Cipromed drops 0.3%
Cipromed (Tsipromed) 0.3% - antibacterial eye drops for topical use. They look like a simple clear or yellowish solution. An ophthalmologist prescribes this remedy for the following infectious and inflammatory processes in the organs of vision:
In this article
- Cipromed drops 0.3%
- Contraindications: when not to use Tsipromed
- Directions for use and doses
- Does Tsipromed have side effects?
- Storage of Tsipromed
- Analogs
- The importance of examination and consultation with a doctor
- conjunctivitis in acute or subacute form;
- anterior uveitis;
- dacryocystitis;
- keratitis;
- blepharitis and other inflammations of the eyelids;
- iridocyclitis;
- meibomite;
- endophthalmitis;
- infectious complications in case of injuries to the organs of vision and after operations.
The effect of Tsipromed begins within 10 minutes, and the effect will last up to 6 hours.
Directions for use and doses
Depending on the disease, the dosage of drops is calculated.
In acute forms of conjunctivitis, it is necessary to drop 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye. The duration of the course and frequency of administration depend on the severity of the disease.
Patients with acute bacterial conjunctivitis, ulcerative or scaly blepharitis should apply drops into the eyes 4-8 times a day (depending on how severe the inflammatory process is). The course of treatment for such diseases is from 5 days to 2 weeks.
Patients with keratitis are recommended to instill one drop at least 6 times a day. If a visible positive effect appears, therapy is extended to 2 or even 4 weeks, depending on the severity of the corneal damage.
For diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the drug is prescribed one drop 8 to 12 times a day. Patients suffering from anterior uveitis can receive the same prescription. Depending on the nature of the disease, treatment may take two to three weeks.
Persons suffering from acute dacryocystitis or canaliculitis should use Tsipromed 6 to 12 times a day. If the disease has taken a chronic form - from 4 to 8 times a day.
In order to avoid infection and inflammatory processes after surgery, Cipromed 0.3% is instilled 4 to 6 times a day throughout the entire postoperative period. As a rule, it lasts from 6 days to a month.
Infectious conjunctivitis
Statistically the leading variant of inflammation of the conjunctiva. Depending on the pathogen, it is divided into subgroups: viral, bacterial, fungal. Moreover, the incidence in children is distributed among these subgroups with approximately equal frequency, while in adults predominantly viral forms are found (over 80%). In the overall structure of morbidity, the proportion of fungal conjunctivitis (ophthalmomycosis) is increasing, which is explained, first of all, by the catastrophically irresponsible and uncontrolled use of antibiotics by the population (when the bacterial flora is suppressed, fungal cultures, including pathogenic ones, are activated).
Drugs for the treatment of viral conjunctivitis
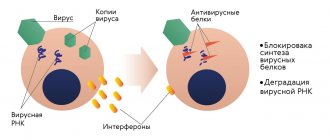
With viral conjunctivitis (it can be caused by influenza viruses, herpes, etc.; in total there are about 40 species dangerous to humans), the main therapeutic goal is to stimulate and intensify the immune response. For this purpose the following are appointed:
- eye drops based on human interferon (Ophthalmoferon, Interferon, etc.);
- drugs that stimulate the production of endogenous, own interferon (Poludan, Tsitovir, Cycloferon);
- eye ointments (Bonafton, Acyclovir, Florenal, etc.);
- according to indications - vasoconstrictor and/or moisturizing drugs (“artificial tears”), similar to Vizin, Oksial, etc.
Drops and ointments for bacterial (purulent) form
For bacterial conjunctivitis, antibiotics are prescribed:
- drops (Albucid, Levomitin, Tsipromed, etc.);
- eye ointments (tetracycline, erythromycin, gentamicin, ofloxacin);
- tablet drugs (Doxycycline, Sumamed, Vilprafen, etc.; for chlamydia, Levofloxacin, Lomefloxacin).
Only a specialist can prescribe medications (and their dosage, frequency and duration of use) and evaluate the effectiveness of their use! By contacting our ophthalmology center, you can be sure of an individual approach and high results in the treatment of eye diseases in children and adults.
