Indications and contraindications
The medicine helps relieve discomfort associated with the following diseases:
- osteoarthritis;
- spondylitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- various forms of arthritis;
- relief of pain associated with ulcers in the stomach and duodenum.
Reasons for prescribing
Contraindications prescribed in the instructions include:
- severe sensitivity to naproxen, esomeprazole or any other additional substance in the composition;
- history of bronchial asthma;
- a history of urticaria or other manifestations of allergies that were associated with taking aspirin or other NSAIDs;
- severe liver dysfunction, kidney failure or severe impairment of their function;
- acute ulcer;
- bleeding in the stomach;
- cerebrovascular bleeding and other abnormalities with bleeding;
- use together with nelfinavir, atazanavir.
A process that inhibits the production of prostaglandins can have a negative impact on pregnancy and the development of the baby in the womb.
Analogs
To date, there are no analogues to Vimovo in terms of active ingredients. As substitutes, drugs from a pharmacological group are used that have the same effect on the body. Among the popular options it is worth highlighting:
- Advil;
- Artrum;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketoprofen;
- Bonifen;
- Ibufen;
- MIG 400;
- Nurofen active and others.
Regardless of which drug will be used, a diagnosis is carried out before prescription. The main purpose of the examination is to determine the effectiveness of therapy, as well as assess the risks of complications. If necessary, the dosage and course of treatment are adjusted.
Vimovo's analogs
There are no analogues of Vimovo tablets based on the active substance. Analogues of Vimovo according to the mechanism of action and belonging to the same pharmacological group include:
- Advil;
- Artrum;
- Algesir Ultra;
- ArthroCam;
- Bonifen;
- Bystrumcaps;
- Dexalgin 25;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ibufen;
- Ketoprofen;
- MIG 400;
- Naproxen-ICN;
- Nurofen active;
- Nurofen UltraCap;
- OKI;
- Rakstan-Sanovel;
- Teraflex Advance;
- Faspik;
- Flexen;
- Khairumath.
pharmachologic effect
- Vimovo is a combination drug that contains a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and a proton pump inhibitor. It is formulated as a sequential delivery tablet containing immediate-release esomeprazole magnesium in the coating and enteric-coated sustained-release naproxen in the core. This releases esomeprazole in the stomach before naproxen dissolves in the small intestine.
- The enteric coating prevents the release of naproxen at a pH below 5.5, thereby providing protection against the possible negative effects of naproxen on the gastric mucosa.
- Naproxen is an NSAID that has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
- Esomeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor, the S-isomer of omeprazole, which reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach by specifically inhibiting the proton pump in the parietal cells of the stomach. The S- and R-isomers of omeprazole have similar pharmacodynamic activities.
Drug interactions
Vimovo, according to the instructions, is not recommended to be combined with antiretroviral drugs; the drug should be used with caution with:
- Acetylsalicylic acid (in small doses);
- Diuretics;
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors;
- Corticosteroids;
- ACE inhibitors;
- Lithium preparations;
- Methotrexate;
- Sulfonylurea and hydantoin derivatives;
- Warfarin;
- Beta-blockers;
- probenecid;
- Drugs whose absorption depends on gastric pH.
Dosage and overdose
According to the instructions, the drug should be taken orally as a whole 30 minutes before meals, with a sufficient amount of liquid. The daily dose is 1000 mg or 2 tablets.
The course of treatment for patients who have mild or moderate renal or hepatic impairment is adjusted depending on the complexity of the case. It is worth noting that reducing the dosage reduces the effectiveness of treatment, so it is advisable to consider a different treatment regimen.
If the dosage regimen is violated, complications are possible that affect various systems. This is mainly due to the high concentration of the active substance. Vomiting, diarrhea and gastrointestinal dysfunction often occur. When the first complications appear, you must seek qualified help. The patient is prescribed maintenance therapy aimed at protecting the kidneys and liver from the negative effects of the drug.
