Gout
- one of the oldest diseases described in medicine. In the 5th century BC, Hippocrates called “gout” (from the Greek words “under” - leg, “agra” - trap) acute pain in the foot. It was called “the disease of kings and the king of diseases,” a disease of aristocrats, and was even considered a sign of genius. Such famous people as Leonardo da Vinci, Alexander the Great, many members of the Medici family from Florence, Isaac Newton, Charles Darwin suffered from it. And this list is far from complete.
Gout is a disease associated with a disorder of purine metabolism, which leads to an increase in uric acid in the blood (hyperurecemia) and its deposition in the tissues of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs.
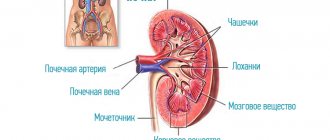
In the human body, purine bases are broken down into uric acid and excreted by the kidneys. When the concentration limit of uric acid in tissues is exceeded, the deposition of its crystals in the form of monosodium urate begins in the joints, kidneys, and soft tissues. Clinical manifestations of arthritis (inflammation of the joint), soft tissue formations (tophi), urate nephropathy (kidney damage) and nephrolithiasis (formation of kidney stones) appear.
Changes in dietary habits and lifestyles have resulted in gout affecting 1-2% of the population in industrialized countries.
What is gout?
Gout can affect any joints: fingers, hands, elbows, knees, but most often the joints of the toes, especially the big toe, suffer from gout, which is associated with a greater tendency to degenerative-dystrophic changes in their cartilage tissue.
History of gout research
Gout was described already in the 5th century BC. Hippocrates, but this was only a description of the symptoms. At the end of the 19th century, scientists discovered an increase in the content of uric acid salts in the blood, and then in the intra-articular fluid of patients with gout. A detailed study of the pathogenesis of gout and the development of drug treatment date back to the middle of the twentieth century.
Interesting are the various theories that link the likelihood of developing gout with various lifestyle features and personal qualities. For example, back in the Middle Ages, gout was called the “disease of abundance”, since only wealthy people suffered from it. Later, this was explained by the connection between the development of gout and the intake of large amounts of protein into the body and the participation of alcohol in its pathogenesis. Another theory was to identify the dependence of the frequency of the disease on the level of intelligence and overall success of a person. Many famous people suffered from gout (Franklin, Newton, Darwin, etc.), which gave reason to assume a similar connection.
Pathogenesis of gout
Hyperuricemia can be associated with a variety of reasons, from intense physical activity and dietary errors to severe kidney disease or oncology. The symptom complex characteristic of gout is not always formed. This diagnosis is made when signs of joint inflammation (arthritis) appear, which is the result of the deposition of uric acid salts (urates) in the joint tissues. Uric acid crystals have an irritating effect on tissues, resulting in their chronic aseptic inflammation and proliferation with the formation of gouty “bumps” or tophi. Tophi can also be located in internal organs (for example, heart valves). The tophi themselves are painless, the pain is associated with inflammation in the periarticular bursae (bursitis) or tendons (tenosynovitis). The inflammatory process causes severe pain and limited joint mobility.
Treatment of inflammation of the joint capsule of the elbow joint
Is your elbow swollen, red and painful? Possibly elbow bursitis
- inflammation of the intra-articular bursae, resulting from microtraumas, local overload of the joint, or as a manifestation of systemic diseases. This inflammatory process is considered one of the most common types of bursitis and is accompanied by an increase in the size of the joint, redness, and the inability to bend and straighten the arm due to severe pain and swelling of the elbow.
Most often it occurs in professional athletes, manual workers, as well as people who, due to their profession, are forced to perform monotonous actions every day with support on their elbows. These are predominantly young and middle-aged people who work as miners, plumbers, roofers, drivers and clerks.
To make a diagnosis and effectively combat this disease, our sports rehabilitation center uses a set of diagnostic measures, conservative and surgical treatment methods. We are attentive to each patient and are ready to select individual treatment that will allow you to get rid of unpleasant sensations and change the quality of life after the first contact with us. Symptoms of the disease
With bursitis of the elbow joint, the patient's condition worsens slightly. There is a general malaise and an increase in body temperature, which can persist for several days. A painful formation may appear on the elbow - a lump that looks aesthetically unattractive and is elastic to the touch.
