In most cases, the cause of deterioration in health is enlarged adenoids (nasopharyngeal tonsils), which consist of lymphatic tissue and help the immune system protect the child’s body from various types of infections. In inflammatory diseases, they swell and increase in size, which causes obvious physical discomfort and complicates the functioning of the respiratory system. Surgical removal of adenoids in children is carried out if conservative treatment does not produce the desired result or a severe stage of hypertrophy is diagnosed.
What are adenoids?
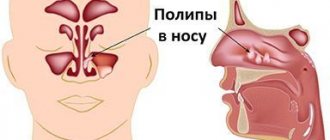
Strictly speaking, the adenoids are the pharyngeal tonsil, which, like other numerous lymphoid formations, is part of the so-called “lymphopharyngeal ring”.
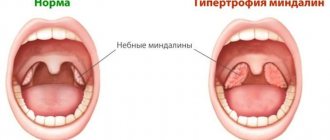
It is located in the nasopharynx, every child and even an adult has it. However, in childhood, it takes a greater part in ensuring general and local immunity, and, apparently, this is why problems with adenoids arise most often between the ages of 2 and 10 years. After 13 years of age, their role in pathological processes decreases sharply, but before this age they manage to cause a lot of trouble for many children. The essence of these troubles is that the adenoids can increase in size and interfere with nasal breathing. Depending on the size, there are 3 degrees of hypertrophy (growth). First degree – the tissue size is minimal and there is no breathing disorder. This is considered normal and does not require any treatment. The second degree can be considered the norm only conditionally, if this does not lead to the appearance of complaints and symptoms. The third degree is an absolute pathology and requires mandatory measures aimed at restoring nasal breathing.
Enlarged adenoids
Adenoids of normal size
Complications
This operation is usually well tolerated with no adverse effects. However, removal of the pharyngeal tonsil can still cause the following complications:
- allergic reaction to the anesthetic used;
- bleeding requiring repeated intervention, the use of general and local hemostatic procedures;
- infection of a postoperative wound with the development of purulent foci in the lymph nodes, retropharyngeal space, mediastinum; in severe cases - sepsis;
- inhalation of removed tissues with the development of asphyxia (suffocation) or aspiration pneumonia;
- injury to the soft palate or root of the tongue, which leads to changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and heavy bleeding.
To avoid such adverse effects, the operation should be done only in a well-equipped clinic by an experienced surgeon.
What does adenoid hypertrophy lead to?
During childhood, growth of the facial skeleton occurs. Long-term (more than 3 months) difficult nasal breathing not only greatly complicates life, but also leads to serious problems. The shape and structure of the face changes, it becomes elongated downwards, the lower jaw moves back, an incorrect bite is formed, the tongue is visible through the slightly open mouth, the child becomes unlike the parents. These changes, unfortunately, are irreversible. A nasal tone of voice appears, snoring during sleep, hearing loss, fatigue, weakness, frequent runny noses and colds. Changes in the composition of the blood, curvature of the spine, enuresis, nervous tics, impaired renal function and other problems may occur much less frequently. Moreover, usually these signs appear gradually, and parents do not notice them immediately, but only when they become pronounced.
Degrees of enlargement of adenoids
Current classification according to the degree of enlargement of the adenoids (and it determines the indications for medical or surgical treatment):
Classification of adenoids according to the degree of enlargement
| I degree | II degree | III degree | |
| Adenoid size | The adenoids cover the upper third of the vomer*. | The adenoids are medium in size, covering two-thirds of the vomer. | The adenoids are large, cover the entire or almost the entire vomer, and completely cover the lumen of the nasopharynx. |
| Difficulty breathing | In this case, breathing through the nose may be free or slightly difficult, more often during sleep. | Breathing through the nose is quite difficult. | Breathing through the nose is severely difficult, the child constantly breathes through his mouth, his lips are dry, covered with cracks and crusts. |
| Method of treatment | A course of conservative treatment is indicated. We talk about adenotomy if the child is often sick, complications occur, for example, recurring otitis media. | Both conservative and surgical treatment are possible. Indications for surgery are determined individually, the main criterion being complications and the incidence of illness in the child. If the child does not receive any treatment at all, the adenoid may enlarge. | The adenoid must be removed. If the child is not operated on in time, an abnormal bite and an elongated “adenoid face” will gradually form, which is subsequently difficult to correct. Even long-term treatment by an orthodontist does not always completely restore the correct facial skeleton. |
| *The vomer is a small plate made from bone and placed vertically. Together with the ethmoid bone, it forms the bony septum of the nose. | |||
When should you be wary?
You should be wary if your child:
- often or constantly with an open mouth;
- wheezes or snores in sleep;
- nasally and speaks unintelligibly;
- often suffers from acute respiratory infections, suffered from pharyngitis, bronchitis, tracheitis, inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media), sinusitis and other colds;
- asks again when he is addressed (sometimes parents perceive this as inattention, become irritated and are unaware of hearing loss);
- gets tired quickly, begins to lag behind peers in development and learning.
Any of these signs should be a reason to contact an ENT doctor.
