Eating dry food, snacking on the run - this has become commonplace in the modern world. Unfortunately, every year the number of patients with gastritis, as well as gastric and duodenal ulcers, is steadily increasing. Today, there are many drugs available to treat these diseases. One of the drugs - De-Nol - is effective and safe, which will help cope with gastritis and ulcers.
pharmachologic effect
The drug has an astringent effect, due to which a film forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum at the site of the lesion. Thus, the affected areas are protected from the aggressive action of gastric juice, which means that the progression of the process is suspended. The presence of a protective film promotes scarring of ulcerative lesions.
De-Nol is harmful to Helicobacter pylori, which is the main culprit in the formation of ulcers on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Not a single strain of this pathogenic bacterium is resistant to this drug.
In addition, taking the drug has a beneficial effect on the digestion process in the stomach due to the fact that it improves microcirculation in the mucous membrane of its antrum.
Pharmacological properties of the drug De-nol
In an acidic environment, De-Nol forms a protective film on the surface of ulcers and erosions, which promotes their scarring and protects them from the effects of gastric juice. De-Nol stimulates the synthesis of prostaglandin E2, which stimulates the formation of mucus and the secretion of bicarbonate ions, leads to the accumulation of epidermal growth factor in the defect area, and reduces the activity of pepsin and pepsinogen. In addition, De-Nol has a bactericidal effect against Helicobacter pylori. Bismuth subcitrate is practically not absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract; only a small amount of bismuth can enter the systemic circulation. Bismuth entering the blood is excreted in the urine, and its concentration in the blood plasma decreases rapidly after treatment. De-Nol is excreted primarily in feces.
What do De-Nol tablets help with?
Taking this medicine is indicated for:
- Acute and chronic gastritis and gastroduodenitis;
- Exacerbations of gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- Gastropathy that developed as a result of taking NSAIDs or alcohol;
- Functional dyspepsia.
In addition, a gastroenterologist may prescribe De-Nol for pancreatitis. In this case, the drug helps eliminate intestinal dyskinesia, which often accompanies a chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas.
How to drink De-Nol
Adults and children over 12 years of age can take 4 tablets per day. They can be divided into 4 or 2 doses.
It is recommended to take the tablets half an hour before meals with water.
The drug is also used for diseases of the stomach and duodenum that are associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. De-Nol is included in schemes for destroying this microbe along with antibacterial drugs.
According to experts, this drug increases the effectiveness of the Helicobacter pylori eradication (destruction) regimen. In addition, taking De-Nol is not accompanied by the risk of developing unnecessary adverse reactions, which is also important when using such a serious treatment regimen.
De-Nol
De-Nol ®
(lat.
De-Nol ®
) is a gastroprotective, antiulcer, antibacterial drug.
Composition of the drug De-Nol
Active substance:
bismuth tripotassium dicitrate
(another name is colloidal bismuth subcitrate
or simply
bismuth subcitrate
).
Excipients:
potassium citrate, ammonium citrate, magnesium stearate, corn starch, povidone K30, polacriline potassium, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 6000, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.
Available in the form of creamy-white coated tablets. One De-Nol tablet contains 120 mg of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate.
Pharmacological action of De-Nol
De-Nol has a pronounced enveloping effect. In the acidic environment of the gastrointestinal tract, De-Nol forms a protective film on the surface of the damaged mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, which promotes scarring of ulcers and protects them from the effects of hydrochloric acid and pepsin. In addition, De-Nol stimulates the synthesis of prostaglandin E2, which in turn stimulates the formation of mucus and the secretion of bicarbonates and leads to the formation and accumulation of epidermal growth factor in the damaged area, which also improves the healing of erosions and ulcers.
Indications for taking De-Nol
- stomach and duodenal ulcer
- gastroduodenitis during exacerbation in patients with peptic ulcer
- gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori
How to take De-Nol and dosage
De-Nol is taken half an hour before breakfast, lunch, dinner and bedtime, one tablet, washed down with 1 - 2 sips of water.