The following symptoms are also observed:
- slight elbow swelling and swelling;
- redness, local increase in temperature;
- moderate pain, limitation of movements.
In most cases, inflammation goes away without complications, excess fluid is absorbed, the skin acquires a natural color, and overall health improves. However, after another injury or overstrain of a joint, the disease may recur and become chronic. With this type of bursitis, pain may intensify with prolonged physical activity and contact with the work table. The lump on the elbow can feel different to the touch - elastic, soft, hard, etc. If the bursa is suppurated against the background of chronic or acute bursitis, the nature of the pain in the elbow changes to a tugging, bursting sensation. The elbow joint becomes hot and painful on palpation, swollen and hyperemic. Hand movements are limited and difficult. Symptoms of general intoxication are also noted: headaches, high fever, weakness, body aches. When inflammation spreads, fistulas may appear, purulent arthritis, abscess or osteomyelitis may develop.
Make an appointment and get a comprehensive consultation from a traumatologist-orthopedist, sports medicine doctor Ondar Temir Evgenievich:
Causes of the disease
If you look inside the joint, you can see that above the olecranon there is an anatomical formation with fluid, which in its shape resembles a bag. It is a bursa that serves as a shock absorber, reducing friction between bones, ligaments, tendons and skin, allowing ease of movement and preventing damage to surrounding tissue. In a healthy person, there is a small amount of fluid inside this formation. With excessive physical exertion or microtrauma, the situation is different: fluid in the bursa is actively produced, does not have time to be absorbed and causes characteristic swelling. The tightly filled pouch begins to bulge, reaching a considerable size. Outwardly, it looks like a “bump”, which can hurt and cause some inconvenience to the patient. If an infection occurs in the bag with liquid, purulent inflammation begins, which can cover adjacent tissues and organs.
Among the main reasons for the onset of the inflammatory process in the bursa are the following:
- repeated injuries to the elbow or pressure on this area, for example, while performing a specific type of work;
- performing monotonous mechanical movements due to professional activities;
- sports loads that involve systematic bending of the arm at the elbow joint (weightlifting, gymnastics, baseball) or a fall on this area (football, hockey, rugby);
- regularly resting your elbows on a solid base, due to the presence of chronic lung diseases and the need to increase inhalation effort;
- forced preservation of body position (most often in patients on hemodialysis);
- local hypothermia of the limb (for example, when performing cargo-loading work in an open warehouse area).
The localization of inflammation can be different, depending on the characteristics of the load. In office workers, miners and wrestlers, the subcutaneous ulnar bursa is mainly affected, and in athletes, the radioulnar bursa is affected. In gout, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases, inflammation is more likely a reaction to the formation of salt deposits in the bursa. The cause of purulent bursitis is the penetration of microbes through existing skin lesions: abrasions, small wounds, pustules or boils. In the case of erysipelas, osteomyelitis, the presence of purulent wounds and bedsores, the infection can be introduced into the bursa along with the flow of lymph or blood.
Undoubted risk factors influencing the likelihood of infection are:
- diabetes mellitus or the presence of other systemic diseases;
- long-term use of steroid drugs;
- metabolic disorders and weakened immunity;
In addition, it matters whether the patient abuses alcohol and tobacco products.
Classification
The most common types of bursitis, as a rule, are aseptic, i.e., germ-free, resulting from overload of the joint, and septic, accompanied by the development of infection due to the contamination of the sac with various microorganisms (mainly bacteria). Aseptic bursitis most often occurs as a result of:
injuries, minor (leaning on the elbow) or excessive, which lead to hemorrhage into the bursa and the development of inflammation; the presence of systemic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Septic bursitis usually develops when bacteria enter the intraarticular bursa. In some cases, these are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus. Infections caused by fungi and mycobacteria are more common in people with weakened immune systems or autoimmune disorders.
Bursitis can also be classified depending on:
localization (inflammation of the radioulnar, ulnar or interosseous ulnar bursa); course (acute, subacute and chronic); the nature of the fluid (serous, hemorrhagic, fibrinous and purulent).
Depending on the type of microorganisms that have entered the pouch, specific (caused by pathogens of specific infections, for example, gonococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis) and nonspecific (caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus) inflammatory processes are distinguished.
Diagnostic methods
The most important diagnostic criteria for establishing a diagnosis are:
- swelling of the elbow, which usually appears a few hours or days after injury to the joint. Most often painless, soft and warm to the touch;
- plasticity and mobility of the joint;
- no pain in the elbow joint except in cases of flexion, when the bursa is compressed.
