Home / Pediatrician / Treatment of dystrophy in children
Dystrophy is a pathological process when tissues lose or accumulate substances that are not typical for normal indicators. The disease is accompanied by cell damage, which leads to serious changes in the functions of various organs.
The metabolism and structure of cells and tissues are disrupted. Dystrophy is most often diagnosed in children under three years of age. The consequences are delayed physical, mental, psychomotor development, as well as metabolic and immune system disorders.
What is dystrophy?
Dystrophy is structural changes in a tissue or organ caused by metabolic disorders within cells.
The most common dystrophies of the following tissues occur in the human body:
- fatty degeneration;
- muscular dystrophy;
- dystrophy of the myocardium (heart tissue).
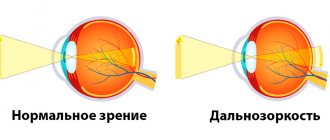
Methods for diagnosing retinal dystrophy
More information about the clinical picture of the disease is provided by an integrated approach, which the specialists of Dr. Trubilin’s clinic use in their work. A complete diagnosis includes the use of the following methods:
- Visual acuity study.
- Carrying out measurements of intraocular pressure.
- Checking the fundus with a dilated pupil.
- Non-contact examination using optical coherence tomography (OCT). The technique is used to identify the causes and consequences of retinal diseases. Profile equipment allows the diagnostician to see the smallest sections of the central part of the organ being examined. Based on the information received, it is easier to assess real visual acuity. Screening is carried out with a laser beam or IR illumination. At the end of the diagnostic procedure, the patient receives a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image of the fundus.
Modern technology makes it possible to detect the earliest manifestations of the disease, which opens up good prospects for preventing the progression of disorders. Patients are encouraged to use simple self-diagnosis methods. You need to pay attention to the following signs:
- deterioration in the quality of vision when trying to look at any object at a distance or at close range;
- decreased visibility when reading or writing texts, if the same glasses that were used earlier are used for this;
- the desire to turn on the light brighter, to make the lighting more intense in a room where previously, under exactly the same conditions, this was not required;
- the appearance of a feeling that there is an obstacle in front of one of the eyes, impairing visibility, the spot has a fuzzy outline and is transparent to light, it cannot be removed with your hands or washed with water.
Any changes in the perception of the surrounding space should alert you: distortion of contours, colors, brightness. These signs are a good reason to contact an ophthalmologist. Patients are also recommended to use the Amsler mesh in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician. This diagnosis is carried out for each eye separately.
Classification of dystrophies
The following types of dystrophy are distinguished:
- congenital,
- acquired.
Congenital dystrophies are genetic in nature and appear in early childhood. Dystrophies in children are very difficult. These include, for example, a fairly common type of muscle dystrophy - Duchenne dystrophy.
Duchenne dystrophy is a genetic disease transmitted from mother to son (the gene is located on the X chromosome). The child develops normally in the first years of life; the disease manifests itself between 3 and 5 years. First, difficulties arise when climbing stairs, then when walking, and later the respiratory and heart muscles are affected. The prognosis is unfavorable; there is currently no treatment for this pathology.
The most common types of dystrophies are:
- general (body mass index less than 16);
- local (of any organ).
Local dystrophies, for example, include:
- liver dystrophy;
- heart dystrophy;
- eye dystrophy;
- nail dystrophy.
Retinal dystrophy is a whole group of diseases of varying severity. Some of them are quite harmless, while others lead to retinal detachment and blindness.
Retinal dystrophy can be congenital or develop with age. The reasons for their development have not been fully established, but among them are:
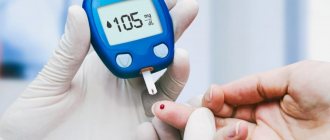
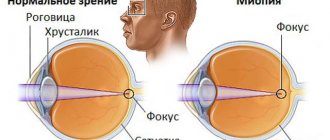
- severe myopia;
- diabetes;
- exophthalmos with thyrotoxicosis (an increase in the size of the eyeball with hyperthyroidism, as a result of which the vessels supplying the retina are compressed).
You can read more about hyperthyroidism in the Nutritionology blog.
