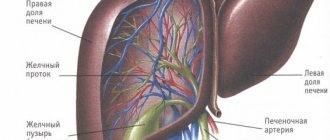
From our school human anatomy course, we remember that the liver is the largest digestive gland in the human body, as well as one of the main “filters” in the body, protecting us from toxicants. Pathological processes in the liver can be divided into several classes. The first is the actual effect of toxic substances (alcohol, some drugs, chemicals, etc.). The second is exposure to viruses. The third is conditions associated with dystrophic changes in hepatocytes (fatty and pigmented hepatoses). In addition, some conditions are accompanied by difficulty in the removal of bile and its “stagnation” in the bile ducts (cholestasis), including inside the liver. Since a person is constantly exposed to factors unfavorable for the liver, many people subconsciously want to “support” or “treat” this organ. These people often come to the pharmacy for advice. Our guide is intended to help the chief captain competently advise such a visitor and help him choose an effective medicine for the liver.
Hepatoprotectors are a whole class of drugs of various origins designed to support the functional abilities of the liver, restoring damaged cells and increasing their resistance to toxicants.
Strictly speaking, at the moment there is no single generally accepted classification of hepaprotectors. Here is the division option most used in practice (1, 2):
Classification and characteristics of hepatoprotectors by type of origin and primary mechanism of action
| Herbal preparations | Based on milk thistle. Licorice based. Based on other plants |
| Preparations of animal origin | Based on animal liver. Derived from placenta |
| Preparations based on essential phospholipids | Based on essential phospholipids. Combination preparations containing essential phospholipids |
| Preparations with a predominantly detoxifying effect | With a predominantly direct detoxifying effect (ornithine aspartate, arginine glutamate). With a predominantly indirect detoxifying effect:
|
| Bile acid preparations | Ursodeoxycholic acid |
| Drugs of other groups | Thioctic acid. Vitamins and antioxidants |
Types of liver damage
- Infectious diseases (viral hepatitis).
- Toxic lesions (alcohol, drugs, etc.).
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Diffuse lesions of the liver parenchyma (metabolic disorders).
- Vascular pathologies of the liver.
- Storage diseases (hemochromatosis, etc.).
- Liver helminthiasis.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
Depending on the location of the pathological process, liver diseases are divided into:
- for diseases of the liver parenchyma and interstitial connective tissue;
- damage to the bile ducts;
- pathologies of the vessels of the portal system and hepatic veins.
Medicines used in the treatment of diseases of the liver and biliary tract
Drugs for the treatment of the liver, depending on the mechanism of pharmacological action, can be divided into 3 large groups.
- Hepatotropic:
- choleretic (choleretics, cholekinetics);
- cholelitholytic;
- hepatoprotectors.
- Etiotropic:
- antiviral,
- antibacterial,
- antifungal,
- antiprotozoal.
- Symptomatic:
- antispasmodics (neurotropic, myotropic);
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiemetics;
- vitamins;
- detoxifying (including antidotes);
- corticosteroids;
- anticytokines;
- probiotics.
Hepatotropic drugs
Choleretic
Choleretic drugs for the treatment of the liver, depending on the mechanism of pharmacological action, are divided into choleretics and cholekinetics.
Choleretics
. These drugs that stimulate bile formation, in turn, are divided into true choleretics and hydrocholeretics. True ones, which contain bile acids, increase the difference in osmotic pressure between blood and bile, enhance intestinal motility and prevent the formation of stones. Hydrocholeretics stimulate bile secretion due to the water component. This group includes drugs of plant and synthetic origin.
Cholekinetics
. Cholekinetic drugs for the treatment of the liver are divided into substances that stimulate the tone of the gallbladder and promote the excretion of bile, as well as antispasmodic drugs that reduce the tone of the biliary tract.
Cholelitholytics
Cholelitholytic drugs are agents for dissolving gallstones. They contain ursodeoxycholic or chenodeoxycholic acid. The mechanism of action of these drugs is associated with impaired absorption of cholesterol in the intestine and a change in the percentage of hydrophobic and hydrophilic bile acids found in the gallbladder. Their use leads to a decrease in the flow of cholesterol into bile and acceleration of the process of dissolution of cholesterol stones.
Hepatoprotectors
Hepatoprotective drugs are drugs that help:
- restoration of homeostasis in the liver;
- normalization of functional activity and hepatic metabolism;
- increasing resistance to the effects of adverse pathogenic factors;
- stimulation of reparative and regenerative processes.