Description and instructions for the drug Vimovo
Vimovo is a combined non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that should alleviate the condition of patients with severe pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. It contains two substances. One is released immediately in the stomach. This is esomeprazole (it is also the active ingredient in the drug Nexium). This compound reduces the acidity of gastric juice. This is necessary for patients forced to undergo treatment with drugs from the NSAID group, which often leads to the development of ulcers of the digestive system. Actually, esomeprazole in this case is a preventive component.
The second substance is naproxen (present, for example, in Pentalgin). It, like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can reduce fever, pain and inflammation. In Vimovo tablets, this component is enclosed in a shell that dissolves only at high acidity. Thus, naproxen is released only in the patient’s intestines, from where it is absorbed into the blood.
The main achievement of the creators of Vimovo is that treatment with it is rarely interrupted due to indigestion or other undesirable effects on the digestive system. And in this way, patients can receive a sufficient course of anti-inflammatory and pain relief.
Vimovo is used for:
- Osteoarthrosis;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Spondylitis;
We have already noted that Vimovo is produced in the form of tablets. They are taken half an hour before meals (or even earlier). According to the standard, it is recommended to take two tablets per day (morning and evening). The instructions for the Vimovo drug warn that under no circumstances should the integrity of the tablet be violated - chew or break it.
If this drug is prescribed to a patient with kidney pathology, the condition of his excretory system should be monitored. If it is discovered that treatment with Vimovo aggravates a concomitant disease, it must be stopped.
Vimovo is contraindicated for:
- Possible intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, so-called “aspirin asthma”, urticaria or rhinitis in response to treatment with such drugs);
- Severe liver or kidney failure;
- Heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
- Exacerbation of ulcers, inflammation or bleeding in the stomach or intestines;
- Other bleeding, such as cerebral hemorrhage;
- Treatment of patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass grafting;
- Treatment of women in the third trimester of pregnancy;
- Lactation;
- Treatment of minor patients;
- Concomitant use of certain antiviral drugs (for example, in HIV-infected patients);
- with caution when -
Many other pathologies and conditions. In any case, before prescribing Vimovo, the doctor must collect complete information about the patient’s health and the possible reactions of his body to the use of this medicine.
Side effects of Vimovo
The unwanted effects of this drug are similar to the side effects that its active ingredients may cause when used on their own. A large section in the Vimovo annotation is devoted to these conditions. When familiarizing yourself with it, the patient will see that the developers have done a lot to improve its tolerability.
However, it is worth listing those undesirable effects that received the most complaints during research and clinical use of the drug:
- Heartbeat;
- Dizziness and headaches;
- Sleep disorders;
- Depression;
- Visual or hearing impairment;
- Digestive disorders, abdominal pain, diverticulitis and so on;
- Allergic reactions;
Side effects
Vimovo may cause the following side effects:
- dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting and stomach pain, heartburn, diarrhea, constipation;
- palpitations, shortness of breath;
- dizziness, headache, drowsiness, lightheadedness, vertigo;
- insomnia, depression;
- visual and hearing impairment, ringing in the ears;
- stomatitis, peptic ulcers;
- swelling, increased sweating, fatigue, thirst;
- itching, skin rash, purpura, bruising;
- diverticulitis.
Infrequent and rare side effects include the following:
- arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, tachycardia, increased or decreased blood pressure;
- hemolytic and aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, lymphadenopathy, agranulocytosis;
- coma, convulsions, fainting;
- vasculitis;
- paresthesia, tremor;
- states of excitement, anxiety, confusion, unusual dreams, hallucinations;
- blurred vision, conjunctivitis, disc edema and optic neuritis, corneal opacities;
- hearing impairment;
- erythema multiforme, nodosum or drug-induced erythema;
- respiratory depression, bronchospasm, bronchial asthma, pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonitis, pulmonary edema;
- stomach ulcers, esophagitis, gastritis, glossitis, bleeding and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, hematemesis; melena, pancreatitis, colitis, exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the intestines, ulcerative stomatitis, non-peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract, rectal bleeding;
- systemic lupus erythematosus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative or photosensitive dermatitis, as well as various photosensitivity reactions;
- liver failure, interstitial nephritis, cholestasis, jaundice, hepatitis, glomerulonephritis, hematuria, oliguria or polyuria;
- renal failure, renal tubular necrosis, kidney necrosis, fluid retention;
- urticaria, exanthema, angioedema;
- muscle weakness, myalgia, asthenia, malaise, fever;
- anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions;
- menstrual irregularities, infertility;
- hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia;
- alopecia;
- sepsis, aseptic meningitis, infection;
- cognitive dysfunction.
