Physiological explanation of bruxism
Teeth grinding occurs due to spasm of the chewing muscles, clenching of the jaws and their strong movement. The peculiarity of the disease is the fact that it occurs involuntarily. Most often this occurs during the patient's sleep at night, but some also worry during the daytime. In the first case, the pathology is called bruxism, in the second - bruxiomania. During the period of primary occlusion formation, the disease manifests itself in at least half of children. This is considered normal if it goes away by age 7.
Signs
Odonterism manifests itself:
- grinding,
- clicking
- creaking,
- clanking,
- knocking
- strong clenching of teeth.
It may intensify during stressful situations, physical exertion, at night or during the day. Night-time grinding often irritates loved ones, and daytime grinding often irritates work colleagues. At night, when a person cannot control himself, attacks can last from 15 seconds. up to several minutes at individual intervals.
Half of children under the age of seven are exposed to odonterism, which more often goes away without a trace with age. This symptom cannot be ignored, so as not to cause serious consequences that are dangerous to the body. Adult bruxers, the name given to people who grind their teeth, make up 15%. Most of them have no idea about this.
Teeth grinding is often perceived as a bad habit that can be overcome by willpower. But the fact that teeth grinding occurs in a sleepy state indicates that this problem cannot be solved by willpower.
Symptoms of Bruxism
Grinding of teeth during sleep is the main symptom of bruxism. Most often, the patient does not notice this symptom on his own, and complaints from loved ones and relatives become the basis for contacting a doctor. At night, the disease manifests itself as short-term attacks of grinding or chattering of teeth, excessive tension in the masticatory muscles. It is also possible to increase blood pressure and increase heart rate during an attack. A person does not wake up from this, so he cannot remember how he is feeling.
During the day, indirect signs of bruxism appear, which can also be the basis for a diagnosis. These include:
- headaches, dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue;
- pain in the temporomandibular joint, fatigue of the masticatory muscles;
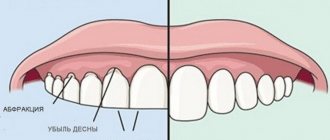
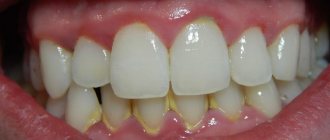
- with a long course of the disease - pathological abrasion of dental surfaces, increased sensitivity of teeth, the appearance of chips and cracks in the enamel;
- it is possible to develop periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth), as a result of which the teeth begin to loosen and fall out;
- During an attack of bruxism, there is a significant load on the dental surfaces, which can cause chips of fillings, crowns, restorations, as well as cracks or complete breakage of dentures.
Teeth grinding at night is not just a dental problem. Patients who suffer from regular bouts of bruxism develop temporomandibular joint dysfunction. Painful sensations appear in this area, which intensify while moving the jaw, when talking or eating. The chewing muscles are symmetrically inflamed and increased in volume, tense. The pain can spread not only to the temporomandibular joint area, but also to the person’s neck and shoulders.
In some cases, constant grinding of teeth causes damage to the oral mucosa. In such patients, the disease is accompanied by gingivitis - inflammation of the gums. There is also a risk of developing lichen planus, growths (fibroids) in the mouth, a scalloped tongue (scalloped), as well as scratches and abrasions if you wear dentures.
Possible causes of the disease
Bruxism can occur in patients of any age. If in childhood it is associated with teething and bite formation, then in adults it has several theories of origin. The disease can be a dental, psychological, neurogenic problem, and is also studied in the field of otolaryngology. Since a single cause for the development of this pathology has not been established, several theories of its development have been identified.
