- Home /
- Blog /
- Notes of the head physician
April 19, 2021
In recent years, it has been fashionable to focus on a healthy lifestyle. People have become especially interested in what they eat and how eating habits affect their bodies. “Horror stories” have appeared about intolerance to dairy and cereals, which contain lactose and gluten. The opinion has gained popularity that such products should be excluded from the diet.
We have already discussed myths and truths about gluten. This time, the issue of lactose intolerance in adults came under close attention: what are the symptoms of the disease, where does it come from and what tests to take to accurately find out the diagnosis. About all this in our article.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance in adults
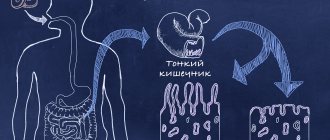
If there is not enough lactase in the small intestine, then lactose is sent to the body in broken down form. As a result, within 20-30 minutes after consuming dairy products a person may have:
- bloating,
- diarrhea,
- pain in the intestines,
- nausea,
- rumbling,
- weakness,
- dizziness.
This is how lactose intolerance manifests itself in adults. This disease is also called “lactase deficiency” (LD).
Don't confuse allergies and intolerances
A milk allergy occurs when the immune system begins to produce specific antibodies against milk proteins entering the body. The immune system mistakes them for enemies and fights them. This occurs due to insufficiently active enzymes and the body's inability to digest (absorb) milk sugar (lactose). As a result, large, underdigested milk proteins (especially casein) are perceived by our immune system as parasites or worms. And then it begins to produce antihelminthic antibodies. It is these antibodies that cause allergies.
In children, allergies manifest themselves in the form of redness on the cheeks and on the folds of the arms. Severe itching occurs. The same reactions can occur on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, that is, an immunological reaction begins there that damages the mucous membrane.
Why is there not enough lactase in the intestines?
All people have a huge amount of lactase at birth. This is how nature took care of man so that he could survive. Babies feed on their mother's milk and need this enzyme to digest their main food.
There are three types of lactose intolerance in adults.
- Alactasia . Congenital lactase deficiency is extremely rare. This is an inherited autoimmune disease. On Earth, such people can be counted on one hand. Previously, babies with congenital lactase deficiency died, but now, thanks to progress, lactose-free formulas have appeared.
- Secondary hypolactasia. Temporary lactase deficiency occurs after intestinal infections, injuries, and operations on the small intestine. In this case, there is no need to take special actions; you should wait out this period and the enzyme production will normalize.
- Primary hypolactasia. This type of lactase deficiency or lactose intolerance in adults occurs in people who, like everyone else, have a large amount of the enzyme at birth, but it decreases with age. This is genetically determined. Depending on the region of residence, the switching age may be different.
Lactose intolerance in adults is a feature which you can fully live. For more serious diseases, there are special treatment programs at the Mashuk Aqua-Therm sanatorium.
What causes lactose intolerance?
The leader in lactose content is mother's milk. Mother Nature is brilliant. She made sure that the mother was able to feed the child. Therefore, almost all of us are born with the ability to digest lactose. So at what point does everything “break”?
When it’s time to switch to a regular diet, the body reduces lactase production. This is how the first type of lactose intolerance is formed.
Primary intolerance
occurs due to a decrease in the amount of lactase with age. This is the most common type of intolerance. It often occurs in a child when breastfeeding ends.
Secondary intolerance
may occur due to gastrointestinal diseases, as a result of intestinal infections or intestinal inflammation.
It became possible to determine whether lactose intolerance exists with the discovery of the MCM6 gene. To understand whether you have lactose intolerance, simply take a lactose intolerance test (with a geneticist’s conclusion) with us at Lab4U with a 30% discount.
Based on the result of the analysis, the geneticist will draw a conclusion on how your body is predisposed to lactose and give practical recommendations on the need to adjust your diet. And, if necessary, he will recommend additional research.
How to replace products with lactose?
Lactose is found in all dairy products, plus some confectionery products, instant foods, meat, tablets, and dietary supplements. Pay attention to the ingredients.
For people intolerant, lactose-free or plant-based milk is suitable. Or fermented milk products, in which lactose has already been broken down by lactic acid bacteria, so kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, as well as butter and cheese do not give an uncomfortable effect.