Vimovo
The drug contains naproxen and esomeprazole, so it is possible to develop the same undesirable effects that were observed when using these active substances separately. Undesirable effects from the gastrointestinal tract, such as dyspepsia, stomach pain, nausea and vomiting, most often develop with the use of naproxen. During the development of the drug, esomeprazole was included in its composition to reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal side effects of naproxen. It was shown that when taking the drug, the incidence of gastric ulcers and adverse events in the upper gastrointestinal tract associated with NSAIDs was significantly reduced compared with naproxen monotherapy.
In placebo-controlled studies, the most common adverse events with Vimovo (n=490) compared with placebo (n=246) included diarrhea, upper abdominal pain, constipation, dizziness and peripheral edema, which are all adverse drug reactions with use. active substances separately. No new safety data were obtained when using the drug in the general patient population (n=1157) compared to the well-known safety profiles of the active substances naproxen and esomeprazole.
There were no differences in the types of adverse reactions when using the drug for 12 months compared to short-term therapy. Patients taking the drug were significantly less likely to discontinue therapy early due to adverse reactions compared to patients taking enteric-coated naproxen alone (7.9% versus 12.5%, respectively). The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to any upper gastrointestinal adverse event (including duodenal ulcers) while using the drug was 4% compared to 12% of patients receiving enteric-coated naproxen alone.
Adverse events are classified by frequency of development and organs and systems. The frequencies of undesirable effects were defined as: very common (> 1/10); frequent (>1/100 to 1/1000 to 1/10000 to
Naproxen
The following adverse events were observed in patients receiving naproxen during clinical trials and post-marketing:
Laboratory indicators: Infrequent/rare - increased liver enzyme activity, increased bleeding time, increased serum creatinine levels.
Cardiac disorders: often - palpitations; Infrequent/rare - arrhythmia, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, tachycardia.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Uncommon/rare - agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Nervous system disorders: common - dizziness, drowsiness, headache, lightheadedness, vertigo; Uncommon/rare: cognitive dysfunction, coma, convulsions, decreased concentration, optic neuritis, paresthesia, syncope, tremor.
Violations of the organ of vision: frequent - visual impairment; Uncommon/rare: blurred vision, conjunctivitis, corneal opacities, papilledema.
Hearing disorders and labyrinthine disorders: frequent - tinnitus, hearing impairment; Infrequent/rare - hearing loss.
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: often - shortness of breath; Uncommon/rare - bronchial asthma, bronchospasm, eosinophilic pneumonitis, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, respiratory depression.
Gastrointestinal disorders: common - dyspepsia, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, heartburn, peptic ulcers, stomatitis; Uncommon/rare - dry mouth, esophagitis, stomach ulcers, gastritis, glossitis, belching, flatulence, stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, melena, hematemesis, pancreatitis, colitis, exacerbation of inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis , Crohn's disease), non-peptic gastrointestinal ulcer, rectal bleeding, ulcerative stomatitis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: Uncommon/rare - glomerulonephritis, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure, renal medullary necrosis, renal tubular necrosis.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: common - itching, bruising, purpura, skin rash; Uncommon/rare - alopecia, exanthema, urticaria, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, persistent drug-induced erythema, lichen planus, systemic lupus erythematosus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, photosensitive dermatitis, photosensitivity reactions, including cases of rash like cutaneous porphyria tarda (pseudoporphyria), exfoliative dermatitis, angioedema.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Uncommon/rare - muscle weakness, myalgia.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders: Uncommon/rare - loss of appetite, fluid retention, hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, hypoglycemia, changes in body weight (associated with edema/fluid retention).