Diagnosis of enlarged adenoids
Hypertrophied tissues of the nasopharyngeal tonsils cannot be seen with the naked eye, so special techniques are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- radiography;
- endoscopy of the nasopharynx;
- tympanometry – assessment of the condition of the eardrum and middle ear;
- examination by an ENT doctor using special instruments.
Particular attention is paid to children with frequent relapses of adenoiditis. Based on the clinical manifestations of the disease and data obtained during the examination, the doctor decides on the need for surgical intervention.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Enlarged adenoids. Endoscopic picture
To establish a diagnosis, a simple examination is sometimes sufficient, but often it is necessary to “see” the adenoids. It is best to look directly into the nasopharynx using an endoscope. However, this procedure is possible in children only from 5-7 years of age, when the child understands how to behave when there is an instrument deep in the nasal cavity. At an earlier age, endoscopy is also possible using 2-3 minutes of superficial inhalation anesthesia.
A more accessible method is x-ray examination. The advantage of this method is that everyone can view the image, including parents, and not just one doctor. Therefore, this method is considered the most objective. One of the X-ray diagnostic methods is computed tomography. But using it only to examine the nasopharynx is absolutely irrational and expensive. I would like to warn parents about a very ancient method of examining the nasopharynx, the so-called “finger”, which was used in the “pre-radiological” era and which doctors sometimes use now. It involves feeling the adenoids with a finger bent and placed behind the soft palate through the mouth. Look at the location of the nasopharynx in the diagram, and you can understand what the unfortunate child experiences. We consider this an inhumane, psychologically traumatic, highly subjective, archaic and unacceptable method. Don't let your children get hurt like that.
Methods for diagnosing adenoids
Classic methods for diagnosing hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil are digital examination of the nasopharynx and examination of the posterior parts of the nasal cavity. But these procedures are difficult and provide little information, especially in the case of children. The most modern diagnostic method is endoscopic examination - a method of examining the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract with an endoscope. The advantage of endoscopy is that it is painless and safe; the doctor gets a complete picture of the size of the nasopharynx, the degree of enlargement of the adenoid tissue and the condition of the mouths of the auditory tubes. Together, these data make it possible to determine a treatment method and diagnose the disease at an early stage.
On the issue of the dangers of X-ray irradiation.
It all depends on the dose. The natural background radiation on the surface of our planet is not dangerous to health. In the city this background is somewhat higher. The total average annual dose in Moscow is 3 mSv per year, the permissible dose is 15 mSv. A single irradiation, subject to accepted standards for any diagnostic studies, is absolutely safe. “Dose accumulation” during repeated irradiation is dangerous. And this needs to be monitored. That is why in our clinic you cannot do an X-ray examination at your own request. Technological progress makes it possible to reduce the required dose with each new generation of devices. With tomography, the radiation dose ranges from 1 to 7 mSv, and with radiography of the nasopharynx using modern equipment – 0.8-1 mSv. Thus, you gain several times more in the city.
How does it manifest itself?
The main clinical signs of adenoids include:
- Impaired (difficulty) nasal breathing, almost constant nasal congestion. This leads to a change in voice timbre and predisposes to headaches, fatigue, and lack of attention.
- Recurrent, prolonged nasal discharge of a mucous or mucopurulent nature. They may be associated with chronic adenoiditis and chronic rhinosinusitis.
- Cough caused by irritation of the back wall of the pharynx by flowing secretions due to adenoiditis.
- Hearing impairment and predisposition to otitis media, which is associated with deterioration of ventilation of the auditory (Eustachian) tube.
- Snoring, and sometimes obstructive sleep apnea (short-term stops in breathing). Adenoid vegetations deform and narrow the upper respiratory tract, and the resulting turbulence of the air flow provokes excessive vibration of the tissues of the soft palate.
- Violation of sound pronunciation, which is caused by a change in the resonating properties of the nasopharynx.
- Formation of a characteristic “adenoid” deformation of the face (with long-term and pronounced adenoid vegetations).
Usually, the symptoms of chronic adenoiditis initially dominate. They intensify with repeated episodes of respiratory infections, complemented by signs of partial obstruction of the nasopharynx due to gradually increasing adenoid vegetations. Most children with adenoids belong to the group of frequently ill people; ARVI in them is often complicated by sinusitis and otitis and takes a protracted course.
How to treat adenoids?
There are two possible ways to treat adenoid hypertrophy: conservative and surgical. There are many conservative methods. They all have their advantages and disadvantages. We quite widely use homeopathy, laser magnetic therapy, and traditional methods of treatment. The main thing to be guided by when choosing a method is to understand the difference between cause and effect. There is a misconception that the cause of numerous complaints and problems is large adenoids. In fact, it's the other way around. The child is constantly sick not because he has large adenoids, but they are so large because he is sick all the time. Knowing the causes of inflammation, you can select the necessary therapy and in most cases achieve complete recovery and reduction of adenoids to normal.
