Heavy periods (hypermenstrual syndrome or menorrhagia) is a condition in which the volume of menstrual blood is more than 100 ml per day. The permissible norm is 80 ml. The pathological process is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms and indicates disturbances in the woman’s body.
More than 30% of the world’s female population suffers from heavy periods, but they don’t even know that the problem can be solved with the right approach. Just one consultation with a gynecologist and the right treatment program will help you avoid wasting money on intimate hygiene products, as well as serious complications.
Causes of heavy menstruation
Gynecologists diagnose natural heavy periods and deviations from the norm. Hypermenstrual syndrome during puberty or the premenopausal period is considered natural, that is, normal. In this case, the reason is hormonal imbalance, but it is a consequence of the restructuring of the body. After a few months, the function of the genitourinary system stabilizes: the cycle normalizes or the performance of the ovaries decreases.
Much more dangerous are hormonal disorders associated with uncontrolled use of drugs (oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs) or diseases of the endocrine glands: diabetes mellitus, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
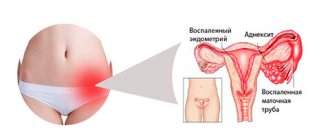
Deviations from the norm occur more often due to diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Endometriosis;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Benign, malignant neoplasms;
- Anomalies of organ development;
- Inflammatory processes.
Miscarriages or ectopic pregnancies, as a result of bleeding, are a normal phenomenon, but they are not classified as heavy menstruation: they do not occur on time and do not depend on natural physiological processes.
Hypermenorrhagia develops in the presence of other diseases:
- Blood clotting disorder;
- Hypertension;
- Neuralgia;
- Psychical deviations;
- Cardiovascular pathologies;
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys.
We must not forget about trauma: for example, careless insertion of a tampon or cup can increase the total blood volume during menstruation. Physical activity and stress also often cause an increase in the volume of menstruation.
Top 6 drugs that reduce abdominal pain during menstruation.
September 10, 2021
6848
4
Content
- How to choose pills for period pain
- The most effective pills for pain during menstruation
- No-Shpa (Drotaverine)
- Galidor
- Buscopan
- Ketoprofen
- Nalgesin
- Ketorol Express
Every woman experiences her periods differently. Some people have such stomach pain that it is literally impossible to get out of bed, and some people even go in for sports during menstruation. We have compiled a list of the most effective medications for abdominal pain during menstruation, which are recommended by doctors and patients themselves.
Symptoms of hypermenorrhagia
Excessive blood loss is an independent symptom indicating the disease. If a woman changes tampons or pads every hour because they are full, she should consult a doctor.
Often the problem is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Blood clots on underwear, pads;
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen, lower back;
- Severe fatigue;
- Weakness.
If hypermenorrhagia is not treated, other symptoms will be added to the existing ones. Against the background of heavy blood loss, despite the restoration of its volume, anemia occurs. You can suspect deviations from the norm based on the following signs:
- Excessive pallor, bluishness of the skin;
- Fragility, dullness of hair, nails;
- Dizziness, headaches;
- Problems with concentration, drowsiness;
- Irritability, insomnia.
Signs
Heavy periods are also called menorrhagia or hyperpolymenorrhea. They are characterized by the following manifestations:
- duration of menstruation 8 days or more
- significant blood discharge, quite large clots present
- per day you lose 150 ml of blood or even more
- you have to change pads and tampons very often, approximately every 60 minutes, even at night
- the menstrual cycle lasts less than 21 days
- blood begins to be released even in the middle of the cycle
- menstrual days are accompanied by significant, sometimes unbearable pain
- bleeding is abundant throughout the entire period of menstruation (and not in the first couple of days)
- bleeding or menstruation occurs 12 months or later after the onset of menopause
Diagnostics - how to determine the causes?
It is usually not difficult to diagnose heavy periods. However, it is important for the gynecologist to find out the cause of this disorder. A chairside examination will help determine the condition of the genitourinary system. The doctor chooses a two-handed method using speculums, examining the vagina and other organs for integrity, the presence of inflammatory processes, and neoplasms. The specialist immediately takes smears for cytology and microflora to rule out precancerous or cancerous conditions.