| Theory | Definition |
Psychological | Many doctors are of the opinion that teeth grinding at night occurs due to a violation of psycho-emotional balance. The cause of involuntary spasm of the masticatory muscles can be either negative events and stress, or strong positive emotions. During the day, patients experience emotional instability, which may also be associated with old events. |
Neurogenic | Another theory for the development of bruxism associates the disease with disruption of the central or peripheral nervous system. Its proof is the fact that teeth grinding often occurs in combination with headaches and insomnia, somnambulism, and sleep apnea (short-term cessation of breathing during sleep). Advanced forms occur against the background of nocturnal enuresis and can be complicated by attacks of epilepsy or muscle tremors (involuntary contraction of the body muscles). During the diagnosis, organic lesions of the trigeminal nerve are detected. |
Dental | Bruxism can be a consequence of pathologies in the structure and functioning of the dental system. Regardless of age, the disease can occur due to malocclusion, dental disease, or prolonged wearing of incorrectly fitted dentures or crowns. Anomalies in the structure of teeth are also included in the list of possible causes of bruxism. |
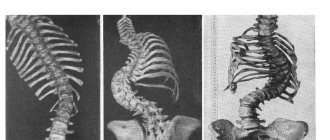
Osteopathic | Some experts consider spasms of the masticatory muscles as a protective mechanism of the body. Thus, in children this phenomenon often manifests itself after a complicated birth with possible weakness of the skull bones and sutures. Many adults who suffer from regular attacks of bruxism are often simultaneously diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Osteopathic pathology also identifies incorrectly performed dental prosthetics as one of the causes of night grinding. |
Other reasons | Another theory, which, however, has no evidence yet, is teeth grinding due to impaired nasal breathing. Thus, attacks can occur in people with a deviated nasal septum and difficulty passing air through the nasal passages. In addition, the presence of adenoids and frequent colds, which manifest as rhinitis (runny nose), may be important. |
The causes of bruxism are determined individually. It is possible that the disease will develop due to a combination of several factors at the same time. The problem of night grinding continues to be studied by leading doctors around the world. In particular, specialists from the Clinical Institute of the Brain successfully diagnose this disease and determine its causes on an individual basis.
What should the mother do and how to help the child?
You can help your child cope with teeth grinding at home. The task of parents is to relax the child, especially in the evening. Suitable for relieving tension:
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- correct daily routine;
- walks in the open air;
- drinking enough water;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that excite the nervous system: chocolate, coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, etc.;
- last meal – an hour before bedtime;
- hot bath before bed;
- refusal of active games, quiet activities in the evening: drawing, listening to lullabies, etc.
In addition, heart-to-heart conversations with your child can help. If the child does not speak out, he will go to bed with anxious thoughts. This will trigger an attack.
The following techniques will help reduce facial muscle tension:
- heat compresses (including for pain in the morning);
- chewing solid food;
- giving up chewing gum.
Diagnostic methods
Since bruxism is considered a polyetiological disease, before starting its treatment it is important to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. To begin with, a standard procedure is prescribed using brux checkers. These devices are mouthguards to be worn at night. After the patient wears them overnight, the impression is sent to the dentist for analysis. This way you can determine which teeth are experiencing overstrain, and how much the disease is related to the bite and location of a person’s teeth.
In order to diagnose pathologies of the masticatory muscles, electromyographic analysis is used. This research method will allow you to assess the condition of the muscles at rest and in motion. This way you can determine myofascial pain syndrome, and by the location and function of the muscles, you can identify incorrectly selected and installed prostheses. In children, the mechanism of development of the disease is often associated with the process of teething. Symptoms of bruxism will help parents identify and pay attention to their child’s malocclusion in the early stages.
You may need to consult a neurologist, otolaryngologist, psychotherapist, or maxillofacial surgeon. Based on the data of a comprehensive examination, a final diagnosis can be made and a suitable treatment regimen can be prescribed. The Clinical Brain Institute employs qualified specialists who have successful experience in treating bruxism in patients of all ages. There are also all conditions for examination using instrumental methods.
Treatment of bruxism
The treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account diagnostic data and the patient’s age. In children under 6-7 years of age, the disease does not require emergency intervention. The patient is monitored by a dentist, but all symptoms in most cases go away on their own, without treatment.
In adults, when signs of bruxism are detected, a set of methods is prescribed. They depend on the form of the disease and its severity, as well as accompanying symptoms. The treatment regimen may include several areas:
- correction of bite and elimination of dental defects;
- drug therapy;
- psychotherapy;
- relaxation techniques;
- massotherapy.
At the first stage, it is important to eliminate all dental problems that can cause spasms of the masticatory muscles. Modern medicine allows you to correct your bite with the help of rigid fixation devices, which also help with anomalies in the location of individual teeth. Missing fragments are successfully replaced with prostheses or implants - the prosthetic method is selected individually. Selective grinding of tooth surfaces may also be necessary. First, it is necessary to completely eliminate those pathologies that interfere with the normal functioning of the temporomandibular joint. When all the symptoms of night grinding disappear, you can begin to eliminate aesthetic problems: restoration of defects, installation of fillings or veneers. Treatment of periodontitis also occurs after the attacks of night grinding stop.