Surgery to remove adenoids is not a tragedy
Otolaryngologist for adults and children
Manevich
Igor Semenovich
25 years of experience
Otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, member of the European Rhinologic Society
Make an appointment
In my practice, I have encountered the fact that many parents refuse to have their children undergo surgery to remove adenoids, because it is associated with many difficulties: blood vessels begin to bleed, the child experiences pain. And this is understandable. But there is no need to be afraid if the operation is performed under anesthesia. Otorhinolaryngologist Igor Semenovich Manevich talks about what adenoids are and what their functions are.
About difficulties in feeding children
The little man has this peculiarity: he cannot suckle, cannot eat, when his nose is not breathing. When a mother brings her child to an appointment, the first thing the ENT doctor asks is how the child is gaining weight. This may seem strange for a mother, but in fact this is the most important thing for us. If the child eats well and gains weight within normal limits, then there is absolutely no reason for concern, even if it seems to the mother that he is making some sounds or sniffling. It happens that a child sucks poorly at the breast due to swelling of the nasal mucosa. This can be corrected with drops and sprays, but it is impossible to give specific advice, you need to look at the child every time, and each time the doctor must prescribe treatment individually. There are situations when children cannot breathe from birth, from the first days. This is due to the fact that due to the anatomical feature, the nose is blocked and the choanae are blocked. The choanae are the 2 “holes” that end the nose (like the two nostrils at the front). Congenital fusion (atresia) occurs when the choana is covered with film or bone. If the child is not gaining weight and is not breathing, then the choanae should be examined. This requires hospitalization and anesthesia. We look with an endoscope to see if the choanae are really blocked. If yes, then we immediately perform an operation and free them. Then you have to wait for them to heal. This is a long process.
About the difference between snoring and snoring
Snoring is not a pathology, it is a soft sound that is pleasant to the mother’s ears. And snoring sounds harsher and is produced by deeper structures of the nose and nasopharynx; the mouth is usually open, and this is always worse. In other words, if a child sniffles, then this is normal, but snoring is a reason to worry.
In children over 1 year of age, snoring and snoring are associated with adenoid problems. If a child snores comfortably in his sleep, then this is good; he can roll over to the other side and stop snoring. But if in his sleep he snores heavily or breathes through his mouth, walks with his mouth open during the day and also often catches a cold, it is noted that he hears worse, this means that adenoids have grown in his nasopharynx and have blocked his nasal breathing and ears from the inside from the outside eustachian tubes. In this case, it is also important not to miss the moment when adenoids can be treated with medication: reducing their size. Doctors divide adenoids into 3, and some into 4 stages. If the first is considered practically normal, then with the second the airways are blocked by 50%. This can be treated with medication, homeopathy, and physiotherapy. The third stage can only be treated surgically. But in this case, we are not talking about a complete cure of adenoids, but about their reduction. They cannot and should not be completely cured.
About adenoids and their functions
Adenoids are useful tissue, special additional protection for children. Adults do not have adenoids. During puberty, at the age of 14–15, they begin to decrease, and by the age of 18 they disappear completely. Normal adenoids (grade zero) are a thin, neat strip of tissue behind the nose in the middle of the skull. If the stripe is slightly wider, this is grade 1, which is also normal. The second degree is when, instead of a strip of tissue, a lump grows that half covers the back of the nose. If the adenoids cover 2/3 of the nose and the child breathes through a narrow slit, then this is considered grade 3. The fourth degree is extremely rare, when the adenoids completely block the nose. At stages 2 and 3, the adenoids begin to block the inside of the ears. The mother is required to notice the problem in time and consult a doctor and try to solve it with medication. The meaning and purpose of treatment is to reduce the size of the adenoids.
If a child, for example in kindergarten, catches an infection, he begins to develop adenoiditis - the adenoids become inflamed, swollen and thereby localize the infection, trying not to let it pass deeper into the bronchi, lungs, sinuses, ears. But when they constantly experience attacks from viruses, they themselves become ill, grow, swell, then problems begin, and instead of benefit they begin to cause harm.
It is very important not to miss the moment when this process can be reversed. There are various methods for this: homeopathic, physiotherapy, rinsing, sprays. True, we do not always win - according to statistics, every 3rd modern child has to undergo adenotomy surgery.
About the myths associated with the operation
Surgery to remove adenoids is not a tragedy. Sometimes parents, instead of maximizing the child’s quality of life so that he can breathe well, try to avoid surgery at all costs. Such parents are subject to the stereotype that there is nothing superfluous in a person, that nothing can be cut out, since it is needed for something. But the operation actually does not contradict this theory at all. This huge lump that has grown in the child’s nasopharynx and prevents him from breathing is diseased tissue. During the operation, we do not remove this lump completely, but cut it right to the root, returning the adenoids to the state provided by nature. As a result, the child breathes well.
The second thing that parents are afraid of is the “pulling out” of the adenoids. In our country, in some clinics, adenoids are still removed without anesthesia, “for profit.” An anesthetic is dripped into the nose and the child is tied up. The operation to trim the adenoids is considered one of the bloodiest, since they are densely supplied with vessels - this is their anatomical feature. When they are removed, all these vessels bleed. The danger is that with this method the doctor removes the adenoids blindly. He inserts the instrument by touch, cuts something off... It looks like medieval torture, and even the operation becomes very poor quality. The doctor is naturally afraid to cut off too much and, as a rule, cuts off just a little. There is a lot of blood, a lot of stress, little effect. In this case, the doctor cannot properly remove the adenoids, so after some time they grow back.