Diagnostics
In terms of symptoms, corneal dystrophy does not differ from other ophthalmological diseases. Outwardly, it is similar to conjunctivitis, keratitis and other inflammatory processes: they are also accompanied by physical discomfort and decreased visual acuity. For a more accurate diagnosis, in addition to external examination and history taking, additional methods are used:
- biomicroscopy
- non-contact examination of the cornea using a slit lamp with multiple magnification; - pachymetry
- instrumental measurement of the thickness of the cornea over the entire surface of the anterior part of the eyeball; - visometry
is an instrumental assessment of visual acuity.
These methods are often sufficient to confirm the diagnosis, establish the type of pathology and determine the degree of its development.
Causes of dystrophy
The development of dystrophy is based on trophic disorders. Literally from the Greek the word “dystrophy” is translated as nutritional disorder. Congenital dystrophies are associated with mutations in certain genes; they are inherited by children from their parents and do not depend on external factors.
Acquired dystrophies are largely associated with environmental influences. For example, general dystrophy is the result of low nutrition or starvation. The cause of general dystrophy is often an eating disorder.
The mechanisms of development of local dystrophy are as follows:
- decreased blood flow to an organ or tissue;
- damage to the nervous system;
- mechanical injuries (for example, prolonged compression);
- action of physical factors (radiation);
- toxic effect.
A toxic effect is possible due to the action of substances:
- penetrating into the body from the environment;
- formed in the tissue itself as a result of the transition of one substance to another;
- synthesis in tissues of substances that normally should not be synthesized there;
- excessive entry into tissues of substances that in normal quantities do not have a toxic effect.
Demo lessons on the program “Nutriciology”
Get access
Main symptoms
Corneal dystrophy begins to manifest itself symptomatically quite quickly
: even with a small lesion, the patient feels discomfort in the eyes, reminiscent of fatigue from reading a book with small print for a long time, and a gradually increasing “fog” in the field of vision. As the disease progresses, these symptoms include:
- increased sensitivity to light;
- lacrimation;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- pain and cramps;
- redness of the cornea;
- visible swelling of the cornea;
- clouding of the eye (thorn).
The described symptoms are found in different combinations, and the intensity depends on the individual characteristics and type of pathology. Thus, the most severe symptoms are characterized by endothelial corneal dystrophy, while the marginal one does not clinically manifest itself until the cornea perforates.
Symptoms of dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy has the following symptoms:
- gradual painless decrease in muscle tone;
- reduction in muscle size (atrophy);
- decreased range of motion;
- loss of acquired skills in children (forgot how to hold a spoon, stand on one leg, etc.);
- severe weakness, fatigue, in young children - apathy, lethargy;
- frequent falls, instability, changes in gait;
- ordinary household load (climbing stairs, etc.) becomes prohibitive.
For other organs, manifestations of dystrophy are:
- reduction in size;
- structure changes;
- reduction in the volume of functions performed.
Symptoms and causes of muscular dystrophy
The causes of muscular dystrophy lie in a chromosomal mutation. The X chromosome is affected, but each form of the disease has its own characteristics and is characterized by a unique set of mutated genes. Moreover, they all contribute to a decrease or complete cessation of the synthesis of dystrophin, a protein necessary for muscles to function normally.
It is this protein that is responsible for their growth and recovery, although its content is very small - only 0.002% of the total amount of proteins in muscles. The lower the amount of dystrophin, the more the disease progresses and the severity of the symptoms.
Among the main symptoms accompanying all forms of pathology, it is worth noting the following signs:
- muscle weakness that progresses over the years;
- falls, clumsiness, changes in gait (a person begins to waddle and cannot control his gait);
- problems with speech, breathing, swallowing, chewing food, coordination of movements;
- muscle pain – the lower leg especially suffers;
- difficulties with memory, concentration, learning;
- cramps and contractures.
If you find yourself with the symptoms listed above, make an appointment with a neurologist at a medical clinic.
Make an appointment The application is preliminary. An operator will contact you to confirm your appointment.
Your application has been accepted, our specialists will contact you shortly. Thank you for contacting the medical
Diagnosis and treatment of dystrophies
Because Most types of dystrophies are of genetic origin; diagnosis is made using a blood test for the presence of DNA mutations.
Help for such patients is provided in clinics specializing in the treatment of muscular dystrophies. Quite often a consultation with a neurologist is required. Particular attention is paid to the function of the lungs and heart, for which regular diagnosis of cardiopulmonary disorders is carried out.