This pharmacological group combines various drugs that have one or another effect on the liver. The category of hepatoprotectors includes products of plant and animal origin, amino acids, ursodeoxycholic acid preparations and essential phospholipids.
Plant hepatoprotectors.
The main components of plant hepatoprotectors: silymarin, cymarin, hophytol. Medicines for liver restoration, containing extracted flavonols, are used for toxic (including alcoholic and drug) lesions, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholangitis, steatosis (fatty liver degeneration).
Hepatoprotectors of animal origin.
Hepatoprotective drugs of animal origin have restorative and detoxifying properties. They are made from hydrolyzed cattle liver or pig liver cells. These medications are indicated for use in the treatment of alcoholic hepatosis, hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Ursodeoxycholic acid.
Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations have hepatoprotective, choleretic, hypocholesterolemic, cholelitholytic and immunomodulatory effects. The active substance reduces the cytotoxicity of fatty acid salts and regulates immunological reactions. Hepatoprotectors with ursodeoxycholic acid are recommended for use in the complex treatment of acute and chronic hepatitis, as well as for toxic lesions and cirrhosis of the liver.
Amino acids.
The main components of hepatoprotective agents in this group are essential amino acids and their derivatives (methionine, arginine, ornithine, aspartate). These compounds, which are part of all cells of a living organism, take an active part in the processes of biosynthesis of proteins, nucleic polymers and lipids. A hepatoprotective drug for the treatment of the liver, containing one of the above amino acids, has pronounced restorative, detoxifying and antidepressant properties.
Essential phospholipids.
These are complex substances of natural origin, which are the main element of cell membranes and mitochondria. By integrating into the membranes of hepatocytes, they recreate their structural and functional integrity and contribute to the restoration of impaired functions. A drug for liver restoration with essential phospholipids improves the clinical status and biochemical blood parameters in patients suffering from steatosis, chronic hepatitis, alcohol and drug damage to the organ and cirrhosis. One of the effective domestically produced products containing phospholipids is Phosphogliv*.
How alcohol affects the liver
Only 5-10% of alcohol consumed is excreted from the body directly.
The rest passes through the liver, where it is broken down into harmless compounds. During processing, a toxic intermediate product is formed - acetaldehydrogenase, which has a destructive effect on the cells of the organ. According to WHO, the safe daily dose of pure alcohol is 40 g for men and 20 g for women, provided that alcohol consumption occurs no more than 1-2 times a week. Hepatocytes have time to recover within a few days, and the harm to the body is minimal. With binge alcoholism, regeneration takes from six months to several years. In this case, complete recovery is impossible.
Help with withdrawal from binge drinking at home
If you drink alcohol regularly and the amount exceeds the permissible limit, metabolic processes are disrupted. Accumulated toxins cause oxygen starvation of liver cells, which prevents their regeneration. As a result, destroyed hepatocytes are replaced by adipose tissue, leading to steatosis, or fatty disease. Alcohol also stimulates increased collagen production, resulting in some of the cells being replaced by connective tissue. Scarring occurs and fibrosis develops.
In the absence of treatment and continued alcohol consumption, the disease develops into hepatitis, and in 25% of cases, alcohol abusers are diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver, which develops into carcinoma and leads to death.
Even after short-term alcohol abuse, it is necessary to undergo rehabilitation therapy to prevent complications. The rate of liver regeneration depends on gender, genetic predisposition, and characteristics of the body. For some people, even a minimal dose of alcohol can be fatal and cause toxic damage to the organ followed by necrosis. The only chance to prevent risks to life and health is to give up alcohol forever and consult a doctor to diagnose the severity of the disorders and prescribe effective treatment.
Etiotropic drugs
Etiotropic therapy drugs are medications whose action is aimed at suppressing vital activity and destroying infectious agents. This group includes:
- antiviral agents
– natural and recombinant interferons. Recommended for the treatment of viral hepatitis; - antibiotics
– macrolides, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, tetracyclines. Used in the treatment of diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract; - antifungals
– medications for the treatment of deep mycoses (fungi). Prescribed for disseminated candidiasis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis, candidomycosis; - antiprotozoal
- antigiardiasis drugs metronidazole and furazolidone.
Which brand of liver medication is best to choose?
Among the huge variety of modern medications, it is difficult to immediately decide which drugs to cleanse the liver and prevent disorders. Domestic and imported pharmaceutical companies offer natural and safe tablets with improved formulas and new compositions.
The presented manufacturing companies are widely known due to the high quality and effectiveness of their products:
- Sanofi is a French-German pharmaceutical company specializing in a large number of medicines. Since its founding in 2004, the company has become the largest manufacturer of quality drugs, with representatives operating in more than 100 countries.