Treatment of fungal infections (mycoses)
For fungal conjunctivitis (ophthalmomycosis), treatment, as a rule, lasts much longer than for other infectious conjunctivitis, and includes specific antimycotic agents, and antifungal eye drops are practically not produced on an industrial scale in the world - they are prepared extemporaneously (as needed): Fluconazole , Amphotericin et al.
Some cases require additional intake of tablet forms of the antimycotic, as well as the simultaneous use of anti-inflammatory, antihistamine (antiallergic) and antibacterial drops and ointments.
Fig. 3 Eye drops are placed behind the eyelid at night and provide long-lasting effects
Does Tsipromed have side effects?
If you are allergic to any components of the drug, a burning or itching sensation may occur after taking the drops. Pain, photophobia, swelling of the eyelids, decreased visual acuity, or active lacrimation may also occur. In patients with corneal ulcers, a white crystalline precipitate may appear.
What happens if you take Tsipromed
It is strictly prohibited to use the drug internally. If a person drinks eye drops, he may experience:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- headache;
- anxiety;
- fainting.
If Tsipromed gets into the stomach, it is recommended to rinse, ensure sufficient hydration of the body and create an acidic reaction for the urine to prevent the occurrence of crystalluria.
Tsipromed and contact lenses
If you wear soft contact lenses, it is best not to use Tsipromed drops, since the preservatives included in their composition can negatively affect eye tissue when interacting with the lens material. The drops are compatible with hard contact lenses. However, before using the drops in your eyes, be sure to remove your lenses. You can put them on again after at least 15 minutes.
Driving and using Tsipromed
After you drop Tsipromed into your eyes, there may be a short-term decrease in vision clarity and a slower reaction. Experts do not advise driving after using Tsipromed, as this may become a potential danger to your health and life, as well as the health and life of other drivers.
Tsiprolet eye drops
INSTRUCTIONS for the use of the medicinal product for medical use
CIPROLET®
Registration number: P N 012765/01 Trade name of the drug: Ciprolet® International nonproprietary name of the drug: ciprofloxacin. Chemical name: 4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-1-cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride monohydrate Dosage form: eye drops
Composition 1 ml of solution contains: Active ingredient: ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (equivalent to 3.0 mg of ciprofloxacin) - 3.49 mg/ml. Excipients: disodium edetate 0.50 mg, sodium chloride 9.00 mg, benzalkonium chloride 50% solution 0.0002 ml, hydrochloric acid 0.000034 mg, water for injection up to 1.0 ml.
Description Transparent, colorless or light yellow solution.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antimicrobial agent, fluoroquinolone.
ATX code: S01AX13
Pharmacological action Pharmacodynamics A broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, a fluoroquinolone derivative, suppresses bacterial DNA gyrase (topoisomerases II and IV, responsible for the process of supercoiling of chromosomal DNA around nuclear RNA, which is necessary for reading genetic information), disrupts DNA synthesis, growth and division of bacteria; causes pronounced morphological changes (including cell wall and membranes) and rapid death of the bacterial cell. It has a bactericidal effect on gram-negative organisms during the period of rest and division (since it affects not only DNA gyrase, but also causes lysis of the cell wall); it acts on gram-positive microorganisms only during the period of division. Low toxicity for the cells of the macroorganism is explained by the absence of DNA gyrase in them. While taking ciprofloxacin, there is no parallel development of resistance to other antibiotics that do not belong to the group of DNA gyrase inhibitors, which makes it highly effective against bacteria that are resistant, for example, to aminoglycosides, penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines and many other antibiotics. Gram-negative aerobic bacteria are sensitive to ciprofloxacin: enterobacteria (Escherichiacoli, Salmonellaspp., Shigellaspp., Citrobacterspp., Klebsiellaspp., Enterobacterspp., Proteusmirabilis, Proteusvulgaris, Serratiamarcescens, Hafniaalvei, Edwardsiellatarda, Providencia spp., Morganellamorganii, Vibriospp. , Yersiniaspp.), others gram-negative bacteria (Haemophilus spp., Pseudomonasaeruginosa, Moraxellacatarrhalis, Aeromonasspp., Pasteurellamultocida, Plesiomonasshigelloides, Campylobacterjejuni, Neisseriaspp.), some intracellular pathogens - Legionellapneumophila, Brucellaspp., Chlamydiatrachomatis, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, My cobacteriumkansasii, Corynebacteriumdiphtheriae; gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus spp. (Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus), Streptococcus spp. (Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae). Most staphylococci resistant to methicillin are also resistant to ciprofloxacin. The sensitivity of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Mycobacterium avium (located intracellularly) is moderate (high concentrations are required to suppress them). The following are resistant to the drug: Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas cepacia, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium difficile, Nocardia asteroides. Not effective against Treponema pallidum. Resistance develops extremely slowly, since, on the one hand, after the action of ciprofloxacin there are practically no persistent microorganisms left, and on the other hand, bacterial cells do not have enzymes that inactivate it.