Lactase enzyme is sold in tablets or capsules. You can drink it before drinking milk. This method should not be used without consulting a doctor.
Advice from a nutritionist for lactose and milk intolerance
“Why do I have such a reaction to milk?” — it is with this question that patients very often come to visit a gastroenterologist. Let's find out!
Milk is an emulsion, and therefore, due to its physical properties, it is a very favorable product for the digestive tract. It has viscosity and enveloping properties, which often has a good effect on the digestive system and the body as a whole.
Milk is a multicomponent product: proteins, fats, carbohydrates. There are as many sides to a product as there are so many possible problems. Complaints about fat content are usually rare, but the carbohydrate composition most often causes complaints, mainly due to the main sugar of milk - lactose!
Lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency) in adults is a fairly common phenomenon and depends both on hereditary predisposition and on the place of residence and tradition of drinking milk. For example, in the northern regions of Europe, lactose intolerance in adults occurs in 25% of the population, and among the indigenous peoples of Africa, Southeast Asia, North and South America, living closer to the equator, its frequency reaches 95%.
Lactase deficiency in adults is divided into secondary and primary. Primary lactase deficiency can manifest itself in childhood and can develop with age. Secondary occurs under the influence of intestinal infections and other causes that cause damage to cells of the small intestine of various origins.
According to the degree of severity, it is divided into hypolactasia - partial enzyme deficiency, and alactasia - complete enzyme deficiency.
What is the difference between lactose and lactase?
Lactose (milk sugar) is a carbohydrate of organic origin, which consists of two molecules of glucose and galactose and is one of the main components of mammalian and human milk. In its undigested form, lactose cannot be absorbed by intestinal cells. Therefore, to assimilate it, a reaction is carried out in the small intestine that separates lactose into its components - glucose and galactose, which, penetrating the cells of the small intestine, enter the general bloodstream and then the liver. In the liver, they are used to synthesize and store glycogen, which is fuel for the processes occurring in our body.
Beneficial properties of lactose
- plays the role of a prebiotic, improving the composition of microflora;
- participates in the synthesis of B vitamins;
- affects the absorption of calcium, magnesium and other microelements and its own enzymatic activity;
- is a source of energy.
Lactase is a special enzyme that is produced by the cells of the small intestine and controls the reaction of lactose breakdown. When the production of this enzyme decreases or stops, undigested lactose enters the large intestine, where a fermentation reaction occurs with the participation of bacteria, which produces an abundance of gases. In addition, if the consumption of dairy products regularly causes loose stools or pain, cramps, then an inflammatory reaction is triggered, which in the future can lead to prolonged duodenitis or functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, changes in the intestinal microflora.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance
The main clinical symptoms are loose stools (diarrhea), bloating, as well as disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract that occur immediately or within 24 hours after drinking milk or dairy products.
In addition, in the presence of intestinal dysbiosis, substances formed during the microbial breakdown of lactose in the large intestine have a toxic effect and can cause general malaise, headaches and, according to some reports, even mental disorders.
People with lactose intolerance are concerned
- diarrhea and loose stools;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- flatulence;
- cramps and pain in the abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue;
- weakness.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the quantity and amount of lactose obtained from food and lactase produced by the cells of the small intestine.
What foods contain lactose?
Milk and animal milk products naturally contain lactose, and many industrially manufactured products may contain added lactose. Any product containing milk, lactose, whey, cottage cheese, or milk powder contains lactose, so before purchasing products, you must familiarize yourself with the ingredients listed on its packaging.
Prepared foods that typically contain lactose include:
- cakes, cookies and pastries;
- cheese sauce;
- puree soups;
- custard;
- milk chocolate;
- pancakes;
- omelette;
- some types of mashed potatoes.
Some products may contain “hidden lactose” and its content may not be declared on the packaging. Examples of products with hidden lactose:
- granola bars;
- bread;
- breakfast cereals;
- margarine;
- some instant soups;
- lollipops, chocolates and chocolates;
- ham or sausage;
- sauce or salad dressing and mayonnaise.