There are children whose adenoids can grow, even if the operation was performed efficiently. They have a genetic predisposition to excessive growth of this tissue, and 5–6 years after the operation the adenoids may become troublesome again. But the percentage of such children is very small. Even if a particular child falls into this percentage, he still lives his life to the fullest during these 5–6 years. Therefore, if the doctor says that the operation must be done, then it must be done.
About lasers and anesthesia
Now in all civilized countries, surgery to remove adenoids is performed under general anesthesia. The child is completely asleep, does not feel anything when he wakes up in the ward - everything has already been done. Of course, his throat hurts, but his mother is nearby, patting him on the head. The quality of such an operation is higher, because when the child is sleeping, we use special endoscopes to penetrate the posterior parts of the nose, and on the monitor screen we see the real picture: what we are removing, which vessels are bleeding. Civilized, bloodless and, most importantly, high quality.
Each case is individual, the laser is used somewhere to a lesser extent, somewhere to a greater extent. If the adenoid lump is very large, then there is no point in burning it out with a laser. It is carefully cut off with a sharp adenotomy, and the vessels are “sealed” with a laser. Often mothers are afraid of anesthesia and believe that it is harmful. This myth is supported by my colleagues, doctors, people of the old formation. Anesthesia is actually not harmful. There are special pediatric anesthesiologists who select dosages, medications, and administer anesthesia. In no country in the world does the question arise whether or not to do it without anesthesia. Anesthesia is definitely necessary: it helps to perform the operation efficiently. Usually operations are performed on children from 3 years of age, but in my practice there were 2 operations on six-month-old children.
About the operation
The operation is called adenotomy, sometimes adenotonsillotomy, when the tonsils are also cut off. The duration of the operation is approximately 20–30 minutes. The recovery period is 5–7 days and a gentle regime. But many older ENT doctors say: “The adenoids are already large, but the child is still small. Let’s wait until he’s 6-7 years old and remove everything for him before school.” They say this because the clinic has poor technical equipment, and these doctors cannot perform operations under anesthesia, as is the norm all over the world. But these 3–4 years can greatly affect the child; for example, he may lose his hearing.
About prevention
The mother should bring the child to an ENT doctor every year for examination. But it may happen that the adenoids grow in 2–3 months. Here the mother should be alerted to snoring and sleeping with her mouth open. A common situation: a child has had a cold, the pediatrician cured him, but the mother sees that the child is breathing poorly through his nose. This is a reason to bring the baby to an ENT specialist, examine them for adenoids, establish an accurate diagnosis and degree, and carry out treatment. Pediatric dentists and orthodontists help us here. Mothers bring to them children who have malocclusion, and they most often do not install braces and plates before examining them for adenoids. Because if a child has them, then they may be the real cause of improper formation of the jaw and bite. Therefore, orthodontic treatment will be pointless without solving the underlying problem.
The mother should also be alarmed that the child’s hearing has become worse, she asks again. The cause may be either banal wax plugs or ears blocked by adenoids.
You should pay close attention to the child’s illnesses - 2-3 prolonged infections lead to the fact that the adenoids are constantly inflamed. If experienced ENT doctors see that the adenoids in a frequently ill child are not amenable to treatment and are progressing, then they suggest that parents do not take the child to kindergarten for three months, where his condition only worsens. The immune system of a little person changes every month. And maybe at some point it is not adapted to infectious attacks, so if you continue to live in the same mode, the immune system will not harden. Most likely, the result of this stupid principle will be that, as an adult, such a person will often get sick, because in childhood he was taken to the garden when he caught a cold. We need to let the immune system recover, grow, and become more mature.
Material prepared by the Med-Info portal
When is surgery needed?
Surgical removal should be performed only if there are clear indications, which depend, first of all, on the degree of enlargement of the adenoids. This is the main condition, but not the only one. Under certain conditions and with the second degree of hypertrophy, such indications may occur. The decision to operate must be made by an experienced surgeon, and the parents must give their consent if they do not doubt the doctor’s correctness. It is always possible to obtain the opinion of several specialists who may or may not advise surgical treatment. So if in doubt, don't waste your time. And remember, if there is no positive dynamics within 3 months of conservative treatment, you need to change either the treatment methods or the doctor.
Types of operations
Adenoidectomy in children is performed in several ways:
- By radio waves. Radio wave exposure allows excision of adenoids without loss of blood quickly and painlessly;
- Laser therapy. The most effective method of adenoidectomy, in which the scalpel is replaced with a laser beam;
- Endoscopy. The endoscope allows the surgeon to fully control the surgical process. The technique can be combined with laser therapy and tissue excision using radio waves;
- Cold plasma method. During the procedure, adenoids are destroyed and removed with cold plasma, which makes it possible to quickly and painlessly eliminate their growths.
When choosing a clinic for adenotomy, parents should pay attention to the technical equipment of the ENT office and consult with a specialist to determine the optimal tactics for the operation.