To stop attacks, a course of drug therapy may be necessary. It includes sedatives and sleep aids. Solutions of magnesium, calcium, and B vitamins are also effective - they have a positive effect on the processes of neuromuscular conduction and normalize the functioning of the central nervous system. Treatment tactics are aimed at reducing the manifestations of convulsive syndrome.
The use of soft mouth guards may be necessary as symptomatic therapy. They are made of rubber or soft plastic and perform a protective function. These devices are designed to be worn at night, when the patient cannot control the functioning of the chewing muscles, and spasms occur involuntarily. Soft materials prevent abrasion of dental surfaces and the development of dangerous complications. However, they cannot reduce the frequency of attacks or prevent their occurrence.
Additional methods for treating bruxism
The psychotherapy method is considered effective for bruxism. Attacks of teeth grinding often occur against the background of a weakened psycho-emotional state, so self-control and relaxation practices come to the fore. The approach to each patient is determined individually by the doctor. It may be impossible to discover the root cause of problems on your own.
At home, you can massage your jaw, neck and chin. You should perform smooth movements with your fingers in the upper part of the neck, as well as on the side surfaces of the jaws. The procedure should not be accompanied by painful sensations. Its essence comes down to mechanical relaxation of muscles, as a result of which their spasms occur less frequently. Exercise therapy, a simple set of exercises to increase muscle elasticity, has a similar effect. Throughout the day, it is important to ensure that you keep these muscles relaxed and do not clench your jaw.
Breathing exercises are also useful. It allows not only to cause relaxation of the masticatory muscles, but also to ensure a sufficient supply of oxygen to the tissues of the nervous system. These exercises are also part of the system of self-control practices that are recommended for involuntary teeth grinding. At home, it is enough to practice deep breathing: air is slowly inhaled through the nose so that it fills the lungs as much as possible, and then exhaled through the mouth.
How to stop grinding your teeth in your sleep
Odonterism is treated by a dentist, or, if psychosomatic causes are present, by a psychotherapist. Therapy for bruxism depends on the reasons that triggered the appearance of teeth grinding. If symptoms appear due to poor-quality prosthetics, you need to replace the prostheses with better ones. Nervous tension, in which a person begins to chatter his teeth, is relieved by complete relaxation before bed.
The dentist is the first specialist who must differentiate the causes of bruxism
Bruxism therapy methods
In most cases, you can get rid of teeth grinding by using the following methods:
- During sleep, special mouth guards are used to prevent teeth from closing and grinding.
- The patient relaxes, getting rid of tension caused by stress.
- Therapy for increased wear of tooth enamel.
- Orthopedic therapy.
In the chronic form of odonterism, orthopedic dental treatment is used. The chronic course leads to abrasion and loosening, as well as displacement in the dentition. In this case, the teeth are strengthened with special devices that fix them.
The production of mouthguards is carried out according to individual orders, which prevents the teeth from closing and abrading. There is no treatment for symptoms. If the patient’s control of the position of the teeth is negative, a day splint can be used, which should be worn without removing it.
The splint has positive properties: it is not visible to others, does not interfere with the chewing process, and does not create difficulties when talking. A malocclusion can also cause teeth to involuntarily close together. In such cases, repositioning splints are used, which eliminates spasms of the facial and jaw muscles.
Ways to relax before bed
To get rid of teeth grinding, you should learn to relax before going to bed. Helps to relax in the evening:
- Listening to calm music.
- Reading books.
- Walking before bed.
- Relaxing baths.
Will medications help?
If the diagnosis reveals more complex cases, the dentist gives a referral to see a psychotherapist to find out why overstrain develops. For spontaneous grinding of teeth, medications are not used. To relieve tension, sedatives are prescribed, and vitamins are prescribed to maintain the nervous system.
In the most advanced cases, Botox injections are used into the jaw muscles to prevent its spontaneous contraction.
Loading jaws
Treatment for nocturnal bruxism involves loading the jaw with movements. Tired masticatory muscles will not spontaneously contract during daytime wakefulness. Therefore, you should load them with chewing solid food during the day.