When examining a patient, a thorough history and clinical examination are performed. In addition, the complex of diagnostic measures includes:
- Laboratory diagnostics. A blood test (clinical, biochemical) and a general urine test are recommended. Based on these tests, the degree of inflammatory activity is determined (leukocyte count, C-reactive protein level);
- Instrumental diagnostics: the patient is prescribed an ultrasound or radiography - the most important components of the study, the conduct of which makes it possible to determine in which particular bursa the inflammation has occurred, and whether this disease can be attributed to bursitis, since similar symptoms can be observed in other diseases (for example, arthritis, ligament ruptures, tumor diseases of the bone and muscle system);
- Other diagnostics. If the measures taken turn out to be uninformative, the patient is prescribed a puncture of the intra-articular bursa - a procedure during which the bursa is punctured to collect and examine fluid (most often for infected bursitis). Allows you to determine the type of microorganisms that caused inflammation in the joint capsule, as well as their resistance to antibiotics.
In some cases that require clarification, an MRI of the joint is performed, in particular, in cases of damage to the interosseous and radioulnar synovial bursae, which are difficult to diagnose due to their deep location. Consultation with other specialists can also be used, including a venereologist, phthisiatrician, rheumatologist (if rheumatoid arthritis, gout, specific bursitis is suspected).
Features of treatment
Treatment of the disease is complex and always begins with ensuring the rest of the limb using a fixing bandage, orthosis or splint. This helps eliminate pain, reduce swelling and prevent joint injury. If the cause of inflammation is microtrauma, immobilization of the hand must be preceded by the application of a cold compress.
Among the modern methods of treating acute bursitis, the following are distinguished:
- Intra-articular injections with GCS (hydrocortisone, betamethasone) to minimize relapses of the disease, instantly relieve pain and eliminate swelling. The procedure is recommended for use only in a medical institution, since infection may occur due to non-compliance with the rules of antiseptic treatment;
- Prescription of medications, including NSAIDs (aspirin, voltaren, diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.) to relieve inflammation and pain relief, drugs with chondroprotectors for tissue regeneration and antibiotics for infectious inflammation;
- The use of local remedies that will help not only relieve pain faster, but also speed up tissue restoration, reduce swelling and inflammation. These can be absorbable compresses with dimexide, as well as ointments with anti-inflammatory components, collagen, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate;
- Physiotherapy and physical therapy, through which it becomes possible to relieve local symptoms of bursitis. They are recommended for patients with a chronic course of the process, as well as in the subacute period. The following physiotechniques are usually used: ultrasound, shock wave therapy, UHF, microcurrents, phonophoresis, electrophoresis, dry heat, paraffin therapy and balneotherapy, massage.
For atrophy or necrosis of tissues accompanying the chronic process, as well as for purulent inflammation of the bursa, surgical treatment methods are used (excision of the bursa under local anesthesia). They are usually carried out if there is no effect as a result of the use of conservative therapy for one to two months, including with the fistulous form of bursitis. In case of frequent exacerbations of the disease, all tissues of the joint capsule or its separate part are removed without opening it, after which a splint is applied and comprehensive rehabilitation is carried out in a sports medicine center.
Thus, only complex therapy in combination with the wide capabilities of a physiotherapy room can give a positive result in the treatment of the disease in question.
The modern equipment of our center allows specialists to use highly effective treatment methods. Immediately after diagnostic measures, an optimal treatment regimen is selected for each specific case, aimed at restoring performance and returning the patient to an active life.
Our specialists have extensive experience in treating elbow bursitis. After just a few weeks, patients forget about pain, and repeated images show positive dynamics in 80–90% of cases.
Complications
The main complications of acute bursitis are: purulent arthritis, sepsis, phlegmon, fistula formation, osteomyelitis, lymphadenitis. With the development of a purulent process, mechanotherapy, as well as any physical procedures, are contraindicated and are not carried out during the first three weeks.
Hospitalization is recommended for patients who have:
- severe infection with high fever, abscess, which requires immediate opening and drainage to eliminate;
- there is no positive dynamics after long-term conservative treatment (usually a referral is issued after two months, but can be issued earlier if significant discomfort persists).