Why is anesthesia needed during surgery?
Adenotomy
- Cost: 50,000 - 80,000 rubles.
More details
The answer to this question is very simple - because in the 21st century it is unacceptable to do otherwise in a civilized country. Now an explanation for those who still think it can be done differently. Firstly, neither lubrication nor spraying of painkillers onto the nasal mucosa provides the main thing - complete anesthesia. During surgery under local anesthesia, the child is always in pain. Secondly, “being present” at one’s operation itself is unacceptable. People who have undergone such an adenotomy remember it all their lives. The sight of blood and pain in a child can cause nothing but horror. The psycho-emotional trauma in this case is so great that it can cause mental and neurological disorders. It would never occur to anyone to perform surgery on the abdominal organs without anesthesia. Thirdly, pain relief affects the quality of the operation. Modern methods of removing adenoids require that the patient does not interfere with the surgeon’s very delicate work. Fourth, all vital functions of the patient must be continuously and carefully monitored. If anyone thinks that there are no problems with local “pain relief,” then he is deeply mistaken. An anesthesiologist-resuscitator has great technical capabilities and experience in this field; he is best able to help the child. Only under such conditions can the surgeon be calm about the patient’s life, can perform the operation correctly, stop the bleeding, etc. This is very important, because unremoved pieces of adenoid tissue are the cause of relapses. Properly selected and correctly performed general anesthesia does not leave any consequences.
Methods of conservative treatment of adenoids
The adenoid is an organ of the immune system. Its tissue contains cells that produce antibodies to pathogens. If conservative treatment is successful, this protective barrier is completely preserved. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed, since adenoiditis (inflammation of adenoid tissue) occurs primarily due to exposure to pathogenic microflora. To remove bacteria from the mucous membrane of the nose and nasopharynx, courses of nasal rinsing are carried out using a vacuum pump. Physiotherapy procedures, such as CUV tube, laser and magnetic devices, quickly relieve inflammation, improve blood circulation and local immunity. In the treatment of adenoids, not only an otolaryngologist, but also an allergist-immunologist is involved; he prescribes general tonic drugs that stimulate the body’s defenses in order to reduce the number of acute respiratory infections. But the effectiveness of conservative treatment methods is about 50% and there remains a risk of repeated exacerbations when faced with an infection, which means that symptoms may recur.
How is adenoid removal done in children?
The technique for removing adenoid tissue (adenotomy) remained unchanged for a long time and consisted of scraping the nasopharynx with a special curette inserted through the mouth. It is clear that the quality of the operation with such a “blind, touch” method depends on many factors: on the child’s behavior, on the experience of the surgeon and his dexterity, on the particular location of the adenoids and the structure of the nasopharynx. The most common complications were bleeding with the need for prolonged tamponade, relapses due to unremoved tissue areas, and neurotic disorders due to psychological trauma. A very rare, but extremely dangerous complication was the entry of pieces of tissue into the lower respiratory tract during surgery. The emergence of special methods of general anesthesia in the second half of the last century made it possible to completely eliminate such a danger. And the use of special optics in the late 80s made it possible to perform this operation under vision control and classify it as “aesthetic surgery.” For visualization, various types of endoscopes, a surgical microscope, and mirror optics are used. Different surgical instruments can be used to directly remove tissue, depending on the specific situation. In certain situations, you can use a traditional adenotome, a microdebrider, special forceps, and even a plasma knife. The more different instruments a surgeon has, the more convenient it is to solve various problems, but the choice of instruments always remains his.
Indications for adenoid removal
An increase in adenoid vegetations forms a chronic focus of infection, reduces immunity, and disrupts the functioning of the auditory tubes. These changes in the body contribute to the indication for adenoid removal:
- ARVI and acute respiratory infections. An obstruction in the form of adenoids appears in the nasal cavity, which impedes the outflow of mucus. Mucus protects us from viruses, but when an obstacle arises, favorable conditions are created in the nasal cavity for the development of infections and inflammatory processes.
- Hearing impairment. The adenoid closes the opening of the eustachian tube, preventing the free passage of air into the middle ear. The eardrum loses its mobility, which is negatively reflected in the auditory sensation.
- Chronic inflammation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil (chronic adenoiditis). Inflamed adenoid vegetations are a good environment for infection to attack. Bacteria and viruses form in the nasopharyngeal tonsil, causing chronic adenoiditis, accompanied by a constant runny nose.
- Multiple otitis media. The growth of the nasopharyngeal tonsil disrupts the function of the middle ear, and favorable conditions are created for the spread and development of infections.
- Respiratory tract diseases - pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis. With an increase in lymphoid tissue, chronic inflammation develops. Due to the growth, mucus and pus are constantly formed, flowing into the respiratory system. In case of contact with the mucous membrane, they cause inflammatory processes that lead to infectious diseases of the respiratory tract.
- Adenoid cough. This occurs due to the stimulation of nerve endings located in the nasopharynx and on the back wall of the pharynx. Most often, doctors associate a patient’s cough with colds and flu, but the patient does not have any bronchial dysfunction, in which case the cough may be a symptom of adenoids. When treating the adenoid, the cough goes away.
