Thrombophilia is a congenital or acquired pathological condition that is characterized by impaired blood clotting and an increased risk of blood clots. It is distinguished by its duration and sudden complications such as the formation of a blood clot in a vein, its fixation to the wall with the development of inflammatory processes (phlebothrombosis) or blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot (thromboembolism). Such conditions pose a danger to the health and life of the patient and require professional medical care.
At the same time, it is worth noting that thrombophilia cannot always lead to complications in the form of thrombosis or thromboembolism - however, the risk of their occurrence with this pathology increases significantly.
Causes
In recent decades, there has been an increase in the number of patients who suffer from congenital and acquired forms of thrombophilia. Scientists explain this by the following factors:
- deterioration of the environmental situation in the world;
- "population aging;
- failure to seek professional medical help in a timely manner.
At CELT you can get advice from a phlebologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
The division into genetic and acquired thrombophilia is carried out based on the cause of the disease. Thus, genetic thrombophilia is the result of structural features of certain genes that lead to disturbances in the functioning of the blood clotting system. The most common hereditary thrombophilias are:
- polymorphism (Leiden mutation) of blood clotting factor V;
- polymorphism in the prothrombin II blood clotting factor gene;
- protein S deficiency;
- protein C deficiency;
- antithrombin deficiency.
They arise due to:
- increased levels of lipoproteins in the blood;
- lack of antithrombin III;
- lack of prothrombins S and C;
- thalassemia;
- factor V gene mutations;
- prothrombin mutations.
Unlike congenital thrombophilia, acquired forms develop against the background of other diseases, including cancer, as well as when taking certain medications. It is customary to highlight the following reasons:
- long-term venous catheterization;
- heart defects;
- cancerous tumors, the treatment of which involves massive chemotherapy;
- autoimmune diseases;
- dehydration of the body, accompanied by an increase in the number of red blood cells.
Forms and stages of the disease
Experts in the field of phlebology classify the disease into two main categories.
The first category includes thrombophilias provoked by pathological changes in the cellular composition of the blood and its normal rheology. Such violations result from the following processes:
- Blood thickening;
- Change in plasma viscosity;
- Defects in the natural shape of red blood cells.
The listed processes are often caused by exogenous triggers.
The second category is caused by primary disorders of coagulation and hemostasis. It includes congenital pathological conditions caused by a deficiency or excess of coagulation factors.
Thrombophilia can be vascular, hemodynamic and hematogenous.
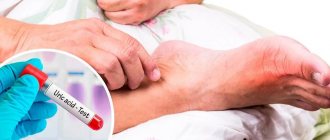
Diagnosis of thrombophilia
Diagnosis of this disease requires laboratory tests. As a rule, testing for the presence of thrombophilia is carried out in the following cases:
- the presence of this disease in relatives;
- an episode of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism at a young age in the absence of conditions that provoke the development of complications;
- relapses (DVT);
- thrombophlebitis of healthy superficial veins;
- 2 or 3 non-consecutive abortions at any stage of pregnancy, fetal loss at a gestational age of more than 20 weeks.
Illness during pregnancy
Hereditary thrombophilia is often diagnosed during pregnancy. The reason for this condition in a woman expecting a child is the appearance of a new additional circle of blood circulation. It is called placental and has its own characteristics. The expectant mother's body begins to feel additional stress. Thrombophilia is associated with a violation of the blood coagulation system and there is a risk of dangerous complications.
As soon as the fertilization of the egg occurs, the body of the expectant mother begins to undergo changes. This also applies to blood. Its coagulability increases. This is due to the fact that in no case should bleeding occur during childbirth, in such a pathological condition as placental abruption or during a miscarriage.
Thrombophilia provokes a high risk of blood clots. If physiological changes (one of them is increased blood clotting) associated with pregnancy are added to this ailment, then there is a great danger to the life of the woman and the fetus.
Pregnant women often suffer from a type of disease called hematogenous. It has an association with antiphospholipid syndrome. It is worth considering that in this case the course of the disease is unpredictable. There is also no exact treatment plan.
Often thrombophilia does not manifest itself in any way. While waiting for a child, the risk of developing the disease increases 6 times.
In early pregnancy, the most dangerous consequence may be a miscarriage. Blood clots may appear in the vessels that lead to the placenta. The fetus does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which leads to hypoxia and developmental delays.
Lack of necessary substances entering the child’s body leads to a complex of morphofunctional disorders, developmental pathologies, placental abruption, miscarriage, and premature birth.
It is impossible to notice the disease before ten weeks of pregnancy. She doesn't show herself at all. There is also no data on its effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy itself in the early stages. Negative signs of the disease rarely appear in the second trimester.
Most often, the risk of complications begins to increase after thirty weeks of pregnancy. The danger is placental abruption.
If the disease does not prevent the child from being born, then labor may begin prematurely. Usually at 35-37 weeks. The birth of a child at this time is the most favorable outcome.
When visiting a doctor and diagnosing thrombophilia, the specialist must tell the expectant mother everything about the disease. Treatment is prescribed immediately.
The course of therapy includes:
- medications;
- special diet;
- physical exercise.
Strictly following all doctor’s recommendations increases the chances of bearing and giving birth to a healthy child.