Infections and infestations: often - diverticulitis; Infrequent/rare - aseptic meningitis, infection, sepsis.
Vascular disorders: Uncommon/rare - increased blood pressure, decreased blood pressure, vasculitis.
General disorders and reactions at the injection site: often - fatigue, swelling, sweating, thirst; Infrequent/rare - asthenia, malaise, fever.
Immune system disorders: Uncommon/rare - anaphylactic reactions, anaphylactoid reactions, hypersensitivity reactions.
Liver and biliary tract disorders: Uncommon/rare - cholestasis, hepatitis, jaundice, liver failure.
Disorders of the reproductive function and mammary glands: Infrequent/rare - infertility, menstrual irregularities.
Mental disorders: often - depression, insomnia; Infrequent/rare - agitation, anxiety, confusion, unusual dreams, hallucinations, nervousness.
Esomeprazole
The following adverse drug reactions were observed or suspected in patients receiving enteric-coated esomeprazole during clinical trials and/or post-marketing. None of these adverse reactions were dose dependent.
Disorders of the blood and lymphatic system: Rare - leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; Very rare - agranulocytosis, pancytopenia.
Nervous system disorders: often - headache; infrequently - dizziness, paresthesia, drowsiness; rarely - taste disorder.
Visual disturbances: rarely - blurred vision.
Hearing and labyrinthine disorders: uncommon - vertigo.
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs: rarely - bronchospasm.
Gastrointestinal disorders: often - abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea/vomiting, constipation; uncommon - dry mouth; rarely - stomatitis, gastrointestinal candidiasis; very rarely - microscopic colitis.
Renal and urinary tract disorders: very rarely - interstitial
Dosage and overdose
The medicine is prescribed for oral use, one tablet twice a day. Drink them at least half an hour before meals. It is recommended to swallow Vimovo whole, without chewing, crushing, or breaking.
As the dose increases, drowsiness, discomfort in the epigastrium, in more advanced cases of gastrointestinal bleeding, and respiratory arrest may develop. There is no specific antidote. In case of accidental poisoning, you need to induce vomiting, then take a laxative and enterosorbents.
Dosage
Overdose symptoms are usually temporary. There is a high probability of general weakness and accompanying signs of discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract.
Vimovo, description of the drug
Vimovo is taken orally
The drug Vimovo is taken orally. Typically, your doctor will prescribe a dosage of one tablet up to three times a day. The medication should be taken 30 minutes before meals. It is recommended to swallow the tablet whole.
Older patients may experience a number of side effects and complications. In other cases, side effects are less pronounced. The drug is taken to get rid of diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and spondylitis. The medicine should be stored at temperatures up to +30 degrees.
Interaction with other drugs
Vimovo should not be taken together with antiretroviral drugs (nelfinavir and atazanavir). It should be combined with caution with diuretics, acetylsalicylic acid, corticosteroids, warfarin, probenecid, methotrexate, cholestyramine, beta-blockers, lithium preparations, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
When taken together with lithium and methotrexate, their toxicity may increase.
Probenecid slows down the removal of the drug from the body, and cholestyramine delays the absorption of naproxen.
Acetylsalicylic acid tablets are taken only in small doses. In the opposite case, the degree of communication of the drug with plasma blood proteins decreases.
Special instructions when using the drug
It is recommended to prescribe the drug with caution to elderly people. Since if there is a certain predisposition, bleeding may occur in the stomach and intestines, the opening of ulcers, which leads to the death of the patient
But studies have not been conducted on elderly patients, so the information is speculative. In patients under 60 years of age, ulcers of this kind do not appear.