The duration of treatment is from 4 to 6 weeks. According to indications - up to 8 weeks. After completion of treatment, a break of 8 weeks is required, during which no medications containing bismuth should be taken. When eradicating Helicobacter pylori
De-Nol is used as part of a ten-day complex therapy with the antibiotics metronidazole and amoxicillin (if the latter is intolerant, with tetracycline). The usual dosage of de-nol is one tablet 4 times a day; metronidazole and amoxicillin are taken together with de-nol, 250 mg each at each dose (tetracycline - 500 mg). You can reduce the number of daily medications you take by half by also doubling the dose of each drug. After completion of treatment according to the eradication scheme, in case of multiple, repeated ulcers or a pronounced decrease in protective forces (for example, with long-term use of steroids), it is recommended to extend the use of De-Nol to 21 days.
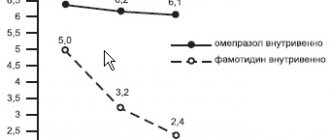
Comparison of De-Nol with other cytoprotectors
At the Russian State Medical University (Yakovenko A.V. et al.), comparative studies of the four main cytoprotectors used in clinical practice were carried out: De-Nol, sucralfate, misoprostol and pentoxifylline.
Cytoprotectors are usually included in complex treatment regimens for the underlying disease, and in some cases are prescribed as monotherapy. It has been shown that De-Nol has the widest range of cytoprotection mechanisms, in particular, De Nol, unlike the other three drugs listed, increases the synthesis of mucus and bicarbonates, increases the content of epidermal growth factor, inhibits NO synthetase and bacterial adhesion. De Nol, unlike sucralfate, improves microcirculation in the mucous membrane, unlike misoprostol and pentoxifylline, has an antioxidant effect, reduces the activity of pepsin, binds bile acids, selectively binds to the proteins of the ulcer bottom and creates a protective layer - a barrier to H+ diffusion, preventing damage to the area of the gastric mucosa lacking a protective epithelial covering. Unlike misoprostol, De-Nol stimulates the synthesis of prostaglandins. The parameter in which De-Nol is somewhat inferior to one of the indicated agents (sucralfate) is the efficiency of binding bile acids. Based on the results of this study at the Russian State Medical University, it was concluded that De-Nol is a preferable drug in comparison with the mentioned cytoprotectors in the treatment of peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis associated with HP, mucositis associated with the use of cytostatics and infectious diarrhea. De-Nol, as well as sucralfate and pentoxifylline, can be the drug of choice for gastropathy caused by alcohol intake and stress ulcers. De-nol, as well as misoprostol, are the best cytoprotectors for gastropathy caused by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. De-Nol is inferior to other cytoprotectors for reflux gastritis and gastropathy caused by taking cytostatics.
De-Nol is not absorbed into the blood from the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, a very small amount of bismuth can be split off from the colloid and enter the blood, which is then excreted in the urine and its concentration in the plasma quickly decreases after the end of treatment. De-Nol is excreted mainly in feces.
De-Nol in the eradication of Helicobacter pylori
De-Nol tends to accumulate inside Helicobacter pylori
, resulting in the destruction of the cytoplasmic membranes of the bacteria and their death.
Therefore, De-Nol is often used in various Helicobacter pylori
. At the same time, De-Nol, unlike other bismuth-containing drugs, in particular bismuth subnitrate and bismuth subsalicylate, is able to dissolve in mucus, which allows bismuth to penetrate under the layer of gastric or duodenal mucus, where the maximum number of bacteria Hp is located. In addition, bismuth contained in de-nol prevents the adhesion of HP to the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract.
According to a number of leading gastroenterologists, the additional inclusion of De-Nol in HP eradication regimens significantly increases the frequency of successful HP eradication without an increase in side effects.
Due to the widespread use of anti-Helicobacter pylori treatment and the frequent use of antibacterial therapy for other infectious diseases, the number of patients with antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori
, which has become an important medical problem.
