Why is zinc needed in a woman’s body?
It takes part in the regulation of brain activity and strengthening of nerve fibers.
Takes direct part in the synthesis of some hormones and neuronal mediators. One of which is serotonin. Zinc is involved in the production of serotonin, the hormone of happiness, which provides us with an excellent mood and positive emotions. Which in turn determines the psychological status, reduces depressive readiness, and increases resistance to stress. For this purpose, zinc supplements for women are used.
Hormonal balance is also important. This is associated with normal gestation, prevention of miscarriages and premature births.
In addition, this mineral takes an active part in the regulation of reproductive function. Thanks to its sufficient content, the absence of PMS symptoms, a calm pregnancy, and the absence of premature menopause are ensured.
The necessary zinc content ensures good vision. This is due to the participation of the trace element in the metabolism of nerve fibers, the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the normal functioning of the macula. Zinc maintains visual acuity and prevents myopia.
Our mineral regulates defenses by promoting the production of antibodies and blood leukocytes, which supports stable immunity. With zinc deficiency, almost the entire immune system suffers.
Thanks to the normal zinc content, the fairer sex has well-groomed and strong hair and nails. Signs of zinc deficiency in women: hair splits and falls out, loses its usual shine, nails become brittle, white spots appear, and flake.
Due to participation in lipid metabolism, beautiful skin is formed. Zinc reduces the manifestations of allergic skin reactions, acne, reduces dry skin, prevents early wrinkles, and regulates sebum secretion of the skin. To eliminate these clinical manifestations, dietary supplements for women are used. The first place among them is zincite.
What vitamins are best for hair and nails
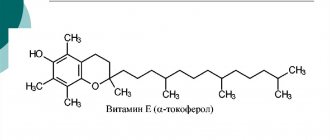
First of all, these are vitamins A, E, C, F. They work in combination with selenium and zinc.
Complex drugs are prescribed only after examining laboratory parameters to ensure that there is a real deficiency of this microelement, since similar symptoms may occur with other deficiencies. The above compounds are good vitamins for hair, nails and skin for women. They participate in metabolism, contribute to the renewal of the surface layers of the epidermis, which stimulates rejuvenation and a beautiful appearance.
Where is zinc found?
Let's start with food.
The body receives most useful minerals from food. Vitamins with zinc for women are found in many foods: turkey, egg yolk, beef, seeds and nuts, buckwheat, seafood, oatmeal, bran, cheese, dairy products.
If you clearly have a zinc deficiency, then vitamins for hair, nails and skin containing zinc, as well as dietary supplements for hair and nails, can come to your aid.
Zinc is an essential trace element
3465 07 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Zinc (mw 65.39) is a vital element, one of the most common microelements in the body, quantitatively second only to iron. The wide range of biological activity of this element is due to its chemical characteristics (mobile coordination geometry, fast kinetics of ligand exchange). The identification of the biological significance of zinc was late due to methodological problems (before the development of atomic absorption methods), since zinc does not form natural colored complexes. Zinc is a component of more than 300 metalloenzymes, including carbanhydrase, alkaline phosphatase, RNA and DNA polymerases, thymidine kinase carboxypeptidases, and alcohol dehydrogenase. The key role of zinc in the synthesis of protein and nucleic acids explains the growth and wound healing disorders observed with a deficiency of this element. It is involved in mechanisms associated with the processes of regulation of gene expression, which is generally associated with developmental biology, including fetal development, as well as with the regulation of the synthesis of steroid, thyroid and other hormones (zinc transcription factors), etc. In food, zinc is mainly associated with proteins, its bioavailability depends on the digestion of these proteins, the most accessible zinc is in red meat, fish, wheat germ and bran are a good source of zinc. Symptoms of zinc deficiency are often associated with a diet low in animal protein and high in cereals containing zinc-binding phytates. Zinc absorption may be reduced by iron supplements. Cases of excess zinc intake into the body are associated with the use of galvanized containers for drinking liquids (rarely); excess zinc can cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract. Absorbed zinc in the liver is actively included in metalloenzymes and plasma proteins. Blood plasma contains less than 1% of the body's total zinc. The main part of plasma zinc is associated with albumin (80%), the rest is mainly with alpha-2-macroglobulin. In erythrocytes, almost all zinc is found in carbanhydrase. The zinc content in erythrocytes is approximately 10 times higher than in plasma. Zinc is excreted from the body through bile and urine.