Release form Vimovo - tablets
In the presence of peptic ulcers, it is not recommended to increase the dosage, as this may lead to undesirable consequences. The drug should be taken at the lowest possible dose and under the supervision of the attending physician. If during administration you notice discomfort in the abdominal cavity, you must stop taking the drug by contacting your doctor.
If you have heart, vascular, or kidney disease, you must undergo a detailed examination before taking the drug to identify possible contraindications. Diagnostics is especially relevant in cases where long-term therapy must be carried out.
In the initial stages of taking the drug, dermatological reactions may occur - rash, itching. With increased sensitivity to the components of the drug, more serious complications may occur - dermatitis, toxic necrolysis. Here you should stop using the drug, as it can be fatal.
The drug has the ability to reduce fever and reduce inflammation, thereby reducing their significance as diagnostic symptoms of fever. Thus, when using the drug, it is necessary to monitor patients, especially if the course of treatment is long (in case of any disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, be sure to consult a gastroenterologist). Presentation of the drug Vimovo in the video:
Tell your friends! Share Share Tweet Telegram Class WhatsApp
Precautionary measures
If Vimovo is prescribed to patients with kidney pathologies, then during the treatment process it is necessary to keep the condition of the urinary system under control. If it worsens, the medicine is discontinued. If necessary, the doctor may reduce the daily dosage.
If the patient has previously suffered from an ulcer, then it is necessary to start taking it with a small dose.
You should take the medicine with caution if you have hypertension, arterial diseases, cerebrovascular accidents, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypovolemia, coronary heart disease, as well as people who smoke.
It is not recommended for people suffering from cardiovascular pathologies to combine Vimovo with diuretics and acetylsalicylic acid, which can aggravate the disease.
Elderly patients should take the medicine only under the strict supervision of a doctor, as they have an increased risk of complications.
Due to the possible occurrence of dizziness, as well as impaired visual and auditory function, a careful approach requires taking the drug in people driving vehicles, as well as those engaged in activities that require special attention.
Women in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy can take Vimovo only under strict indications and under the close supervision of a doctor.
Patients who take the medicine for a long time should also be under the supervision of a doctor. Low acidity weakens the barrier function of the stomach, which increases the likelihood of intestinal infections. With a long-term change in acidity to the neutral side, the formation of benign neoplasms is possible. But when you stop taking Vimovo, a reverse development of tumors is observed.
Compound
Content
According to the Russian Register of Medicines (RLS), the active substances are naproxen (500 mg) and esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate (22.3 mg). In addition, the medicine includes the following auxiliary ingredients:
- croscarmellose sodium;
- magnesium stearate;
- iron oxide;
- triethyl citrate;
- glycerol monostearate;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- ink;
- methyl parahydroxybenzoate and others.
Given the rich composition of the product, before use it is necessary to carefully study its description and instructions for use. This will make it possible to assess the likelihood of complications due to individual intolerance to the substance.
Vimovo release form
According to the instructions, Vimovo is produced in the form of enteric film-coated yellow oval tablets, with the black inscription “500/20” on one side, in plastic bottles with a screw cap, with first opening control.
One Vimovo tablet contains 500 mg of naproxen and 22.3 mg of esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate, as well as:
- 50 mcg carnauba wax;
- 35 mg hypromellose 3 mPas77;
- 2.69 mg glycerol monostearate 40-55;
- 10.85 mg hypromellose 6 mPas;
- 680 mcg hypromellose 50 mPas;
- 580 mcg iron oxide yellow (E172);
- 22 mg croscarmellose sodium;
- 2.62 mg colloidal silicon dioxide;
- 1.38 mg magnesium stearate;
- 5.85 mg macrogol 8000;
- 20 μg methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218);
- 4.55 mg polysorbate 80;
- 11 mg povidone K90;
- 6.3 mg polydextrose (E1200);
- 10 µg propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216);
- 54.6 mg suspension 30%;
- 8.18 mg triethyl citrate;
- 13.26 mg titanium dioxide.
The tablet shell contains black ink - qs, which consists of 22% black iron oxide, 7% hypromellose 6 mPas, 10% propylene glycol, 12% isopropanol and 49% purified water.