- Kanonpharma Production is a closed joint stock company in Russia, founded in 1998. In a short period of time, the company quickly acquired a modern production base.
- Madaus GmbH is a German company from Cologne, founded in 2007. The main slogan is the production of medicines using natural resources.
- Pharmcenter Vilar is a domestic pharmaceutical company specializing primarily in the creation of herbal medicines. Since its establishment in 1959, phytochemical production has been continuously improved.
- Clinic of the Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology - the company has a patented technology for the serial production of drugs of natural origin. Founded in 2002 in St. Petersburg.
- Renaissance - a series of natural remedies for immunity, joints, women's and men's health, ENT organs. The company traces its history back to 1942; in 2005 it joined the Biotek group. It has over 115 types of biological additives. Available forms of release - dragees, capsules, powders, tablets.
- Evalar is the largest production of dietary supplements and natural medicines in Russia, founded in 1991. Today, it is the absolute leader in the country in terms of sales and creation of natural medicines.
- Richard Bittner AG is an Austrian company with the patented trademark “BITTNER”, which is considered a sign of high quality throughout the world. The main activity is the creation of natural and safe medicines.
- Laboratories Rosa - Phytopharma is a French manufacturer specializing in the production of various groups of medications for the treatment of internal diseases.
- Europe-Biopharm is an NPO in Russia, founded back in 1991. Since then, production has been aimed at providing people with natural medicines, dietary supplements and functional foods.
- Merz Pharma is a German world-famous manufacturer of the best drugs of all groups and classifications. The main focus is on the fields of neurology, dermatology and psychiatry. The main advantage is extensive experience, since the company was founded in 1908.
- Falk P harma GmbH the company was founded in Germany in 1960 on the basis of a family pharmacy by Dr. Herbert Falk. Since then, the main activity has been aimed at producing drugs for the needs of hepatology and gastroenterology.
- Merkle GmbH - the creator was the richest man, Adolf Merkle. The company was founded in 1881, first in the Czech Republic and Slovakia, and after the war the activities moved to Germany.
- Sopharma is a private Bulgarian manufacturer that has been giving people health for more than 80 years. In 1933, an association of pharmacists began to create a laboratory; since then, technologies have been constantly improved and natural, effective medicines are created.
- Abbott Laboratories is a chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturer from America, founded in 1888. In addition to medicines, it produces baby food, medicinal products and supplements.
- R.P. Scherer GmbH & Co. KG is a German company founded in 1950 by Robert Pauli Scherer, who developed the soft capsule form. In addition, they produce various essential oils, multivitamins, and dietary supplements.
Means of symptomatic therapy
Medicines for symptomatic therapy, unlike pathogenetic drugs, reduce the manifestations of the disease, but do not affect the cause of its occurrence.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodic drugs are prescribed for spastic pain accompanying hepatic colic. In this situation the following can be used:
- neurotropic drugs that disrupt the innervation of myocytes of the gallbladder and biliary tract;
- myotropic, changing biochemical processes in smooth muscle cells of the liver;
- combined (neuromyotropic) complexes.
Analgesics
For short-term relief of pain in the liver area, narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics are used.
- Opioid (narcotic) drugs
. They affect the central nervous system and are prescribed in strictly defined doses to relieve severe pain. - Non-narcotic drugs (derivatives of salicylic acid, aniline, pyrazolone)
. Used for less severe pain symptoms. They have an analgesic effect, reduce the permeability of the walls of liver capillaries, suppress the synthesis of prostaglandins and interleukin-1, and prevent the release of bile enzymes into tissues and blood.
Antiemetics
To relieve nausea and vomiting, which are frequent accompaniments of liver diseases, antiemetic drugs (gastrokinetics) are used.
Vitamins
The most essential micronutrients for the liver are ascorbic and lipoic acid, vitamin E, which maintains the stability and integrity of hepatocytes. B vitamins and retinol are also necessary to restore and maintain the normal functioning of the organ.
Detoxifying agents
Detoxifying medications used to stop exposure to toxic substances include:
- laxatives and emetics;
- osmotic diuretics;
- water-electrolyte balance regulators;
- sorbents;
- blood and plasma substitutes.
In case of toxic liver damage, antidotes (chemical or biological antagonists) are used to neutralize the poison, prevent or eliminate the effect it causes.