About 20% of prescription drugs, such as birth control pills, and about 6% of over-the-counter drugs, such as those for heartburn, contain lactose. Therefore, people with lactose intolerance (especially alactasia) should tell their doctor about it when prescribing new medications.
How to replace milk if you are lactose intolerant?
Dairy products are a good and affordable source of calcium, proteins and vitamins. Therefore, people with lactose intolerance need to use alternative sources.
Some people with reduced lactase production retain some lactase activity and can include varying amounts of lactose in their diet without experiencing symptoms. For example, they have difficulty digesting fresh milk but eat certain dairy products, such as cheese or yogurt, without discomfort. These products are made using fermentation processes that break down most of the lactose in milk. In this case, yoghurts with live cultures, cheeses in which lactose has already been fermented by bacteria, or low-lactose dairy products are recommended.
If it is necessary to completely eliminate milk, you can use lactose-free milk, in which lactose has already been broken down into glucose and galactose, as well as its plant alternatives - nuts (almond, cashew, etc.), flaxseed, cereals (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, etc.), coconut or soy milk. Grocery stores often offer a wide selection of lactose-free alternatives to various foods.
Instead of milk, you can add calcium sources of plant and animal origin to your diet:
- sesame;
- nuts and seeds;
- soy milk and cottage cheese;
- legumes;
- greens - dill, parsley;
- fatty fish such as salmon, tuna and mackerel;
- eggs.
Alternative sources of vitamin A include:
- carrots, broccoli, sweet potatoes, pumpkin,
- melon, apricot, papaya, mango;
- legumes;
- liver, eggs.
Vitamin D levels can be increased through exposure to natural sunlight, fatty fish, eggs, fish oil and some fortified foods.
Basic principles of a lactose-free diet
For both primary and secondary lactose intolerance, a lactose-free diet is the mainstay of treatment. Successful adherence to it ensures recovery and cessation of disturbing symptoms.
The diet is selected individually depending on the severity of symptoms and involves limiting or excluding foods containing lactose from the diet. The duration of the diet also depends on the cause of the disorder and the severity of the symptoms. The amount of lactose that can be consumed without harm to health depends on the nature of the disorder. Many people have residual lactase enzyme activity, so everyone needs to determine their individual lactose tolerance threshold after consultation with their doctor.
When using a product with lactose, two factors are taken into account - the amount of milk sugar in it and its volume. To create a diet, it is convenient to use tables with lactose content per 100 g of product.
The basis of the diet for a lactose-free diet is products that do not contain lactose. Lactose-free dairy products are a good replacement for conventional products.
low-lactose dairy products :
- fatty foods - butter, cream;
- fermented foods - cheeses, yoghurts, fatty cottage cheese.
The higher the fat content, the lower the milk sugar content.
When preparing dishes, almond, soy, oat milk and any other plant-based drinks will help replace regular milk. Using alternative milk, you can make not only drinks, such as smoothies or cocktails, but also pancakes, omelettes, waffles and baked goods.
The diet of a person with lactose intolerance should be balanced and replenish the protein, vitamins and calcium that he is deprived of, excluding dairy products.
If you are concerned about symptoms of lactose intolerance, do not switch to a lactose-free diet without consulting your doctor. It is possible that these symptoms may be caused by other causes, and in particular inflammatory bowel disease. Food additives (enzymes containing lactase) can be an addition to the diet; they are taken in capsules or added to milk, or used in the home production of lactose-free fermented milk products.
Cow's milk protein food intolerance in adults
It remains to discuss the last facet of milk - protein . We will mainly discuss cow's milk protein as the most common protein consumed in our country.
Most often, it, as a “foreign” protein for our body, can trigger allergic reactions that are detected in childhood due to the brightness of the manifestations - rashes, skin itching, vomiting or Quincke's edema after consuming cow's milk or products made from it.
In adulthood, food intolerance to cow's milk protein is more common - this is a slow reaction of the immune system with sluggish, but no less inconvenient symptoms: bloating, unstable stool, cramps, pain, belching, mild periodic incomprehensible skin itching, general weakness, aching pain in the joints. In the case of this reaction, the main thing is that against the background of the symptom, local inflammation does not start - the gastrointestinal tract or systemic.