Therapy in the acute phase of the disease is more successful compared to that of the chronic form. That is why the patient should not delay visiting the clinic and should not self-medicate.
Prevention
For patients with damage to the elbow joint, specific preventive measures have not yet been developed. But dynamic observation by a specialist is recommended after complex treatment, which should be provided at least once every quarter of the year.
The following recommendations may also be helpful:
If there are abrasions, scratches and small cuts, it is always necessary to disinfect these areas using antiseptic agents; If you experience the slightest pain in your elbow, you should avoid intense physical activity; It is advisable to switch to dietary nutrition and ensure complete rest of the limb.
The modern rhythm of life obliges many of us to move a lot and actively, undergoing unusual physical activity. As a result, even the strongest joints may fail. That is why it is necessary to take care of yourself in advance and protect your joints, especially if the profession involves heavy physical labor. For these purposes, special bandages and emollients can be used when resting on the elbows. When performing long-term work, it is imperative to take short breaks and allow yourself to rest.
Before training, athletes are recommended to do “warm-up” exercises to help stretch their muscles. Swimming, walking or running are recommended as additional exercises for all patients with joint problems.
The result of treatment can be negatively affected by:
- patient refusal to visit a physiotherapy room;
- his dishonest attitude and non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations, in particular, refusal of antibiotics in the event of the development of infectious complications;
- the use of physical activity during treatment.
Causes of gout
Risk factors for the development of gout include all conditions that increase the level of uric acid in the blood. This may be an increase in its intake, for example, by eating large amounts of protein, especially red meat. Uric acid can be endogenous, that is, formed from the tissues of one’s own body, for example, during antitumor therapy or autoimmune processes. If the pathological process develops as a result of any disease or its therapy, they speak of secondary gout.
Hyperuricemia may result from disruption of normal urate excretion in kidney diseases complicated by renal failure. There are situations when an increase in the production of uric acid is accompanied by a violation of its excretion - during states of shock, alcohol consumption. For this reason, combining gout and alcohol is not recommended.
A hereditary predisposition to gout has also been proven, which lies in the peculiarities of purine metabolism. Genetically determined gout is called idiopathic. It is quite rare, accounting for approximately 10% of all cases of primary gout (the remaining 90% are associated with impaired excretion of uric acid).
Hereditary predisposition to gout
The source of uric acid in the human body is purine bases (adenine and guanine), which are part of nucleic acids, and purine nucleosides (a structural component of ATP). Nucleic acids enter the body with food or are synthesized endogenously (mainly). Several enzymes are involved in the metabolism of purine bases, defects in the structure of two of them have been proven to lead to increased synthesis of uric acid: deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HKGPT) and increased activity of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-synthetase. In the presence of these transformations, the development of gout in children is possible. Both of these enzymes are controlled by genes linked to the X chromosome, so males are more likely to suffer from hereditary gout.
Provoking factors
An attack of gout is usually preceded by exposure to provoking factors:
- alcohol intake (the mechanism is presumably associated with an increase in the formation of urates due to the intensive breakdown of ATP when alcohol enters the body, as well as with an increase in the content of lactic acid, which impairs the excretion of urates by the kidneys);
- changes in diet, while a gout attack can be triggered by both overeating (especially fatty meat or fish) and starvation;
- injury or overload of the joint (for example, during long walking);
- taking certain medications, especially diuretics.
Signs of gout
The deposition of uric acid crystals does not immediately lead to pain. At the initial asymptomatic stage, the disease is diagnosed extremely rarely, although almost half of the patients experience attacks of renal colic before the onset of joint pain - urolithiasis develops before gout.
Most often, gout is diagnosed after the first attack of arthritis. The affected joint swells, the skin over it becomes hyperemic and hot, severe pain appears, which limits mobility in the joint. Symptoms of gout depend on the location of the lesion. Most often, isolated monoarthritis of the metatarsophalangeal joint occurs (up to 65% of cases); other joints of the legs are much less often affected (gout in the knee, ankle, other joints of the foot). Gout on the hands is extremely rare, which is due to the structural features of cartilage tissue.
Gout: symptoms and signs, photos
A characteristic sign of pathology is the formation of tophi. The pain is localized in the area where the lump appears. Over time, pain occurs not only with pressure. The pain becomes chronic, bothers you at night, and significantly reduces your quality of life.