Glucocorticosteroids
Can be recommended for use as a means of pathogenetic treatment for severe liver diseases. These drugs regulate immunological activity, suppress the production of antibodies, inhibit the formation of connective tissue, reduce the manifestations of the inflammatory reaction, have a tonic effect, and inhibit the development of intrahepatic bilestasis.
Probiotics
Probiotic preparations are complexes of viable beneficial bacteria. They normalize the composition of the intestinal microflora and are used to restore the normal functioning of the hepatobiliary system and the entire digestive tract after etiotropic therapy. These drugs are also used in the treatment of patients with liver cirrhosis. Colonization of the intestines with beneficial bacteria significantly reduces the level of serum ammonia concentration, preventing the development of hepatic encephalopathy.
Which drug for the liver is better to buy?
Release form, country of origin, composition, principle of operation, indications and contraindications, doctor’s recommendations and patient reviews, as well as advice from the presented rating will be the best assistant in finding the ideal medicine.
Taking into account all the described advantages and distinctive properties, the following recommendations can be summarized:
- Ovesol is perfect for pregnant women and nursing mothers, as it has no contraindications or risks of side effects;
- Ursofalk is considered the most popular option for doctors; it is most often prescribed to patients, since its safety and pharmacological value have been proven in clinical trials;
- If you have glandular problems accompanied by depression, you should definitely take Heptral; it is also suitable for those who struggle with alcohol addiction;
- For the treatment of children, experts approve Karsil from Sopharma, which provides a noticeable improvement in overall well-being;
- Hepatol is used to protect and restore liver cells as a result of exposure to alcohol, toxins, and free radicals;
- The most reviews and trust from the population can be seen in Essentiale Forte N, this is due to good advertising and the absence of risks.
The basic rule of choice is to visit a doctor who specializes in liver diseases, make a diagnosis, and then prescribe a suitable remedy. The review contains only recommended, proven products; within it, preference should be given to those that are approved by the doctor.
Phosphogliv* – restoration and protection of the liver
Phosphogliv* is a liver treatment drug with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antifibrotic properties. In its production, two active components are used: essential phospholipids and glycyrrhizic acid.
Essential phospholipids
– structural elements of liver cell membranes. In the treatment of liver diseases, phospholipids have restorative and regenerative effects.
Glycyrrhizic acid
is a substance with pronounced anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic and antioxidant properties.
Acting in combination, the active components of the drug Phosphogliv* mutually enhance and complement each other, significantly increasing the effectiveness of therapy. The hepatoprotector Phosphogliv* can be indicated for use as a drug for the restoration of liver cells in the treatment of acute and chronic forms of viral hepatitis, steatosis, toxic lesions and as part of complex therapy for liver cirrhosis.
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is often discovered unexpectedly during examination for another reason. Specific diagnostics include assessment of complaints, examination of the skin and oral mucosa. In addition, laboratory techniques are used.
The main indicator is a biochemical blood test. An increase in the values of ALT and AST, bilirubin and globulin fractions, as well as a decrease in the number of albumin fractions indicates persistent dysfunction. Deviations in creatinine and urea indicate abnormalities in kidney function.
General expanded shows reduced hemoglobin, elevated leukocyte levels and decreased platelets.
Specific markers of viral hepatitis using qualitative PCR.
Ammonia test. It does not break down and accumulates, causing intoxication.
Detection of oncology - alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test.
Determining the concentration of immunoglobulins A and G, as well as T-lymphocytes, reveals autoimmune aggression towards its own components.
Fecal occult blood testing reveals signs of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to laboratory tests, accurate information is obtained through hardware testing.
- MRI and computed tomography can detect necrosis at the beginning of development. They detect tumor neoplasms and fibrotic foci.
- Ultrasound detects fibrous areas, determines dimensions and changes in structure. Examination of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, shows an enlargement of the gland - hepatomegaly and spleen - splenomegaly, the size of the portal vein. The conclusion is used to select the correct therapeutic tactics.
- Elastometry determines the degree of fibrosis.
- Biopsy - collection of biomaterial by puncture is done in a hospital. An informative method allows you to determine the type, root cause and degree of damage.
- FEGDS reveals varicose veins in the stomach and esophagus and the presence of nodes.
- Scintigraphy is a radionuclide examination that helps evaluate functioning. A chemical radiopharmaceutical compound is administered. By its further distribution in the body, the ability to capture and neutralize toxins is judged. In such a situation, this function is reduced. The settling of the element in the bones of the spine and pelvis indicates a critical situation.
In the compensated phase, destruction can be stopped. It will not be possible to recover completely. It is important to detect changes in time and take action. To do this, you need to consult a specialist - a hepatologist or gastroenterologist.