lesser extent;
- Both parasites have the same transmission pattern - exclusively fecal-oral, that is, for the development of invasion, you need to ingest a certain number of parasite eggs;
- The transmission routes are the same. These are unwashed vegetables and fruits, raw meat, contaminated water, contact with pets or contaminated surfaces;
- They have some similarities in symptoms. Pinworms and roundworms cause mainly intestinal symptoms, intoxication and an allergic reaction;
- There are similarities in the parasite's life cycle. In particular, the peculiarity is that the invasion develops with constant repeated self-infection;
- In both species, males are much smaller than females;
- Both species are present in the intestines in entire colonies.
It is important to take into account that mixed invasions are currently widespread, when several types of parasites are present in the intestines at the same time. Roundworms and pinworms may well exist together in the body, causing the characteristic symptoms of both invasions.
At what temperature do pinworm eggs die?
The bulk of the offspring die at temperatures below - 8 degrees or at high temperatures (42 degrees).
What you need to do to destroy eggs in the house:
- You can use an iron and steam over all surfaces of sofas, armchairs and other upholstered items.
- The procedure must be repeated, because the eggs die at a temperature of + 42 degrees for a period of 10 days. Steam slows down the active development of parasites. This treatment must be used for 2 weeks.
- It is advised to wipe the floors with hot water; wet cleaning effectively eliminates the bulk of the eggs, and the amount that remains on the floors no longer produces the kind of offspring that should be for infection.
You need to resort to many methods to save a small child from the disease and protect yourself and the whole family from unwanted pinworm infection.
Pinworm eggs under a microscope (photo): what color and size
Worm eggs are very small in size and can be easily detected only under a microscope.
Using special equipment, you can see oblong or rounded shapes. They are asymmetrical and have double-circuit shells. The color is white, close to gray.
This is what pinworm eggs look like under a microscope
Is it possible to see pinworm eggs with the naked eye?
A person who is already a carrier of this parasite may notice adult helminths in the feces. It is impossible to visually identify eggs due to their size. To examine them, you need to go to a special laboratory and use a microscope.
Pinworm eggs with mobile larva
Basically, a person focuses on the signs of pinworms and only then understands that he is infected. The main symptoms in most cases do not appear at the time when the pinworm matures as a full-fledged individual, but most often during the stage of eggs or larvae, in the process of migration through the human body.
Get tested for pinworms
Prevention
- Mandatory drug therapy for persons with a confirmed diagnosis and persons in close contact with the patient.
- Proper sanitary and hygienic education of children from an early age. Children should be taught to wash their hands with soap after using the toilet, before eating and after going outside. Wash vegetables and fruits before eating.
- Change underwear daily. Don’t be shy and don’t hide the symptoms of enterobiasis from parents, talk right away to exclude advanced forms of the disease.
- In crowded places such as a kindergarten or school, where there was a child with enterobiasis, it is necessary to carry out deworming for preventive purposes.
- In the house where a patient with enterobiasis lives, carry out general cleaning, washing the floors with disinfectants.