On foot
Gout most often affects the legs. In numerous medical photographs you can see an enlarged, reddened ankle. The skin is tightened and acquires a glossy shine.
On hands
Tophi are formed especially actively on the elbow bends. Over time, pain develops and there is difficulty in bending or straightening the arm.
On the soles of my feet
The classic presentation is an enlargement of the joint between the metatarsal bone and the phalanx of the big toe. The joint enlarges many times, turns red, and causes pain when walking.
Shoulder joint
Pathology on the shoulder is more difficult to diagnose than on the knee or foot. A characteristic symptom is the inability to raise the arm high, the development of pain, and the appearance of lumps when palpated.
Knee joint
The knee area is susceptible to salt deposits due to its structural features. Knees experience increased daily stress. The development of the disease at the initial stage is expressed by crunching of the knees when squatting, and the occurrence of sharp pain in the evenings and mornings.
Finger joints
If the hands suffer from pathology, then tophi become visible to the naked eye. The fingers swell into different shapes. The phalanges swell, turn red, and a glossy sheen appears in the modified areas.
Arthritis
Relapsing arthritis is the clinical manifestation of gout. A classic example is inflammation of the big toe.
Classification of gout
- Acute attack of gout. Sharp pain in the affected joint is accompanied by changes in the skin over it and a deterioration in overall health. As a rule, one joint is affected; polyarthritis is rare and predominantly affects women. Fever can be febrile, with severe intoxication. Movement in the joint is impossible due to severe pain. An acute attack most often begins at night after exposure to provoking factors. The first attack occurs suddenly, and subsequent ones may be preceded by tingling sensations. Without treatment, gout attacks become more frequent and new joints may become inflamed.
- Subacute course. For a long time, the patient may experience mild pain in the area of the affected joint, swelling and other signs of inflammation periodically appear.
- Interictal period. Between attacks, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient feels absolutely healthy, so doctors talk about the intermittent course characteristic of gout. Remission can last for several years, but usually attacks recur 1-2 times a year.
Atypical forms of gout
Diagnosis of atypical forms of gout is especially difficult; there are several of them:
- rheumatoid-like;
- pseudophlegmonous;
- polyarthritic (migratory);
- asthenic;
- periarthritic form, that is, when the inflammation is localized in the tendons and periarticular bursae (bursitis and tendonitis) without involving the joints. This form is most often localized in the heel tendon area.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Gout as a joint disease
Gout is a joint disease associated with increased uric acid in the body. Its historical name is “disease of kings.” It was believed that rich people, leading an idle life, overeated and abused alcohol. The consequences were dire: pain in the joints due to salt deposits.
At one time, gout was considered a type of osteoarthritis. In the 17th century, doctors proved that this is a separate disease. The disease is typical for middle-aged males (40-45 years old). Women suffer during climate change.
Formation of tophi in gout
Diagnosis of gout
Diagnosis of gout includes clinical and laboratory criteria. The clinical criterion is the identification of tophi, and the laboratory criterion is an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood. It is important that the threshold values for this indicator for diagnosing gout are different in men and women (>0.42 mLmol/L in men and >0.36 mLmol/L in women). The content of uric acid in urine is also determined, sometimes dynamically, after a week of following a therapeutic diet.
To diagnose gout, other tests (blood, urine) can be prescribed, but the most important is blood biochemistry. Hyperuricemia without clinical signs does not warrant a diagnosis, since arthritis develops in less than 10% of patients with elevated uric acid levels.
ultrasound of joints are used as auxiliary methods for diagnosing gout.
, which allows for a more reliable assessment of the presence and size of tophi. Tophi can have not only subcutaneous localization, they can be located in bones and internal organs. Such formations can only be detected using instrumental diagnostic methods.
In chronic gout, signs of cartilage destruction (narrowing of the joint space) and marginal bone erosions are determined by X-ray. The longer the disease lasts, the more pronounced the destruction becomes. Changes can be detected even in those joints that do not bother the patient.
Sometimes, in order to clarify the diagnosis, a trial treatment with colchicine is prescribed. In most cases, gout shows rapid positive dynamics, which serves as the basis for confirming the diagnosis. But it is worth considering that colchicine is also effective for some other diseases.
Treatment of gout
Exacerbation of gout: what to do?