Although, most likely, the baby will be born prematurely, there is no need to worry. Modern medicine makes it possible to deliver a baby born at an earlier stage. Thrombophilia is dangerous during pregnancy, but it is not a death sentence for expectant mothers.
It is important to know that if you are diagnosed with genetic thrombophilia, you should plan your pregnancy in advance. In this case, the risk of complications becomes less.
If symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is better to prevent a disease than to fight it and its consequences.
Our doctors
Drozdov Sergey Alexandrovich
Cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
47 years of experience
Make an appointment
Malakhov Yuri Stanislavovich
Doctor - cardiovascular surgeon, phlebologist, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Proper nutrition when sick
As with other diseases, thrombophilia requires nutritional adjustments. During illness, an antithrombotic diet is prescribed. You should avoid foods that increase blood viscosity. The following products are prohibited:
- lard, fatty meat and rich broths;
- chocolate and whole milk;
- celery, parsley, spinach and legumes;
- beef liver and hard cheese;
- you will have to forget about coffee, but green tea is ok, but in small quantities;
- fatty and spicy dishes.
Foods that reduce blood clotting are recommended for consumption. We are talking about the following:
- cranberries and viburnum, lingonberries and chokeberries;
- seafood and seaweed;
- dried fruits (dates, figs, dried apricots, prunes and raisins);
- ginger;
- cereal porridges (pearl barley, barley, oatmeal, buckwheat);
- red juices and fruit drinks.
Treatment
Treatment of thrombophilia is prescribed individually with the obligatory participation of a hematologist and directly depends on the factors that led to the onset of this disease. It is aimed at combating thrombosis and treating the underlying disease.
Conservative treatment methods provide an integrated approach, in which special attention is paid to eliminating the cause of the pathology. In addition, a general regimen for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis is used.
This is due to the fact that there is no specific therapy for the treatment of thrombophilia. Treatment is as follows:
- Prescribing a diet that limits the consumption of fatty and fried foods and completely eliminates foods high in cholesterol;
- Taking medications that inhibit platelet aggregation (Aspirin, Curantil), anticoagulants (Warfarin), drugs that have a strengthening effect on vascular walls (Papaverine, Trental);
- The use of traditional medicine: freshly squeezed grape juice, cranberry tea, tincture of Japanese sophora seeds.
Treatment of thrombophilia resulting from a deficiency of coagulation factors and antithrombin III involves the transfusion of large volumes of plasma, which are combined with the introduction of Heparin into the blood. Congenital thrombophilia, which occurs due to a lack of antithrombin III, requires the use of replacement therapy: the introduction of drugs with antithrombin III into the blood three hours after the administration of Heparin. Treatment of mild forms of thrombophilia is carried out by subcutaneous administration of lyophilized plasma and Heparin 4 times a day. Intravenous administration of antithrombin III can achieve good results.
In severe forms of the disease, direct-acting anticoagulants are used, which are combined with fibrinolytic agents. This treatment gives especially good results when the drug is administered at the level of the affected vessel.
Symptoms
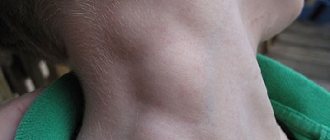
The disease often occurs without any visible signs. Sometimes thrombosis can be diagnosed in the veins located in the lower leg. This disease provokes the appearance of redness, discomfort and swelling. They get rid of the problem with the help of special blood thinning medications. The disease with thrombophilia can be determined using ultrasound or x-ray.
Blood clots can be fatal if they break off and enter the bloodstream leading to vital organs.
The appearance of a blood clot is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- breathing is difficult;
- feet and legs go numb;
- chest pain appears when inhaling;
- rapid heartbeat and heart attacks at an early age;
- coughing up blood;
- frequent miscarriages;
- The most obvious sign of thrombophilia is pain in the area where the blood clot forms, swelling.
Our services in phlebology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Appointment with a cardiovascular surgeon (phlebologist), MD. Malakhova Yu.S. with ultrasound examination (primary) | 4 500 |
| Duplex scanning of the veins of both lower extremities | 6 000 |
| Duplex scanning of the veins of one lower limb | 3 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Folk remedies
A large number of folk recipes will help cope with the disease thrombophilia. Anticoagulants:
- Sophora japonica (tincture). Take 100 g of plant seeds. They are filled with good vodka (500 g) and infused for 2 weeks. Definitely in a dark place. Taken 3 times a day before meals. 10 drops of infusion are diluted in a quarter glass of water.
- Grape juice received good recommendations. It reduces platelet activity when consumed daily.
- Raspberries. Infusions and decoctions, jams and compotes from berries and plant leaves are an excellent preventive and therapeutic agent.
- Meadowsweet (infusion). Two teaspoons of herb are poured into a glass of boiling water. The broth is filtered. Drink a third of the glass before meals.
- Garlic is one of the unique plants that can thin the blood. That's why it is recommended to eat 2-3 cloves a day.
- Collection. It includes 20 g of St. John's wort and string; 10 g each of licorice root, coriander seeds, chamomile, marsh grass, toadflax, sweet clover. Everything is mixed, 0.5 liters of boiling water is poured. The decoction is infused for 2 hours. Strained. Use 2 times a day an hour after meals. The daily norm is 20 ml.
It is strictly forbidden to use plants that cause blood clotting - nettle, water pepper.
Before using traditional medicine recipes, consultation with a doctor is required. Many products have contraindications.