Low- and medium-cost treatment regimens that include reserve antibacterial agents are attracting increasing attention. In Russia,
a multicenter study was carried out to study treatment regimens for Helicobacter pylori infection based on De-Nol, furazolidone, amoxicillin and clarithromycin and the following results were obtained:
- De-Nol 240 mg, furazolidone 100 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg, all drugs 2 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 71.4%
- De-Nol 240 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg, all drugs 2 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 93.3%
The study showed that anti-Helicobacter therapy, including De-Nol and furazolidone, can quite effectively solve the problem of eradication of Hp strains resistant to metronidazole, and, given its low cost, without large financial costs (Kalinin A.V.).
Comparative studies have been conducted regarding the use of different anti-Helicobacter therapy regimens in pediatrics
.
Data have been obtained that the use of De-Nol and furazolidone in children is effective, safe, and economically justified.
According to the results of economic examination, both in children and adults, the De-Nol + furazolidone + amoxicillin regimen has the greatest clinical and economic effectiveness
When eradicating Helicobacter pylori, monotherapy with De-Nol is not used
.
only
be achieved when using De-Nol as part of a complex regimen of several drugs. "Maastricht-IV" recommends only four-component regimens with bismuth preparations and, in most cases (not always), as second-line regimens (if the first line fails), alternative, etc. (Isakov V.A.).
HP eradication schemes with De-Nol, published by the manufacturer:
- De-Nol 240 mg, 2 times a day for 1 month; metronidazole 400 mg, 3 times a day for 7 days; Flemoxin Solutab 500 mg, 3 times a day for 7 days; eradication - 81%
- De-Nol 120 mg, metronidazole 400 mg, tetracycline 500 mg, all drugs 4 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 89%
- De-Nol 240 mg, metronidazole 400 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, all drugs 2 times a day for 10 days, eradication - 95%
- De-Nol 240 mg, 2 times a day, furazolidone 100 mg, 4 times a day, Flemoxin Solutab 500 mg, 4 times a day, take all drugs for 14 days, eradication - 86%
- De-Nol 240 mg, furazolidone 200 mg, tetracycline 750 mg, all drugs 2 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 85%
- De-Nol 240 mg, furazolidone 100 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, all drugs 2 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 92%
- De-Nol 240 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, Flemoxin Solutab 1000 mg, all drugs taken 2 times a day for 7 days, eradication - 93%
- De-Nol 120 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, tetracycline 250 mg, all drugs taken 4 times a day for 10 days, eradication - 72%
- De-Nol 120 mg, 4 times a day, Flemoxin Solutab 500 mg, 4 times a day, omeprazole 20 mg, 2 times a day, take all drugs for 14 days, eradication - 77%
- De-Nol 120 mg, 4 times a day, clarithromycin 500 mg, 2 times a day, omeprazole 40 mg, 2 times a day, take all drugs for 7 days, eradication - 83%
Note. The Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia recommends slightly different HP eradication schemes (see “Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of acid-dependent and Helicobacter pylori-associated diseases (4th Moscow Agreement) adopted by the X Congress of the NOGR on March 5, 2010”).
Professional medical publications regarding the effectiveness of De-Nol on the gastrointestinal tract
- Yakovenko E.P. Ways to increase the effectiveness of antiulcer therapy. Symposium “Mysteries of gastroduodenal ulcers or how ulcers heal.” 12th Congress of Gastroenterologists of Russia. – M. – 2006.
- Kalinin A.V. Peptic ulcer: from pathogenesis to treatment // Farmateka. – 2002. – No. 9. - With. 64–73.
- Belousova Yu.B., Karpov O.I., Belousov D.Yu., Beketov A.S. Pharmacoeconomics of the use of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate for peptic ulcer disease // Therapeutic archive. – 2007. – No. 2. – T. 79. – p. 1–9.
- Maev I.V. Modern approaches to the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers // Treating Doctor. – 2003. – No. 5. – p. 4–8.
- Potapov A.S., Pakhomovskaya N.L., Dublina E.S. and others. Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of triple eradication therapy for helicobacteriosis in children with the drugs helol, de-nol and flemoxin solutab // Almanac of Clinical Medicine. – 2006. – volume XIV. - With. 87–94.
- Yakovenko A.V., Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko E.P. and others. Cytoprotectors in the treatment of stomach diseases. Optimal approach to drug selection // Experimental and clinical gastroenterology. – 2006. – No. 2. – p.1–4.