- Bronchitis, pneumonia
- Speech disorders
- Retarded physical development
- Neurological disorders – headaches, enuresis, convulsions
- Malocclusion with the formation of an “adenoid face”
- Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment
How is adenotomy performed in our clinic?
- Only under general anesthesia. In our clinic we have been performing this operation for over 20 years. During this time, more than 6 thousand operations were performed.
- Only under visual control. We have been using endoscopic technology since 2001.
- The day surgical hospital, which is part of the multidisciplinary private clinic CELT, allows us to use all its capabilities. The organization of our work involves staying in the clinic during the day, but if necessary, the stay can be extended.
- The child is in the clinic with his parents.
Anesthesia for adenoid removal
Local anesthesia
In children over 7 years of age, adenotomy under local anesthesia is possible. Before the operation, a sedative is administered intramuscularly to the child, an anesthetic solution (10% lidocaine solution) is sprayed into the nasopharynx, and then a less concentrated anesthetic solution (2% lidocaine or ultracaine) is injected into the adenoid tissue to enhance the anesthesia effect. During the operation, the child is conscious and perceives everything that is happening around.
General anesthesia (anesthesia)
In children under 7 years of age, adenotomy is performed under general anesthesia (anesthesia), so the intervention takes place without pain and, which is especially important for the child, without psychological stress. The clinic uses drugs that belong to a high safety class, they are non-toxic, do not cause such complications, so anesthesia is easily tolerated even in childhood and feels similar to normal sleep.
In the photo, an anesthesia device from the German company Drager is used in the clinic.
Doctors anesthesiologists
The clinic employs highly qualified anesthesiologists, including specialists from the Children's Clinical Hospital named after. N.F. Filatov, who have academic degrees of candidates and doctors of medical sciences, many years of unique work experience. Our specialists use an anesthetic apparatus from the German company Drager and the latest generation of medicines. All this allows removal under general anesthesia (anesthesia) that is safe for the patient’s health, with rapid recovery in the postoperative period.
Anesthetics used
In their work, anesthesiologists use the drugs Sevoran, Diprivan, Esmeron, Enfluron, Isoflurane, Dormicum and others. The choice of a specific drug is at the discretion of the anesthesiologist and depends on each specific case, test results and other factors.
What happens on the day of surgery?
On the appointed day, you come to the day hospital at the agreed time. On the day of the operation, we strongly recommend giving a light breakfast at home in liquid form in a volume of 100-150 ml (yogurt, kefir, milk, very thin porridge or at least sweet tea). The surgeon examines the patient, checks tests, talks with the parents and decides on the possibility of performing the operation. The patient is asked to drink a soothing mixture and wait 20-30 minutes. Then he is invited to the operating room, where, while lying on the operating table, a breathing mask is applied to his face, and after 10-15 seconds the child falls asleep. All operations are carried out with mandatory monitoring of respiratory and cardiac activity. After the patient has fallen asleep, a catheter is inserted into the vein to administer the necessary medications. Removal of adenoids is carried out under visual control using special optics and an endoscope. The awakening occurs in the ward, where the little patient immediately sees his parents. After the operation, we monitor the child for 4-5 hours. If his condition does not cause concern, then the doctor will let you go home. The postoperative period lasts 7-10 days and requires special care for the patient at home. Upon discharge, you receive detailed instructions and the surgeon's mobile phone number, where you can contact the doctor 24 hours a day.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
The postoperative period passes quite quickly; the patient is discharged the next day after the procedure, and rehabilitation occurs at home.
In the first few days after the operation, some unpleasant phenomena may be observed, which, with proper control, will soon go away:
- nausea, dizziness and weakness after general anesthesia;
- vomiting with dark clots of coagulated blood due to slight bleeding during tissue excision;
- slightly elevated temperature as a reaction to surgery;
- breathing problems due to natural post-operative tissue swelling.
In the first days after adenoidectomy, the child should eat mainly liquid food; he should not play outdoor games, run or visit crowded places.
The child will need rest for several days after the operation and should be excused from school for approximately 10 days. This is necessary in order to reduce the risk of infection.
Keep your child away from people with coughs and colds, and away from smoke and air pollution.
Ice cream after surgery will not bring any benefit, but there is no need to limit the child from it - cold will help reduce swelling and relieve sore throat.
Important! These symptoms usually go away on their own, but if the temperature rises above 39° and purulent discharge appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Teach your child to breathe not only through the mouth. This will help reduce the risk of new respiratory diseases. Talk to your doctor about what exercises are best for this.
What is needed for elective surgery?
To remove adenoids or tonsils, the following conditions are necessary:
- consultation with an otolaryngologist who will perform the operation;
- do not get sick for a month;
- Avoid childhood infections for three months (measles, chicken pox, scarlet fever, rubella, mumps, whooping cough).