Clinical manifestations of zinc deficiency (as follows from the diversity of its biological functions) do not show specificity, vary and depend on the degree and duration of the deficiency. Symptoms of deficiency include growth retardation, increased incidence of infections associated with impaired immune system function, diarrhea, loss of appetite, changes in cognitive function, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, anemia, enlarged liver and spleen, teratogenesis, skin lesions, hair loss, visual impairment, etc.
To study the status of zinc in the body, serum or plasma is preferable (hemolysis can distort the result!). Blood zinc levels follow a circadian rhythm, with a peak in the morning around 9am and then another around 6pm. After eating, zinc levels decrease. The conditions under which the sample was taken should be monitored (time of day, food intake, presence of drug therapy). The level of albumin in the blood (a negative reactant of the acute phase of inflammation) can affect the result, so it is advisable to simultaneously examine the level of albumin (test No. 10) and C-reactive protein (test No. 43). The study of zinc excretion in urine is an indicator of the loosely bound, metabolic pool of zinc and does not always reflect the total reserves of the element in the body. The content of zinc in urine depends on its level of entry into the body and the direction of metabolic processes in the body. Urinary zinc excretion can increase threefold after short-term fasting as a result of activation of catabolic processes. Low levels of zinc in children's hair correlate with slower overall growth, and zinc hair tests are used to assess zinc deficiency. It should be borne in mind that the result of the study may be influenced by the rate of hair growth, external pollution - hair dyes, medicated shampoos, hair cosmetics containing zinc.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Overdose
Excessive consumption of Zincite causes the same symptoms of overdose that occur with excess zinc in the body:
- rapid pulse;
- vomiting, diarrhea, nausea;
- dizziness;
- pain in the head and lower back;
- ulcers in the mouth and throat;
- fever and other flu-like symptoms;
- the level of “good” cholesterol drops sharply;
- taste sensations change or disappear completely;
- immunity decreases;
- the amount of copper in the body also decreases sharply.
Zinc overdose is very dangerous. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that he can relieve the symptoms and prescribe a different, more strict dose. You will need to be hospitalized in the toxicology department of the hospital. As a diet, the patient is prescribed milk and given activated charcoal. All doctor's recommendations must be followed.
Contraindications
If there are cases when it is impossible to take Zincit, then the doctor prescribes another drug. Zinkit has very few contraindications:
- severe diseases and kidney damage;
- allergy to the components of the product, high sensitivity to them;
- acute renal failure;
- immune encephalitis;
- autoimmune diseases and active processes.
A doctor's consultation is required. The doctor must examine the patient and either allow him to take this medicine or prescribe another remedy.
Important to remember
Zincite is a dietary supplement, not a medicine. A visit to your doctor will allow you to anticipate possible allergic reactions and other complications that may arise from taking the drug. It is often drunk by athletes during long training sessions with heavy loads, as well as by people on a strict diet to lose weight. This remedy not only treats zinc deficiency, but also serves to prevent this condition.
Well-known analogues of “Zinkit” are “Zinketral”, “Tsinketral-teva”, “Roaccutane”, “Zinkorol”, “Sotret”, “Solgar zinc picolinate”.
All vitamins and minerals are beneficial to the body. Health deteriorates both with their deficiency and with their excess. Additional nutritional supplements will compensate for the lack of essential substances caused by poor nutrition or due to impaired absorption of zinc. You should take the pills only after visiting your doctor.
Forms of zinc - which one to choose
Almost any manufacturer of dietary supplements has its own line of zinc-containing additives, so you can choose a jar with the optimal price-dosage ratio. But in order not to make a mistake and not always waste money, always pay attention to the composition indicated on the label. The effectiveness of zinc-containing complexes is determined by the form of the active substance.
There are several forms of zinc: oxide, sulfate, glycinate, acetate, picolinate, gluconate, citrate and monomethionine. They differ in purpose, degree of absorption and the presence/absence of side effects.