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there are subsections “Gastroprotectors, cytoprotectors, hepatoprotectors, esophagoprotectors” and “Diseases of the stomach and duodenum (DPC)”, containing articles for healthcare professionals on relevant topics.
special instructions
- Long-term use of large doses of De-Nol can cause reversible encephalopathy.
- Half an hour before and half an hour after taking De-Nol, it is not recommended to drink any drinks, milk, eat food or antacids.
- Alcoholic drinks are prohibited during De-Nol therapy.
- When treated with De-Nol, black stool is possible.
Side effects:
sometimes nausea, vomiting, increased bowel movements are possible, rarely - skin rash, itching. Taking de-nol often causes a “metallic taste” in the mouth.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
, as well as in case of impaired renal function, De-Nol is not recommended.
In case of overdose
Reversible renal failure may develop, symptoms of which may appear 10 days or later after taking large doses of De-Nol.
Interaction with other drugs:
De-Nol reduces the absorption of tetracycline. When using De-Nol simultaneously with other drugs containing bismuth, the risk of increasing the concentration of bismuth in the blood increases.
According to the pharmacological index, De-Nol belongs to the group “Antacids and adsorbents”. According to ATC - to the group “Antiulcer drugs and drugs for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux” and the code A02BX05 corresponds to it.
Disadvantage
De-Nola is its relatively high price.
Manufacturer:
Astellas Pharma Europe B.V. (Astellas Pharma Europe BV), Netherlands.
Manufacturer's instructions
(pdf): “Instructions for medical use of the drug De-Nol.”
Other medicinal products containing active ingredients
bismuth tripotassium dicitrate
currently* registered in Russia: Vicanol Life, Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate, Vitridinol, Novobismol, Ulkavis, Escape, as well as not registered and not currently sold* in the Russian Federation: Ventrisol, Pilocid, Tribimol.
A Ukrainian-made drug not registered in Russia: Gastro-norm. *As of July 2021
De-Nol has contraindications, side effects and application features; consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Back to section
Is De-Nol an antibiotic?
Despite the fact that the drug is capable of destroying Helicobacter pylori, it does not belong to the group of antibacterial agents. Consequently, its use is not associated with the appearance of such unpleasant side symptoms as diarrhea and mucosal candidiasis.
Bacteria cannot develop resistance to De-Nol due to the peculiarities of its pharmacological action. That is why the inclusion of this drug to destroy the pathogenic bacteria helps to completely get rid of the infection.
Side effects of the drug De-Nol
Taking the drug may be accompanied by the following side effects:
- Nausea and vomiting, frequent bowel movements or constipation.
- On the part of the central nervous system – the development of encephalopathy. This phenomenon is observed only with long-term use of the drug in high doses.
- Skin itching and rashes in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The development of adverse symptoms when taking De-Nol is rare. Usually, if all the rules for taking this medicine are followed, patients do not encounter such problems.
Special instructions for the use of the drug De-nol
Bismuth sulfide formed as a result of taking De-Nol may turn stool black, in which case you should consult a doctor. 30 minutes before and after taking the drug, you must refrain from taking milk and antacids, since the presence of gastric juice is necessary for the formation of a protective layer. Long-term use of bismuth compounds is not recommended due to the occurrence of encephalopathy in rare cases. If you follow the recommended regimen of taking the drug, the risk of this side effect is very low. However, while using De-Nol, it is not recommended to take other drugs containing bismuth. During pregnancy and breastfeeding . Not recommended. Children . De-nol is used in children over 14 years of age. data on De-Nol’s ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles and working with machinery . However, such an effect of the drug is unlikely.
Overdose symptoms
An overdose of De-Nol is accompanied by impaired functional activity of the kidneys. These changes are reversible: after discontinuation of the drug, kidney function is completely normalized.
In case of overdose, saline laxatives and enterosorbents are used. Gastric lavage is also recommended.
In rare cases, if the dose is repeatedly exceeded, renal failure may develop. In this case, renal dysfunction can only be compensated for by hemodialysis.