For these purposes, elimination diets or restriction in the consumption of certain food groups are used. The timing should be determined by a doctor; it is also important to prevent a lack of protein, vitamins D, calcium in the diet and to select the best available replacement for all components of cow's milk and fermented milk products made from it.
You can get advice from a nutritionist-gastroenterologist specializing in the management of patients with milk intolerance (lactase deficiency and milk protein food intolerance) at the Expert Gastroenterological Center. For express diagnostics of the above conditions, we suggest using the comprehensive LactoCheck program developed by the center’s specialists.
How to determine lactase deficiency?
Whether there is lactase in the body or not is determined by a biopsy of the small intestine, but this route is rarely used. For example, during operations.
Other methods are stool carbohydrate and stool pH tests and the hydrogen breath test. Because hydrogen content increases in adults with lactose intolerance, these quantitative changes can be measured and the presence of deficiency can be determined.
Interesting fact. In China, lactose intolerance in adults is observed in 90% of the population, since they do not drink animal milk at all, but prefer plant milk: soy, almond, etc. This is due to the region of residence and diet: the Chinese love rice, seafood and fish, and from there they get all the necessary substances. Therefore, if you have been diagnosed with lactose intolerance, do not despair and look for an alternative!
Why is it important to know if you have an intolerance?
When dairy products enter our body, they give us:
- macroelements: calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, chlorine, sulfur, phosphates, citrates and chlorides
- trace elements: iron, copper, zinc, manganese, cobalt, iodine, molybdenum, fluorine, aluminum, silicon, selenium, tin, chromium, lead, etc.
- vitamins: almost the entire line of B vitamins, vitamins E, D, H, C, beta-carotene
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates
We are now clear that dairy products are important. They are essential for maintaining bone mineral density. Regular intake of dairy products helps reduce the risk of bone fractures and osteoporosis.
Recent studies claim that consuming dairy products reduces the risks of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Now let's imagine that after taking milk, you feel unwell, and you decide to completely eliminate it, which means that everything useful that is in milk. But discomfort after eating has happened to everyone, and not necessarily due to lactose intolerance. Therefore, you should not decide without tests that you need to eliminate dairy.
Take a blood test for lactose intolerance with a geneticist's conclusion with a 30% discount
A geneticist will examine the results, tell you whether you have genetic prerequisites for lactose intolerance, and advise you on how to adjust your diet (if necessary).
Valio initiatives
Valio in Russia represents centuries-old Finnish experience and unique developments for the well-being of Russian consumers. The company strives to develop public knowledge about the problem of lactose intolerance, therefore it is introducing a number of initiatives aimed at maintaining awareness of both adults and children, considering this important and significant not only in Finland, but also in Russia. The company also strives to communicate how to approach the issue of lactose intolerance from a scientific point of view.
Thus, together with the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, there was the first study on the current problem of lactase deficiency among school-age children in Russia, which helped to find out the main causes of intolerance to dairy products, the proportion of the child population of the Leningrad region and St. Petersburg with the existing problem and the level of awareness about correct nutrition in these cases, which does not exclude dairy products, but corrects the diet with the help of specialized food products.
Valio currently supports projects to popularize the topic and works closely with Russian organizations in the field of nutrition. For example, together with the Union of Pediatricians, schools for expectant mothers, scientific conferences and seminars were organized.
Valio lactose-free milk is a unique product, the lactose content of which is less than 0.01%, which makes the product suitable for all consumers - including those who are completely lactose intolerant. Also, starting from 2021, Valio in Russia presents a unique range of Finnish lactose-free ice cream.
Diagnosis of inability to digest lactose
The fact that a person cannot digest milk sugar can be guessed from the symptoms, but in order to confirm the diagnosis, a certain examination is required. The easiest and fastest way is by measuring blood sugar.
First, you need to find out your fasting glucose level. Then they load the intestines with lactose, at the rate of 1 g per 1 kg of the patient’s weight. An hour later, a repeat blood test is performed to determine the sugar content, and if its amount increases by 20% compared to the initial state, we are not talking about lactase deficiency.