Pharmacological properties
Vimovo is a combination drug containing a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substance and a proton pump inhibitor.
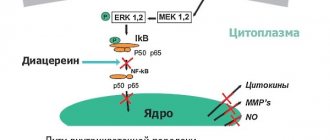
The peculiarity of this drug is that it is created in the form of tablets with a sequential release of substances: their shell contains immediate-release esomeprazole, and the core itself contains sustained-release naproxen. Thus, after oral administration of Vimovo tablet, esomeprazole is released in the stomach before naproxen dissolves in the small intestine. At the same time, the enteric coating protects naproxen from release at pH levels below 5.5, thereby providing the gastric mucosa with protection from its negative effects.
The active substance of Vimovo - naproxen - has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects. Its mechanism of action, like other NSAIDs, is not fully understood, but is presumably related to its ability to inhibit prostaglandin synthetases.
Representing a proton pump inhibitor, esomeprazole, the second active component of the drug, is the S-isomer of omeprazole. This substance, by specifically inhibiting the proton pump located in the parietal cells of the stomach, reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Medicinal properties
Esomeprazole is included in the tablet shell. Therefore, it is released immediately after entering the stomach and suppresses the secretion of hydrochloric acid, minimizing the adverse effects of naproxen on the digestive mucosa and preventing the development of ulcers.
Naproxen is placed in the core of the tablet and is released only after reaching the intestines. It relieves fever, relieves inflammation and swelling in joints, eliminates morning stiffness, muscle and joint pain, and helps increase range of motion. Therefore, naproxen has a therapeutic effect, and esomeprazole has a preventive effect.
Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs negatively affect the gastric mucosa, leading to irritation, causing gastritis, erosion and ulcers. Therefore, doctors, along with such medications, prescribe drugs that protect the gastric mucosa. Vimovo already has such a drug (esomeprazole). Therefore, the drug has an anti-inflammatory effect and at the same time has an inhibitory effect on the proton pump (it is responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid).
Naproxen is eliminated within 9-15 hours after administration. About 95% is excreted in urine and 3% in feces. Esomeprazole is eliminated within an hour. About 80% is excreted in urine and less than 1% in feces.
Additional Information
Vimovo is available from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription. Its shelf life is 2 years.
Popular articles Read more articles
Walking and calories 12/02/2013
We all walk a lot during the day. Even if we have a sedentary lifestyle, we still walk - after all, we...
612765 65 More details
How to lose weight at 50 10/10/2013
Fifty years for the fair sex is a kind of milestone, crossing which every second...
455226 117 More details
Running and calories 12/02/2013
Nowadays, running no longer evokes a lot of enthusiastic reviews, as it did thirty years ago. Then society would...
358384 41 More details
Hypoallergenic diet 09/11/2013
A hypoallergenic diet is used for all types of allergies, regardless of their origin, as it allows…
304477 2 More details
Balanced diet 11/19/2013
A balanced diet is one that fully and in the correct proportion ensures the intake of...
249629 8 More details
Calorie content of pies 11/26/2013
We all love pies. For many, pies are memories of childhood, of Saturday mornings, of the village; grandma's pi...
246420 13 More details
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- children and adolescents up to 18 years of age;
- severe liver failure and/or renal failure;
- active liver disease;
- severe heart failure not controlled by medication;
- hyperkalemia;
- bleeding (gastrointestinal, cerebral hemorrhage and others);
- peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum, as well as inflammatory bowel diseases that occur in the acute phase;
- recovery period after coronary artery bypass surgery.
Do not prescribe when taking nelfinavir and atazanavir simultaneously, or if there is a history of asthma, urticaria, or allergic reactions to NSAIDs and acetylsalicylic acid.
Prescribed with caution for the following pathologies:
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic heart failure;
- cardiac ischemia;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- peripheral arterial disease;
- risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, such as smoking, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, etc.;
- hypovolemia;
- history of gastrointestinal diseases.