For a more thorough examination, the gynecologist performs a colposcopy. The doctor performs a diagnostic curettage - it is necessary to submit particles of the upper layer of the vaginal mucosa and cervix for histology and microscopy.
After a general and gynecological examination and questioning of the patient, the doctor prescribes general and specific laboratory blood tests and urine tests. Laboratory assistants determine the level of hemoglobin, the degree of blood clotting, cancer cells, antibodies to bacteria and viruses. Blood agents are present in the urine of liver and kidney diseases.
Additionally, the gynecologist prescribes ultrasound, MRI, CT, and radiography of the pelvic organs. Studies will reveal structural changes in the genitourinary system.
Abnormal uterine bleeding
What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Abnormal uterine bleeding is intense or unusually heavy bleeding from the uterus (through the vagina). It can occur at any time, including during menstruation.
Symptoms Vaginal bleeding between periods is a symptom of abnormal uterine bleeding, as is extremely heavy bleeding during menstruation. Very heavy bleeding during menstruation and/or bleeding lasting longer than 7 days is called menorrhagia. For example, a woman with menorrhagia may need to change her tampon or pad every hour.
Causes and risk factors Abnormal uterine bleeding can be caused by various factors. One of the most common is pregnancy. Polyps or fibroids (growths of different sizes) in the uterus can also cause bleeding. In rare cases, abnormal uterine bleeding may be caused by thyroid problems, cervical infections, or uterine cancer.
In most women, abnormal bleeding is caused by hormonal imbalance. If the cause really lies in hormones, doctors call such cases dysfunctional uterine bleeding. Typically, abnormal bleeding caused by hormonal imbalances is more common among teenagers or women approaching menopause.
Of course, these are just some of the possible causes of the violation. In general, women can encounter this problem at any age, but the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding in most cases is associated specifically with age.
Teenagers and women aged 20-40 The most common cause of abnormal bleeding in young women and teenagers is pregnancy. For many women, such bleeding accompanies the first few months of pregnancy. Some oral contraceptives or intrauterine devices may also cause bleeding.
Sometimes in young women with abnormal uterine bleeding, the egg does not leave the ovary (ovulation) during the menstrual cycle. Most often, this occurs in adolescents when menstruation appears. This causes a hormonal imbalance in which estrogen causes the lining of the uterus (endometrium) to become significantly thicker than normal. When the body gets rid of the endometrium through menstruation, bleeding can be extremely heavy. In addition, hormonal imbalance can also disrupt the body's ability to change the endometrium on time (during menstruation). This phenomenon is called spotting bleeding.
Women from 40 to 55 years old During the period before menopause and at the beginning of menopause, women begin to experience months without ovulation. This, in turn, can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, including heavy periods and less noticeable spotting.
Thickening of the uterine lining is another cause of bleeding in women in this age group. At the same time, such thickening may be a symptom of uterine cancer. That is why, if you are in this age group and experience abnormal uterine bleeding, be sure to tell your doctor about it. It is quite possible that what is happening is just part of the natural aging process of the body, but in any case you need to exclude the possibility of cancer.
Post-menopausal women Hormone replacement therapy is a common cause of uterine bleeding after menopause. Other possible causes include endometrial and uterine cancer. These forms of cancer are much more common among mature and elderly women. At the same time, cancer is not always the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. After menopause, it can be caused by many other disorders. That is why, if there are problems, a preliminary consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Diagnostics The tests and diagnostic procedures prescribed by the doctor depend on the age of the patient. If you may be pregnant, your doctor will order a pregnancy test. In case of severe bleeding, among other procedures, a blood test may be prescribed to determine the number of blood cells. The fact is that a very low value due to excessive blood loss can lead to iron deficiency and anemia.
An ultrasound examination of the pelvic area will allow you to examine the uterus and ovaries. In addition, it will help identify the cause of bleeding.
The doctor may also perform a biopsy of the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. This procedure is performed by inserting a thin plastic tube (catheter) into the uterus to remove a tiny sample of tissue, which is then sent to be examined in a laboratory. A biopsy can reveal the presence of cancer or any cellular changes. This procedure is performed in a doctor's office and is accompanied by mild discomfort.