In adults, treatment of bruxism is based on the presence of good self-control, which helps achieve long-term results. Doctors recommend relaxing the muscles of the shoulders, neck, and mouth using cold or hot compresses, as well as self-massage and special exercises.
It is recommended to use remineralizing toothpaste and gel to strengthen weakened enamel
You should exclude strong tea, coffee, and hard foods from your diet, and drink enough high-quality water. Procedures to restore dental aesthetics are permitted after complete relief from bruxism.
Possible consequences and complications of the disease
Bruxism, if left untreated, gradually progresses. Attacks occur more often and begin to occur even during the daytime. At the same time, a person’s sleep quality deteriorates, performance, memory concentration and attention decrease. The functioning of the central nervous system is also disrupted, and constant daytime sleepiness develops. In addition, the disease can cause more dangerous complications:
- abrasion of the surfaces of individual teeth or dentition, which is accompanied by pain and increases the risk of developing caries;
- inflammatory diseases of the structures surrounding the teeth;
- bleeding gums, which are damaged when the jaws involuntarily close;
- weakening and inflammation of the temporomandibular joint - pain increases while eating or any other jaw movements;
- tension often spreads to the cervical vertebrae, which can trigger the development of osteochondrosis.
It is worth understanding that complications develop only in advanced cases. Modern medicine has all the necessary means and methods for treating bruxism, which allows you to get rid of its manifestations at any age. Despite the fact that attacks occur mainly at night, they are not the only symptom of the disease. Feeling of discomfort, tension and pain in the temporomandibular joint, increased sensitivity of the teeth - these problems should be addressed to a specialist.
Adults
Adults suffering from bruxism account for only 10-15% of the total number of patients. However, this category of patients cannot hope for self-elimination of the problem. In this case, the chronic course of the disease leads to a number of serious problems, including:
- gradual tooth decay;
- erasing crowns and dentures;
- arthritis of the temporomandibular joint.
These problems are formed against the background of a decrease in the quality of life: a person does not get enough sleep, is constantly under stress, feels psychological discomfort, and depression cannot be ruled out in the future.
It has been established that people in professions that require high concentration, precision and accuracy in work (jewelers, watchmakers, surgeons, senior managers) more often suffer from bruxism.
If you have a marked tendency to bruxism, you should: learn to relax, minimize stress factors, limit food intake before bed, include fruits and solid vegetables in your diet, leave only quiet activities for the evening, take warm baths before bed (all of the above is relevant against the background of competent medical treatment) .
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for bruxism is favorable. Treatment is long-term and can take several months. In childhood, these symptoms require constant monitoring and often go away on their own. As a preventative measure, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- avoid stress and nervous tension;
- normalize sleep and wakefulness;
- do not eat immediately before bed, avoid active physical activity in the afternoon;
- undergo regular preventive examinations at the dentist.
Bruxism is a common pathology. It manifests itself in no less than 40-50% of preschool children and 7-10% of adults. The main difficulty is to detect its symptoms, since they appear at night. Specialists from the Clinical Brain Institute will conduct a full diagnosis, taking into account the patient’s age and physiological condition, and select the most effective treatment regimen.
Lifestyle and home remedies –
These self-help steps will help prevent or reduce bruxism...
- Reduce stress – listening to music, taking warm baths and any other pleasant little things will help you relieve stress, and thus reduce the psychological component of the cause of bruxism.
- Avoid stimulants in the evening - do not drink caffeinated coffee or tea after lunch, avoid alcohol and smoking in the evening, because. they can make bruxism worse. Try to avoid drinking sugary carbonated drinks (Cola, Pepsi, etc.), as well as chocolate.
- Get enough sleep - a good night's sleep will help reduce the symptoms of bruxism.
- Heat compresses - before going to bed, use a heating pad to apply heat compresses to the muscles of mastication (these are those located in front and below the ear, outside the branch of the lower jaw). This will allow them to be relaxed at night.
- Avoid bad habits - try not to chew a pencil/pen, do not chew chewing gum, because... all this stimulates the tone of the masticatory muscles. It is very important to train yourself not to clench your teeth too hard during the daytime. If you notice that your teeth are clenching excessively, then try to keep the tip of your tongue between your teeth while pursing your lips. This practice trains the jaw muscles to relax.