VimovoTM (VimovoTM)
Elderly patients
Naproxen
: In elderly patients, an increased incidence of adverse reactions has been observed with the use of NSAIDs, in particular gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to death of the patient. In clinical studies of Vimovo™ in elderly patients, there was no increased incidence of gastric and duodenal ulcers compared with patients younger than 60 years of age, and the reduction in ulcer risk was maintained in this elderly patient population. However, ulcer complications such as bleeding, perforation and gastrointestinal obstruction were not studied in these studies of Vimovo™.
Effect on the gastrointestinal tract
Naproxen
: Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to death of the patient, has been observed with the use of all NSAIDs at any time during treatment, with or without the development of symptoms of the lesion, with or without a history of serious gastrointestinal diseases. Vimovo™ contains esomeprazole to reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal side effects of naproxen, including ulceration. Although Vimovo™ significantly reduces the incidence of gastric ulcers compared to naproxen alone, the development of ulcers and accompanying complications is still possible. The risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract when using NSAIDs increases with increasing dosages in patients with a history of ulcers, especially if the ulcer is complicated by bleeding or perforation, and in elderly patients. Such patients should be prescribed therapy with the lowest dosage.
Patients with a history of gastrointestinal adverse events, especially elderly patients, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially gastrointestinal bleeding) and especially at the beginning of treatment.
NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients already taking medications that may increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or antithrombotic drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid.
If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers develop, use of Vimovo™ should be discontinued.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with caution to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) due to a possible exacerbation of this disease.
Esomeprazole
: If any warning symptom develops (eg, significant, unintentional weight loss, recurrent vomiting, dysphagia, hematemesis, or melena) and there is a suspicion or certainty of developing a gastric ulcer, malignancy must be excluded, as esomeprazole magnesium may relieve symptoms and delay presentation diagnosis.
Treatment with proton pump inhibitors may slightly increase the risk of gastrointestinal infection with microorganisms such as Salmonella
and
Campylobacter
.
Effect on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems
Naproxen: As with any NSAID, it is necessary to monitor and advise patients with a history of arterial hypertension and/or chronic heart failure, since NSAID therapy is accompanied by fluid retention and the development of edema.
Patients with uncontrolled hypertension, chronic heart failure, coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular accident should be prescribed naproxen only after careful evaluation. The same examination should be performed before starting long-term therapy in patients with risk factors for cardiovascular disease (for example, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking).
Based on clinical and epidemiological studies, naproxen therapy (1000 mg daily) may be associated with a lower risk of arterial thrombosis than selective COX-2 inhibitors, but this small risk cannot be excluded. Overall, the data do not support a cardioprotective effect.
Effects on the kidneys
Naproxen
: Long-term use of NSAIDs has led to the development of medullary necrosis and other kidney damage.
Nephrotoxicity has also been observed in patients in whom renal prostaglandins play a compensatory role in maintaining renal perfusion. In these patients, the use of NSAIDs may lead to a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin synthesis and, secondarily, a reduction in renal blood flow, which may precipitate the development of overt renal failure. The greatest risk of developing such a reaction is present in patients with impaired renal function, hypovolemia, heart failure, liver failure, with excessive excretion of sodium chloride from the body, in patients taking diuretics, ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and in elderly patients. After discontinuation of NSAID therapy, the patient's condition usually returns to its original state.
Use in patients with renal failure
Since naproxen is largely (95%) eliminated by the kidneys via glomerular filtration, great caution should be used when administering it to patients with renal impairment, and monitoring of serum creatinine levels and/or creatinine clearance in these patients is recommended. It is not recommended to prescribe Vimovo™ to patients with an initial creatinine clearance of less than 30 ml/min.
Hemodialysis does not reduce plasma concentrations of naproxen due to high binding to plasma proteins. Certain patients, especially those with impaired renal blood flow due to depletion of interstitial fluid volume, cirrhosis of the liver, limited salt intake, chronic heart failure and pre-existing kidney disease, should have their renal function assessed before and while taking Vimovo™. Some elderly patients with suspected renal impairment, as well as patients taking diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin II receptor antagonists, also fall into this category. To prevent possible excessive accumulation of naproxen metabolites in these patients, the daily dose of the drug should be reduced.