You may also have a hysteroscopy, in which a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the uterus, allowing the doctor to examine the inside of this organ in detail. If any abnormalities are detected, a biopsy will most likely be performed.
Prevention. Is it possible to prevent bleeding? If abnormal uterine bleeding is caused by hormonal changes, it cannot be prevented. At the same time, if the cause is excess weight, losing weight can solve the problem. The fact is that body weight affects the production of hormones. Maintaining a healthy body weight helps prevent abnormal uterine bleeding.
Treatment There are several treatment options for this disorder. The specific option you choose will depend on the cause of the bleeding, your age, and your desire to become pregnant in the future. Your doctor will help you make the best decision in your case. If he suspects that the abnormal bleeding is caused by a hormonal imbalance, a possible treatment option is to wait for the symptoms to subside. Here are just a few techniques:
Intrauterine contraceptive. Your doctor may recommend inserting an intrauterine device (IUD). This is a small plastic pregnancy prevention device that a doctor inserts into the uterus through the vagina. Some types of such products release hormones, thereby significantly reducing the intensity of abnormal bleeding. At the same time, along with oral contraceptives, intrauterine contraceptives themselves can cause bleeding. If something like this happens to you, contact your doctor immediately.
Oral contraceptives. Oral contraceptives contain hormones that can stop the lining of the uterus from further thickening. In addition, they normalize the menstrual cycle and reduce discomfort. However, some types of these pills, especially low-dose progestogen-only oral contraceptives, may themselves cause bleeding in some women. If the drug you are taking does not reduce abnormal bleeding, tell your doctor.
Expansion and curettage. This procedure requires that the cervix allows the insertion of a special surgical instrument into the uterus, with which the doctor scrapes out its inner lining. The removed tissue is subsequently studied in the laboratory. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia (the patient is in a state of sleep).
In case of extremely heavy bleeding, the doctor can carry out dilation and curettage at the same time to find out the cause of the disorder and to stop the bleeding. The fact is that this procedure itself often helps solve the problem. However, only a doctor can decide whether it is advisable.
Hysterectomy. This is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed. After a hysterectomy, a woman stops menstruating and cannot become pregnant. A hysterectomy is a major surgical procedure that requires general anesthesia and hospitalization. The recovery period can take a very long time. Discuss with your doctor all the pros and cons of this treatment method.
Endometrial ablation is a surgical procedure that involves destroying the lining of the uterus. Unlike a hysterectomy, this procedure does not involve complete removal of the organ. For some women, endometrial ablation stops menstrual bleeding completely. At the same time, others may continue to have light menstrual flow, and in rare cases, the menstrual cycle is completely restored. After endometrial ablation, women still need some form of contraception, even though the procedure reduces the chance of conception to a minimum.
Ablation can be performed in several ways, and the latest techniques for performing this procedure do not even require general anesthesia and subsequent hospitalization. With any chosen method, the recovery period is much shorter than with hysterectomy.
Impact on quality of life Abnormal uterine bleeding can negatively affect a woman's daily life. The inability to predict the moment when heavy bleeding will begin leads to a constant state of anxiety. In addition, heavy menstrual bleeding can significantly limit the options available to you. In some cases, the woman cannot even leave the house.
For extremely heavy menstrual bleeding, try taking ibuprofen on or a few days before your expected period. Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that helps reduce bleeding.
Also, make sure you have enough iron in your diet. If necessary, your doctor may prescribe you to take iron supplements to prevent the development of anemia.
APPOINTMENT FOR AN EXAMINATION WITH A GYNECOLOGIST Examinations by a gynecologist are an integral part of every woman’s life. Doctors at the Avicenna multidisciplinary clinic create convenient conditions for consultation - each patient can make an appointment online and also visit the doctor on Saturday.
A personal gynecologist will help maintain a woman’s health, and the price of a visit is always significantly lower than treatment of the disease.
You have the opportunity to make an appointment right now by filling out the online form on our website or by calling 91-80-70.
Appointment with a doctor of the highest category 720 rubles
Treatment of heavy periods
The gynecologist must not only reduce the symptoms, but also eliminate the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it is impossible to get rid of hypermenstrual syndrome.