Treatment of gout during an exacerbation most often requires hospitalization in a specialized department, especially if the exacerbation is the first and detailed diagnosis is necessary. When asked which doctor treats gout, there may be several answers. Ideally, this is a rheumatologist, but not all hospitals have this specialist, so you can contact a therapist or surgeon.
General measures include fixing the limb at rest, applying ice, and when the pain subsides, applying a warm compress. Drinking plenty of fluids or infusion therapy is prescribed to enhance the excretion of urate.
Treatment of gout with medications has two main goals: suppressing inflammation and reducing pain. Colchicine or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed, which in most cases give a fairly quick effect.
If the condition does not improve, then glucocorticosteroids (GCS) are used, sometimes even injecting them directly into the joint cavity. The drugs are prescribed orally or parenterally; there are ointments and creams for gout, which mainly contain NSAIDs.
To more quickly restore joint mobility and resolve the inflammatory infiltrate, physiotherapy is used (ultraviolet irradiation, UHF electric field, pulsed currents, dimexide applications).
Without treatment, a gout attack goes away on its own, but this process can drag on for several days, which is painful for the patient.
Treatment of gout during the interictal period
Between attacks, during the period of remission, active therapy is not required, although there are a number of recommendations, the implementation of which helps reduce the frequency of exacerbations. Treatment of gout during the interictal period is carried out at home.
The most important thing for gout is proper nutrition. The diet for gout should be minimal in foods containing purines (meat and fish, coffee, tea, cocoa). Very often, a disorder of purine metabolism is accompanied by dyslipidemia, so unsaturated fatty acids are included in the diet for gout. Fasting is strictly contraindicated, as it leads to the breakdown of one's own tissues and an increase in the level of purines and uric acid.
To reduce the amount of urate in the blood, drug treatment for gout may be indicated. For this purpose, uricodepressants (reduce the synthesis of uric acid) and uricosuric drugs (increase the excretion of uric acid, reducing reabsorption and increasing the secretion of urate in the renal tubules) are used. There are medications for gout of mixed action. The choice of drugs depends on the pathogenesis of the disease in a particular patient. Taking uricosuric drugs (anturan, urodan) is indicated only if renal function is not impaired and there are no signs of urolithiasis. When prescribed, daily diuresis should be at least 2 liters.
Allopurinol is one of the most well-known medications for gout. It inhibits xanthine oxidase, preventing the formation of uric acid from purines, that is, it belongs to the group of uricodepressive drugs.
Physiotherapy courses are often prescribed between attacks: ultrasound for crushing and resorption of crystals, phonophoresis with hydrocortisone to combat inflammation, heat therapy.
Treatment of gout with folk remedies
Folk remedies for gout are recommended to be used during remission or in subacute cases - during an attack they can only have an auxiliary value.
- Treatment of gout with iodine and aspirin - 5 aspirin tablets should be crushed and dissolved in 10 ml of iodine. Before going to bed, wipe the affected joints with the resulting liquid and wrap them in a warm cloth. You can take baths with iodine (9 drops of iodine per 3 liters of water) - this is one of the most popular folk remedies for gout of the legs.
- Treating gout with herbs is a very gentle but effective method if used for a long time. You can make chamomile baths, brew tea from a string or lingonberry leaves.
- Treating gout with bay leaves is becoming increasingly popular. Decoctions and ointments are made from it, as it is believed that laurel has a beneficial effect on joint tissue.
Compresses
Carrying out these therapeutic procedures will eliminate swelling of the joints and mild discomfort that occurs when the weather changes, exacerbation of other chronic pathologies, and after physical activity. Fresh young leaves of cabbage, horseradish, plantain, and burdock are used for compresses. They are washed with running water and soaked for a couple of hours, then dried with a paper towel. Doctors recommend additionally scalding plant materials with boiling water to prevent infection.
Compress for toes for gout.
Leaves for compresses can be used in two ways:
- vegetable raw materials (1 large leaf or 2-3 small ones) are crushed using a blender or simply ground to a pulp in a porcelain mortar. Add a teaspoon of almond, peach or wheat germ cosmetic oil, mix thoroughly and apply to sore joints;
- The leaf is kneaded well until drops of juice appear on its surface, then a layer of liquid honey is applied to it. Rub any fatty cream into the joint and apply a sheet.