Pharmacokinetics The maximum concentration of the drug (Cmax) in plasma when using eye drops is less than 5 ng/ml. The average concentration is below 2.5 ng/ml. After instillation, systemic absorption of the drug is possible. The drug is excreted through the kidneys mainly unchanged (50%) in the form of metabolites (up to 10%), about 15% is excreted through the intestines, and in nursing mothers it passes into breast milk.
Indications for use Local treatment of various infectious diseases of the eye and its appendages caused by bacteria sensitive to the drug: acute and subacute conjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blepharitis, bacterial corneal ulcers, bacterial keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis, chronic dacryocystitis and meibomitis. Preoperative prophylaxis in ophthalmic surgery. Treatment of postoperative infectious complications. Treatment and prevention of infectious complications of the eyes after injuries or foreign bodies.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin and other quinolone drugs, viral keratitis, pregnancy, lactation (breastfeeding), children (up to 1 year).
with caution in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular accident, and convulsive syndrome.
Method of administration and dosage Locally. For mild and moderately severe infections, instill 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye every 4 hours, for severe infections - 2 drops every hour. After the condition improves, the dose and frequency of instillations are reduced. For bacterial corneal ulcers: 1 drop every 15 minutes for 6 hours, then 1 drop every 30 minutes during waking hours; on day 2 – 1 drop every hour during waking hours; from days 3 to 14 – 1 drop every 4 hours during waking hours. If after 14 days of therapy epithelialization has not occurred, treatment can be continued.
Side effects Allergic reactions, itching, burning, mild soreness and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, nausea, rarely - swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, unpleasant taste in the mouth immediately after instillation, decreased visual acuity, the appearance of a white crystalline precipitate in patients with corneal ulcer, keratitis, keratopathy, corneal infiltration, development of superinfection.
Overdose There are no data on overdose of the drug when applied topically. If the drug is accidentally taken orally, there are no specific symptoms. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, fainting, and anxiety may occur. Treatment: standard emergency measures, adequate fluid intake, acidification of urine to prevent crystalluria.
Interaction When combined with other antimicrobial drugs (beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, clindamycin, metronidazole), synergism is usually observed; can be successfully used in combination with azlocillin and ceftazidime for infections caused by Pseudomonas spp.; with mezlocillin, azlocillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics - for streptococcal infections; with isoxazolepenicillins and vancomycin - for staphylococcal infections; with metronidazole and clindamycin - for anaerobic infections. Ciprofloxacin solution is pharmaceutically incompatible with drugs with a pH value of 3-4 that are physically or chemically unstable.
Special instructions Eye drops can only be used topically; the drug cannot be administered subconjunctivally or into the anterior chamber of the eye. When using Tsiprolet® eye drops and other ophthalmic solutions, the interval between their administrations should be at least 5 minutes. During treatment with the drug, wearing contact lenses is not recommended. Patients who temporarily lose clarity of vision after application are not recommended to drive a car or work with complex machinery, or any complex equipment that requires clarity of vision, immediately after instillation of the drug.
Release form: Eye drops 3 mg/ml. 5 ml of the drug in a plastic dropper bottle with a screw cap. 1 bottle is placed in a cardboard box along with instructions for use.
Storage conditions List B. In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life 2 years. Use the drug within 1 month after opening the bottle. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription.
Manufacturer Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Manufacturing Location Plot No.2, Sudarshanpur Industrial Estate, Bais Godam, Jaipur 302006, SP-918, Phase III, Industrial Estate, Bhiwadi District, Alwar, India.
Address for sending claims: Representative office 115035, Moscow, Ovchinnikovskaya embankment, 20, building 1 tel., 783-29-01; Fax