Unfortunately, currently treatment for congenital muscular dystrophies is palliative and aimed at improving the quality of life. However, research institutes are constantly developing new promising treatment methods: muscle tissue transplantation, injection of antibodies, gene and hormonal therapy.
Dystrophies of individual organs can be treated quite successfully. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a highly specialized doctor, for example, an ophthalmologist or dermatologist. For treatment, local medicines containing vitamins and amino acids are used. Physiotherapeutic methods are used to improve blood flow.
Nutritional correction is also carried out. Nutrition plays a huge role; it must be complete and balanced. To create a diet, you can consult a dietitian or nutritionist.
Causes of the disease
Age-related macular degeneration, also called retinal dystrophy, is a chronic disease with a progressive course. Medical statistics over the past 10 years have shown that AMD is one of the top three diseases responsible for decreased vision and blindness in patients whose age exceeds 50-55 years.
It is difficult to single out a single cause of pathology. The anomaly is triggered by a number of factors, the most common of which are:
- Old age - an increase in risk is observed in the period from 50 to 80 years. However, in recent years, the disease has become significantly “younger”, as it increasingly began to appear in people of working age.
- Gender - the female half of society is more susceptible to degenerative changes in the retina. Men are 50% less likely to have such disorders.
- Genetic prerequisites - it is noted that AMD in direct relatives increases the risk of developing the disease.
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels - patients with changes in blood pressure, atherosclerosis of vascular structures and other similar disorders should be careful, since the risk of eye damage is very high.
- Excess ultraviolet radiation - prolonged exposure to the sun on unprotected eyes is as dangerous as prolonged exposure to laser or ionized radiation.
Additionally, among the provoking factors for the development of retinal dystrophy, experts indicate smoking, diabetes, poor nutrition with a lack of vitamins and nutrients. Poor ecology, injuries and eye surgeries can affect health.
Nutritional dystrophy (Nutritional insanity)
The pathology develops gradually, and often the patient may not be aware that he is suffering from this disease. Usually, the first signs of cachexia appear only after a long period of restriction of the body’s intake of not only calories, but also protein, fats, essential amino acids and vitamins (usually fat-soluble). The first symptoms may not be noticed or not regarded as dangerous: increased urination, polyuria (increased daily urine volume), weakness and irritability, decreased performance, constant drowsiness. Thirst and increased appetite are often disturbing. One of the specific symptoms is a tendency to eat salt.
If nutrition is not established, the disease progresses and enters the next stage. At the same time, the skin becomes very flabby and dry, sagging in folds, reminiscent of parchment. It becomes very difficult to do any physical work, and the general condition suffers quite severely. The first signs of dystrophy and dysfunction of internal organs appear (constipation and other dyspeptic manifestations, cardiac dysfunction, endocrine disorders - women lose menstruation and infertility occurs). There is a tendency to lower the temperature. Heart rate slows down, blood pressure is low. Changes in the psyche may appear.
The last stage of the disease is characterized by a clear manifestation of the extinction of all body functions. The subcutaneous fat layer is absent, the muscles become very thin and flabby. A person at the third stage is no longer able to move independently. There is a decrease in the level of all blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), and immunity is suppressed. There is a very low level of protein in the blood and a tendency to decrease glucose levels. The reserves of vitamins and minerals are completely depleted, bones become brittle. Since the body starts catabolism (destruction) of its own proteins, toxic products of their breakdown begin to accumulate in the blood. This leads to an even greater deterioration of the condition, the appearance of severe mental disorders (the result of the action of decay products on the brain). Usually, in the last stages of the disease, even the beginning of treatment and nutrition cannot prevent a sad outcome.
The most severe condition that develops in the last stages of nutritional dystrophy is starvation coma. It occurs due to a significant decrease in blood glucose levels and the inability to provide the brain with the necessary amount of energy. The clinical picture of this condition is quite clear: sudden loss of consciousness, pale and cold skin, wide pupils. Body temperature is significantly reduced. Breathing is shallow, may be rare and irregular. Muscles lack tone and cramps may develop. The pulse is practically undetectable, weak, and the blood pressure is low. If timely assistance is not provided, death will occur from cardiac and respiratory arrest.