To enhance the therapeutic effect, you can apply plastic film and thick fabric over the compress, securing the bandage with gauze or an elastic bandage. The duration of the treatment procedure is 1-2 hours. If pain, burning, or a “twitching” sensation occurs, you should quickly wash off the remaining mixture from the surface of the skin.
Pain in the joints of the fingers due to gout.Diet for gout
Nutrition for gout is one of the key treatment points. It is the correction of the intake of purines in the body that makes it possible to minimize the frequency of exacerbations and alleviate the course of the disease as a whole. The treatment table for gout and urolithiasis, which has a similar pathogenesis, has No. 6. Its features are:
- exclusion of foods rich in purines and oxalic acid;
- limiting protein intake, dietary meats (turkey, rabbit, chicken) are recommended;
- limiting the consumption of refractory fats;
- moderate salt restriction;
- increasing the amount of fluid consumed (if there are no contraindications to this, for example, arterial hypertension or kidney disease with impaired excretory function);
- alkalization of food through dairy products, vegetables, fruits, a vegetarian diet is ideal for gout;
- greens are allowed, but parsley and green onions are limited;
- It is recommended to boil meat and fish; other products can be cooked in any way.
What should you not eat if you have gout?
For gout, it is recommended to completely exclude from the diet offal, smoked meats, salty and spicy cheeses, animal fats, as well as fried and salted fish, caviar, and canned food. The consumption of legumes (peas, beans, etc.) is also prohibited. Sauces, spices, and alcohol can worsen the course of the disease. From sweets, chocolate and cream are prohibited, from berries - raspberries, grapes, figs.
What to drink for gout?
If you have gout, it is recommended to completely avoid coffee, cocoa, strong tea and, of course, alcohol. All types of alcoholic beverages are prohibited, including beer. Juices are allowed, especially freshly squeezed, fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir), as well as regular milk.
Diet during a gout attack
In case of exacerbation of gout, meat and fish are strictly excluded, sometimes fasting days are arranged (every other day). Fasting days are by no means fasting, which will lead to the breakdown of your own tissues and an increase in uric acid in the blood. Fruit and vegetable fasting days involve the consumption of 1-1.5 kg of vegetables and fruits (except legumes), cottage cheese and kefir fasting days - approximately 400 g of low-fat cottage cheese and 500 g of kefir per day, dairy or kefir fasting days - 1-2 liters of milk or kefir. Such fasting days contribute to the effective alkalization of urine, that is, they increase the solubility and intensity of excretion of uric acid.
Why is gout dangerous?
Gout, diagnosed in the early stages, with adequate treatment does not lead to serious consequences and can become aggravated very rarely. In other cases, a progressive increase in uric acid levels leads to irreversible deformation of the joints with limited mobility. Very often, gout occurs together with urolithiasis, which has similar mechanisms of pathogenesis. This combination is potentially dangerous due to the possibility of reducing renal function and worsening hyperuricemia.
Risk group for developing gout
The risk group for the development of gout consists of older men, especially those suffering from atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, and arterial hypertension. There is also a high risk of developing gout during antitumor therapy. If there are cases of gout in the family, then the likelihood of developing the disease is much higher. The risk group includes people who consume large amounts of protein foods and abuse alcohol.
Prevention of gout
The main thing in the prevention of gout is proper nutrition, especially if a biochemical blood test revealed an increase in uric acid or there is a hereditary predisposition. It is also recommended to limit alcohol consumption and treat concomitant diseases that may contribute to the development of gout.
Dietary recommendations are similar to those for gout, although they do not require such strict adherence. It is recommended to limit proteins and fats, spicy and smoked foods, preservatives and spices with a parallel increase in the diet of vegetables (except legumes) and fruits, and dairy products. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids to improve urate elimination.
General strengthening of the body will help maintain its ability to regulate the balance of metabolic processes. For this purpose, dosed physical activity that trains the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is recommended.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Comments from nutritionists. Pros and cons of the diet.
Treatment of gout at the Gorny sanatorium necessarily includes dietary nutrition. Patients receive recommendations on how to eat properly if they have gout at home, which helps avoid exacerbations and complications.
“The right choice of a sanatorium is a significant step towards maintaining and increasing health. “Gorny” is a resort complex that combines the experience and knowledge of Russian and Soviet balneology. The presence of modern medical equipment and innovative installations, the professionalism of the staff and love for their work will serve as the key to extending longevity,” - head doctor of the sanatorium Alexander Olegovich Karaulov.