Documents required for hospitalization:
- general (clinical) blood test;
- blood test for HIV, RW, HBsAg, HCV;
- blood test for group, Rh factor and antibodies to Rh factor with phenotyping;
- general (clinical) urine analysis;
- certificate from the dentist about oral sanitation;
- conclusion of a pediatrician (and other specialists in the presence of diseases) about the absence of contraindications to surgery.
coagulogram (prothrombin time, aPTT, thrombin time, fibrinogen, antithrombin III) or hemosyndrome (platelets, blood clotting time, bleeding time);
All necessary tests can be performed in our clinic.
Contraindications to adenotomy
The operation is not performed on children under 2 years of age, except in emergency situations. General contraindications to adenotomy are:
- ARVI, influenza and other acute infections;
- exacerbation of allergies;
- blood clotting disorder;
- cleft lip and palate;
- malignant tumors of any location;
- intolerance to drugs for pain relief or anesthesia;
- concomitant pathologies (heart malformations) in specialized centers;
- anomalies of nasopharyngeal vessels.
A temporary ban may be the recent performance of other surgical interventions. Preventive vaccinations are also a reason to postpone surgery. It is recommended to wait at least 1-2 months after vaccination.
What if the tonsils are still enlarged?
Sometimes, along with the adenoids, the palatine tonsils, which are popularly called “tonsils,” grow. They are clearly visible when examining the pharynx. Unfortunately, in this situation there may be indications for additional surgical intervention. If both the tonsils and adenoids are enlarged, it is advisable to solve both of these problems at the same time, i.e. during one operation, remove the adenoids and partially remove the tonsils (to a physiologically normal size). In our clinic, this operation is performed using a bloodless technique, using radiosurgical instruments.
Recommendations for maintaining health after adenoid removal
After surgery, restorative and restorative therapy is necessary to prevent relapse. General hardening of the body, breathing exercises, as well as treatment and observation by an allergist-immunologist, especially when it comes to children with concomitant diseases such as atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis. Normalizing the functioning of the immune system is very important - by increasing resistance to infections and colds, the likelihood of lymphoid tissue proliferation decreases.
What kind of rehabilitation is needed after surgery?
After surgery, the child needs special care. He should not be allowed out of the house and left alone.
Mode. On the first day - strict bed rest, and in the next 7-10 days - at home. For at least 2 weeks, it is necessary to exclude any physical activity, etc. For a week, the child should not take a hot bath or undergo any thermal procedures (inhalations, compresses, warming).
Diet. Feed the child regular, non-rough food, excluding hot, very cold, spicy, salty, and sour foods. The duration of such a diet is from 3 to 10 days, depending on the doctor’s instructions.
Staying in hospital
After removal of adenoid vegetations, doctors recommend staying in a hospital under the supervision of an on-duty specialist. Usually this takes no more than a day. The advantages of being in a hospital are that the risk of complications is reduced and the best post-operative recovery is guaranteed.
In the photo, a ward in the hospital of the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic.
After surgery, physical activity should be avoided for one month. The child should not be bathed in hot water for three days. It is important to maintain proper nutrition. It is better to avoid exposure to open sun and stuffy rooms.
Treatment results
Nasal breathing improves, as a rule, immediately after surgery, hearing is often immediately restored, and the mouth closes. With very large adenoids, after surgery the child may develop a nasal tone, which quickly disappears. The final effect of the operation can be assessed after a month. After it becomes easier for the child to breathe, and therefore to live, snoring, oxygen starvation and endless colds will disappear, appetite and mood will improve, and a feeling of joy and endless energy will appear.
Where to go?
If a child shows signs of adenoids, consultation and treatment with an ENT doctor is necessary. If necessary, surgical intervention is prescribed. Our clinic invites residents of Moscow and the regions to contact the paid services department for treatment. The price for adenoid removal is 16,000 rubles, excluding anesthesia and the cost of hospital stay.
In our clinic, in addition to the traditional one, laser adenotomy is performed using a holmium laser (Ho:YAG) with a radiation power of 4.8 W (energy - 0.6 J, frequency - 8.0 Hz). This modern technique is accompanied by a low risk of complications, absence of bleeding and pain.
You should not postpone the removal of adenoids, since in the future the disease will lead to slower growth and mental development, deformation of facial features and other irreversible changes. After surgery, most children experience better colds, less frequent otitis media, and normal breathing through the nose.
How much does it cost to remove adenoids in children at CELT?
The cost of an operation to remove adenoids in a child at the CELT clinic costs from 45,000 to 75,000 rubles, depending on the category of complexity. It is important for the patient’s parents to know that in the price list we always show the full financial costs, and not just the cost of the surgical intervention itself.
Make your main choice! If after removal of the adenoids there is no recovery, the child breathes poorly through the nose, and continues to get sick, it means that the cause of the inflammation remains. To prevent this from happening, the most important thing is to find an experienced doctor and a good clinic for your child. We hope this article will help you avoid mistakes. About all the advantages of adenoid removal at the Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy, read “Endoscopic removal of adenoids. Why choose us?
Contraindications
In addition to age restrictions, there are a number of other contraindications for adenoid removal:
- malignant neoplasms of any location;
- exacerbation of other chronic diseases;
- infections of any etiology – influenza, chickenpox and others;
- decreased blood clotting rates;
- some anatomical features of the structure of blood vessels in the nasopharynx;
- recently received vaccinations.