Zinc oxide and sulfate
- inexpensive forms of zinc, but they have the lowest bioavailability (up to 48%), and when taken orally they can cause heartburn, stomach pain, and nausea. The presence of this form in supplements is undesirable.
Zinc oxide and sulfate are added to cosmetics; they are harmless for external use. Often used as anti-inflammatory and anti-aging components.
Zinc acetate
has good digestibility (up to 60%), but is suitable as an immunostimulating supplement during colds and flu.
Zinc gluconate
- one of the most inexpensive and easily digestible forms (up to 60%), in addition to replenishing the deficiency, this supplement can be used during colds.
Zinc citrate
has a maximum degree of digestibility (up to 61%), is easily accepted by the body and does not cause side effects.
Zinc Picolinate
- the king among supplements, as it combines absolute safety and high bioavailability. The disadvantage of this form is, perhaps, the price - due to complex production, such an additive is much more expensive than its analogues.
Chelated forms (glycinate, monomethionine)
also belong to highly effective (absorbed up to 58%) and safe forms that do not cause side effects and are suitable both for eliminating deficiency and as support for diseases of a viral and bacterial nature.
Knowing about the active forms of zinc, remember not to purchase a supplement where the form is not specified in the description. Perhaps this is an oversight by the manufacturer and there may be a high-quality product in the jar, but you can’t know for sure, which means it’s better to choose those brands that have nothing to “hide”.
Indications
The doctor prescribes “Zincit” in cases where the patient has a noticeable lack of zinc. Indications may vary:
- intestinal diseases in which zinc absorption is impaired;
- poor nutrition;
- prolonged fasting;
- strict diet;
- acne;
- skin diseases caused by zinc deficiency;
- dysplasia of joints, bones or connective tissue;
- active sports activities;
- smoking and alcoholism, in which zinc is intensively removed from the body.
Zinc is found in sunflower and pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, pine nuts, oatmeal, raspberries, black currants, potatoes, oranges, bananas, legumes, cheese and chocolate.
Signs of Zinc Deficiency
The main reason for the lack of a mineral in the body is poor nutrition. Zinc is found in plant and animal products:
- in seafood its concentration and bioavailability are the highest, oysters and mussels are especially useful;
- in red meats and poultry, the most accessible source is chicken thighs and drumsticks;
- in hard cheeses this mineral is also present in a bioavailable form;
- legumes, cereals and other seeds are also rich in zinc, but it is difficult to absorb from them; however, sunflowers, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and all types of nuts help fight mineral deficiency and prevent its occurrence;
- Another source of zinc is dark chocolate and other products with a high cocoa content.
A person needs about 10 mg of zinc per day. Children - 11 mg, adults - at least 8 mg. In women during pregnancy, as well as with the onset of menopause, the need increases to 12 mg per day.
Microelement deficiency is expressed by various symptoms, usually nonspecific:
- legs and hair become brittle and dull;
- the skin begins to peel off;
- wounds and abrasions heal poorly and bleed for a long time;
- Chronic loss of strength is possible;
- often suffer from insomnia, bad mood, and depressive thoughts;
- problems with concentration develop;
- immunity decreases;
- convulsions and tremors may appear;
- weight loss for no reason;
- the intestines do not work well: diarrhea and constipation appear;
- hearing, vision and smell become less acute.
In women, a lack of zinc is fraught with the development of reproductive problems: disorders of the menstrual cycle, ovulation, miscarriage, infertility. In men, chronic deficiency of the element leads to early decline in sexual function due to insufficient testosterone production. Regardless of gender, zinc deficiency accelerates the overall aging of the body.
Vegans and vegetarians, whose diet does not contain animal food, usually suffer from such problems. If the diet is rich in essential foods, but there are still adverse symptoms, it is important to pay attention to the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. Digestive disorders often interfere with the absorption of zinc: gastritis, enzymatic deficiency, intestinal inflammation, liver disease, kidney failure. People who abuse alcohol also have poor absorption of the mineral.
It is important to promptly identify and eliminate the causes of micronutrient deficiency. Better yet, take care of its prevention. Pharmaceuticals help with this. Zinc tablets: regular, effervescent or in capsule form contain the required daily doses of the mineral. Many of them are additionally enriched with copper, ascorbic acid and other elements necessary for complete absorption.