Effect on the hematopoietic system
Naproxen
: It is necessary to prescribe drugs containing naproxen with caution to patients with coagulation disorders or receiving therapy that affects hemostasis.
The risk of bleeding in patients at high risk of bleeding or receiving full anticoagulation therapy (for example, dicumarol derivatives) increases with concomitant use of drugs containing naproxen. Naproxen reduces platelet aggregation and prolongs bleeding time. This should be kept in mind when determining bleeding time.
If active or clinically significant bleeding develops in any area in patients taking Vimovo™, therapy should be discontinued.
Dermatological effects
Naproxen
: Very rarely, serious skin reactions have occurred with the use of NSAIDs, some of which have resulted in death, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. The greatest risk of developing such reactions exists at the beginning of therapy, and in most cases the onset of such reactions occurs in the first month of treatment. At the first sign of skin rash, lesions of the mucous membranes or other symptoms of hypersensitivity, you should stop taking Vimovo™.
Effect on visual function
If visual disturbances occur while taking Vimovo™, consultation with an ophthalmologist is recommended.
Anaphylactic (anaphylactoid) reactions
Naproxen
: Hypersensitivity reactions may occur in susceptible patients. Anaphylactic (anaphylactoid) reactions may occur in patients with or without a history of hypersensitivity, or with or without hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, other NSAIDs, or naproxen-containing drugs. These reactions may develop in patients with a history of angioedema, bronchospasm (eg, bronchial asthma), rhinitis and polypous rhinosinusopathy.
Patients with bronchial asthma
Naproxen
: The use of acetylsalicylic acid in patients with aspirin-induced asthma was accompanied by the development of severe bronchospasm, which could lead to the death of the patient. Since cross-reactivity, including bronchospasm, between acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs has been observed in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, it is not recommended to prescribe Vimovo™ to patients with such hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and use caution in patients with bronchial asthma.
Inflammation
Naproxen
: The antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties of naproxen may reduce fever and other signs of inflammation, thereby reducing their usefulness as diagnostic factors.
Combinations with other drugs
It is not recommended to use Vimovo™ concomitantly with NSAIDs (other than acetylsalicylic acid), including selective COX-2 inhibitors, due to the cumulative risks of developing serious adverse events associated with NSAIDs.
According to the results of the studies, a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interaction was noted between clopidogrel (loading dose of 300 mg and maintenance dose of 75 mg/day) and esomeprazole (40 mg/day orally), which leads to a decrease in exposure to the active metabolite of clopidogrel by an average of 40% and reducing the maximum inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation by an average of 14%. Therefore, the simultaneous use of esomeprazole and clopidogrel should be avoided (see section “Interaction with other drugs and other types of drug interactions”).
Fertility in women
Naproxen
: There is some evidence that drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin synthesis may reduce fertility in women by affecting ovulation. This effect is reversible after discontinuation of therapy. In this regard, women who have problems conceiving or are undergoing examination for infertility should consider discontinuing Vimovo™ (see section “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
Are common
If the daily dose of naproxen 1000 mg is not acceptable, alternative treatment regimens should be used.
Patients receiving long-term therapy (especially more than 1 year) must be constantly monitored. Individual observational studies indicate that proton pump inhibitor therapy may modestly increase the risk of osteoporosis-related fractures, but other similar studies have not reported an increased risk.
Randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trials of omeprazole and esomeprazole, including two open-label studies of long-term therapy (more than 12 years), did not confirm the association of osteoporotic fractures with the use of proton pump inhibitors.
Although a causal relationship between the use of omeprazole/esomeprazole and osteoporotic fractures has not been established, patients at risk of developing osteoporosis or osteoporotic fractures should be under appropriate clinical supervision.