The decision on when to perform an adenoidectomy is made by the doctor, taking into account all possible risks and the likelihood of complications.
Endoscopic adenotomy
Endoscopic adenotomy is currently the best method of surgical treatment of adenoids. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 10-20 minutes. Thanks to the high technical characteristics and wide capabilities of endoscopic equipment, the surgeon removes hypertrophied adenoids with precision without damaging healthy tissue. Due to minimal trauma, there is no long rehabilitation period.
Endoscopic operations are easily tolerated by children. Adenoid vegetations may reappear and must be removed again. In this case, the endoscopic method of excision of adenoids is most preferable. It is indispensable for the growth of adenoid vegetations along the mucosa, when pathological growths are an obstacle to the passage of air along the auditory tube and can provoke hearing loss.
How is endoscopic adenoid removal performed?
After using an anesthetic drug, the doctor inserts an endoscope into the nasal cavity. At the end of the instrument there is a video camera that provides high-quality visualization and allows you to carefully examine the surgical field. Severing the hypertrophied pharyngeal tonsil can be carried out using various endoscopic instruments (resection loop, electric knife) - depending on the equipment of the installation used. In some cases, the doctor will excise the abnormal tissue through the mouth.
One of the types of endoscopic adenotomy is the removal of adenoids using a shaver, which is a micro-mill placed in a tube. There is a hole on the side of the tube, through which the instrument grasps and excises hypertrophied tissue. They are aspirated from the nasal cavity, which eliminates the risk of adenoid fragments entering the respiratory tract and causing aspiration.
In our Clinic, endoscopic adenotomy is performed under general anesthesia. But when using an endoscope equipped with a video camera and micro-instruments, tissue trauma is minimal. The effect of anesthesia on the child does not last long, since the operation itself lasts only 10-20 minutes.
Not all medical institutions have ample opportunities to use modern endoscopy in the treatment of adenoids. The CONSTANTA clinic employs experienced otolaryngologists and surgeons who are fluent in the technique of endoscopic removal of hypertrophied pharyngeal tonsils. The pediatric anesthesiologist calculates the dose of anesthesia and is constantly present during the operation, monitoring the child’s condition and the functioning of all body systems. The high professionalism of the Clinic’s team of specialists allows us to minimize any risks and remove pathological tissue as efficiently as possible.
Local anesthesia or general anesthesia?
Removal of adenoids is carried out mainly at the age of 3-10 years, when the child, due to psychological characteristics, cannot calmly accept the operation under local anesthesia. Children are afraid of blood and the painful sensations that are still present when removing adenoids in the classical way will cause physical discomfort and act as a stress factor.
When choosing an anesthesia method, the doctor takes into account the following factors:
- age and psychological characteristics of a particular child;
- direction of growth and number of adenoids;
- general health;
- degree of nasal breathing impairment.
General anesthesia ensures complete absence of sensitivity throughout the entire period of surgery and for some time after it. The child does not see what the doctor is doing and does not feel fear. Local anesthesia will dull sensation, but some pain will remain. As you know, children do not tolerate pain well, and fear increases sensations and anxiety. Therefore, general anesthesia is preferable for children under 8 years of age. Local anesthesia is possible at an older age, when the process and significance of the procedure can be explained to the child, and he can sit quietly for 10-20 minutes without making sudden movements.
Laser reduction of adenoids
See also Treatment of ENT diseases Treatment of adenoids Laser removal of adenoids - reduction Treatment of adenoids in children
Advantages of removal of adenoid vegetations by laser reduction:
- Low level of pain. To minimize physical discomfort in children, local anesthesia is sufficient.
- Bloodlessness. The laser beam does not lead to cutting off hypertrophied tissues with exposure of blood vessels, but to local vaporization (evaporation) of enlarged tonsils.
- Preservation of the lymphadenoid ring. With laser reduction, the doctor is able to remove only excess vegetation; the tonsils are then able to perform their protective function.
- The procedure has a local antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous effect. Therefore, laser reduction can also be carried out during exacerbation of chronic adenoiditis; there is no need to first achieve the subsidence of inflammation.
- Low risk of intraoperative infection, due to the lack of direct contact between the instrument and tissues.
- Rapid onset of effect. Postoperative swelling when using laser reduction does not last long; according to reviews, after a few hours an improvement in nasal breathing is noted. And the volume of the tonsils decreases during the procedure.
At Dr. Korenchenko’s Clinic, laser reduction of adenoids has been successfully performed for many years. Our doctors have extensive clinical experience and possess all the necessary practical skills.
Doctor Korenchenko’s clinic is a reliable and safe diagnosis, modern treatment of adenoids using high-quality equipment with quick results.
Functions of the adenoids
Adenoids are not some useless organ that can be removed without indication - at the request of the patient. They perform an important protective function in the body. Adenoids are part of the lymphatic pharyngeal ring, which belongs to the peripheral organs of the immune system.
Healthy tonsils perform a protective function. They, like a wall, do not allow infectious pathogens entering the nasopharynx into the respiratory tract. But with hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsils, they become a source of infection and cause exacerbation of respiratory tract diseases.