Conservative treatment methods are limited to normalizing hormonal levels, the functioning of the endocrine glands, restoring blood circulation and hematopoiesis.
To reduce blood loss, doctors prescribe ascorbic acid, rutin, and anti-inflammatory drugs. For heavy discharge, specialists use calcium gluconate. To restore hemoglobin levels, doctors choose drugs rich in iron.
The patient may be undergoing inpatient or outpatient treatment, but in both cases she is shown complete rest and a balanced diet. Immediately after the end of menstruation, the woman is prescribed physical therapy: electrophoresis, phonophoresis, diathermy, ozokerite.
Surgery
If the doctor has diagnosed injuries or other violations of the integrity of the tissues of the vagina, uterus or cervical canal, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. Endometriosis, neoplasms, and inflammatory processes also do not always respond to conservative therapy.
Surgeons excise the affected tissue and connect it by suturing the edges of the wound. In situations where a woman is over 40 years old, gynecologists often choose to remove the uterus in order to completely eliminate complications. Sometimes specialists perform supravaginal amputation of the uterus - removal of the genital organ while preserving the vagina.
Also, sometimes operations are performed to excise or remove organs of other body systems: for example, to restore hormone levels, part of the overgrown thyroid gland is removed.
Hemostatic drugs during menstruation
If there is heavy blood loss during menstruation, the best thing to do is consult a specialist to conduct a full examination and rule out possible diseases. For heavy periods, the following medications may be prescribed:
Vikasol
This drug is a synthetic analogue of vitamin K, which takes an active part in blood clotting, namely, it affects the formation of prothrombin. Vikasol for heavy periods can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, since this drug has certain indications and contraindications. You need to understand that Vikasol is effective for heavy periods only if the cause of blood loss is a deficiency of vitamin K. Therefore, it is categorically not recommended to prescribe such a drug yourself.
Dicynone
Dicynone is also quite often used for menstruation. This is a hemostatic drug prescribed for heavy bleeding. Dicinone during menstruation is usually prescribed when the cause of bleeding is fibroids, as well as vascular diseases. Like any other drugs, dicinone has specific indications, contraindications, and side effects, so you can take dicinone during your period strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
Diferelin
This drug is a synthetic analogue of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and belongs to the group of antitumor drugs. A drug such as diferelin regulates menstruation at the level of sensitivity of peripheral receptors to GnRH. The drug is used for endometriosis and uterine fibroids. Only after examination by a doctor and confirmation of the appropriate diagnosis can diferilin be prescribed. Heavy periods should definitely be a reason to consult a specialist.
Tranexam
Tranexam is used quite often during menstruation. This hemostatic drug during menstruation can be prescribed in different situations. This is a modern hemostatic drug, the mechanism of action of which is the activation of fibrinolysin and the formation of plasmin. Tranexam during menstruation is usually prescribed in tablet form, and its use should be under the supervision of a doctor.
Askorutin
Ascorutin is a drug that contains vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, and rutin. It is used during menstruation quite often. Its action is to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, as well as reduce the fragility and permeability of capillaries. This drug also has antioxidant properties, which improves overall health.
There are many reasons for heavy periods. Many women try to solve this problem on their own by taking hemostatic drugs during menstruation. However, to achieve the desired effect, it is very important to understand the cause of blood loss. But only a specialist can correctly determine this.
Traditional methods of treatment
One of the methods by which heavy uterine bleeding is treated is traditional methods of treatment. They are first discussed with the attending physician to eliminate the risk of developing an allergic reaction. It is important to remember that unconventional methods will not completely eliminate bleeding. They help and prevent the development of complications due to the use of basic medications. The following types of medicinal herbs are used:
- nettle;
- yarrow;
- viburnum;
- bloodroot;
- yasnotka.
Herbs can be used alone or mixed. To do this, place a small amount of them at the bottom of a 200-250 ml container. Boil water and pour it in. Allow to cool completely. In order for the active components to be absorbed faster into the systemic bloodstream, it is recommended to consume 100-200 ml every day before meals.
Traditional medicine methods not only eliminate the pathological process, but also protect the body. They contain a large amount of vitamins that stimulate local and systemic metabolism. This triggers the regeneration of renewed tissue, including in the genital area.