The process of obtaining a substance
Lactose monohydrate is obtained by evaporation from whey. To do this, the milk sugar contained in it is exposed to low temperature until crystals form, and then the remaining moisture is evaporated. The resulting raw material is sent to a roller or spray unit, processed until a powder is formed.
Reference
There are two forms of lactose in milk with different chemical structures - alpha and beta lactose. Only alpha-lactose is suitable for producing lactose monohydrate.
Industries that use lactose monohydrate
The main areas where this substance is used are the pharmaceutical and food industries, as well as agriculture.
Use in pharmaceuticals
Lactose monohydrate is one of the most popular excipients, which is used in the production of drugs in the form of tablets, capsules and sachets. There are many options for its use in the pharmaceutical industry:
- used as a safe preservative that extends the shelf life of drugs;
- used as a filler for drugs due to its minimal effect on the action of the active substance;
- allows you to shape tablets due to their ability to be easily pressed;
- creates a nutrient medium for beneficial bacteria contained in a number of preparations;
- used as part of medications against intestinal disorders.
Use in the food industry
Lactose monohydrate is used in the production of a wide range of food products:
- Baby food. Thus, in milk formulas, lactose occupies up to 85% of the composition.
- Bread and pastries. Milk sugar is included in the recipe of baked goods because it adds fluffiness and forms a golden crust on the surface.
- Semi-finished meat products (sausages, sausages, etc.). In these products, lactose is used to remove bitterness and also as a stabilizer and preservative.
- Confectionery products (jelly, marmalade, candy, etc.). Using milk sugar as a sweetener can reduce the calorie content of these products and make them accessible to diabetics.
- Alcoholic drinks. Lactose makes their taste less harsh and smoothes out the negative effects of ethyl alcohol.
- Sauces, instant soups and cereals, canned food, etc.
Application in agriculture
Milk sugar is used in the production of animal feed and biologically active additives to accelerate the growth of animals. Its inclusion in the diet of cows can increase milk yield and improve the quality of milk.
What is lactose monohydrate
Lactose monohydrate is a substance obtained by adding a water molecule to the lactose molecule. It is an oligosaccharide, that is, a type of polymer carbohydrates that, during the process of hydrolysis, form several monosaccharide molecules. In the case of lactose, two monosaccharides are formed - glucose and galactose, so it is also classified as a disaccharide.
The source of lactose is milk and dairy products, which is why its other name is milk sugar.
Important!
The shelf life of anhydrous lactose is significantly shorter than that of a substance with an added water molecule. Therefore, the latter is specially added to lactose for longer storage.
Properties of lactose monohydrate
The substance is a white or creamy crystalline powder with a sweetish taste and odorless. It has the following physical and chemical properties:
- melting point is more than 202 °C;
- easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol;
- boiling with the addition of acids gives a hydrolysis reaction;
- when interacting with an alkali solution, it is oxidized to form saccharin acids.
From the point of view of industrial use, the following properties of lactose monohydrate can be distinguished:
- is a natural preservative;
- increases nutritional value and nutritional value of products;
- has low hygroscopicity, and therefore does not change properties under the influence of humidity;
- well compatible with active ingredients of drugs;
- has low production cost;
- It is capable of retaining odors, thanks to which it serves as the basis for flavoring and aromatic additives to food.
Types of lactose monohydrate
Varieties of the substance differ in the size of its components: from microscopic particles to large fractions. This indicator is important mainly for the pharmaceutical industry, since it affects the rate of absorption of the active substance. It is not significant in the food industry.
Depending on the production method, the following forms of lactose are distinguished in pharmaceuticals:
- Sifted. This method makes it possible to obtain particles of uniform size that have good fluidity and are suitable for preparations in the form of granules and sachets.
- Shredded. The substance is mechanically crushed to various degrees of grinding. The lactose produced in this way is highly compressible and suitable for pressing.
- Spray dried. A suspension is prepared from the finely ground monohydrate, which is dehydrated by spraying to form crystalline agglomerates. The result is a product that is characterized by both high compressibility and fluidity.
- Granular. During special processing of crushed lactose monohydrate, agglomerates are formed that have good fluidity and compressibility.