Treatment
The occurrence of repeated corneal erosions requires the use of drugs to restore the epithelial layer, as well as keratoprotectors in the form of eye drops and ointments that moisturize the corneal surface and relieve pain. As a rule, drops are prescribed to be used several times during the day, and the ointment is to be placed behind the lower eyelid at night, since its effect is longer.
Also, for therapeutic purposes, the wearing of soft contact lenses can be prescribed, which relieves pain and the sensation of a foreign body, creating favorable conditions for the speedy restoration of the corneal epithelium.
And yet, the main method of treating corneal dystrophies is surgery. If the epithelial layer and the underlying Bowman's membrane are damaged, areas of dystrophy can be removed using the laser method. In case of damage to deeper layers, an operation is performed - keratoplasty. It consists of surgical removal of the affected tissue and transplantation of a donor graft in its place.
Keratoplasty can be penetrating, when the central area of the cornea is completely removed, or layer-by-layer, when individual layers are removed. The functions of the patient's damaged cornea cells are taken over by the donor's cornea cells. The transparency of the cornea is restored, the signs of the disease disappear. However, in some cases, despite the positive results of the operation, signs of dystrophy return again after several years, in which case the keratoplasty operation is performed again.
About diseases and technologies
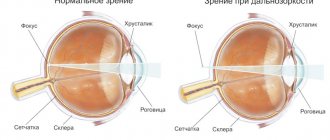
Retinal dystrophy is a degenerative disease characterized by progressive deterioration of visual functions. Specialists consider retinal diseases to be one of the most dangerous, since they block the functioning of the entire visual channel. Here, on the retina, the primary perception of light and image formation occurs.
Therefore, even if other visual functions are preserved, retinal impairment can lead to blindness.
The disease is especially common in older people, but in recent decades it has been increasingly diagnosed in younger people. Therefore, each of us should be informed about retinal dystrophy and the degree of its danger.
Initially, the disease affects central vision without causing complete loss of vision and acute complaints. It can develop over a number of years without causing much concern. However, it is one of the most serious causes of subsequent blindness worldwide. The likelihood of its occurrence increases after 40 years of age, and becomes critical upon reaching 55 years of age.
In general, ophthalmologists diagnose it late for two reasons: at an early stage, retinal dystrophy often develops asymptomatically, and patients perceive it as something “natural” for old age and turn to specialists too late.
Retinal dystrophy and its types
According to the mechanism of development, two types of dystrophy are distinguished.
Exudative form.
In this case, abnormal vessels begin to appear inside the choroid of the eye, which allow exudate - blood and lymph - into the retinal area. This is the so-called choroidal neovascularization, causing optical distortion of visual information.
In this case, the patient begins to see wavy lines instead of straight lines, and blind spots appear in the field of vision. Long-term entry of exudate into the retinal tissue can result in complete loss of central vision.
Non-exudative form.
This form of the disease is characterized by yellow deposits in the central segment of the retina. Small deposits do not cause serious disturbances. But over time, the size of the yellow spots increases and the symptoms of the disease become more noticeable. This is a decrease in light sensitivity and visual acuity, darkening of vision.
For the later stages of dystrophy, thinning of the light-sensitive layer of cells is typical, with its further atrophy and tissue decomposition. Blind spots in the visual field are a characteristic sign of the atrophic course of the disease, gradually leading to the complete loss of central vision.
In most patients, doctors note a non-exudative form of dystrophy. But in many cases it gradually turns into an exudative form.
Causes of retinal dystrophy
The main cause of retinal dystrophy is aging. It affects the entire body and causes a gradual disruption of all its functions. At the same time, the elasticity of tissues and their ability to regenerate decreases, and the volume of fluid circulating in the tissues decreases. The retina of the eye also ages. And at a certain age, irreversible changes begin to occur, leading to its dystrophy.
Research data indicate that heredity significantly influences the development of the disease.
A gene that influences the appearance of retinal dystrophy. Certain disorders in this gene, identified by scientists, are directly related to pathology. Normally, the gene is responsible for the development of the immune system and the synthesis of proteins involved in protecting the body from pathogenic factors.
A gene responsible for the development of the circulatory system during embryonic development. Its role in the development of the disease is also noted by researchers. Its excessive activity causes abnormal growth of the structure of retinal vessels in the exudative form of the disease.
Risk factors for retinal dystrophy
- The patient belongs to the Caucasian race (and women get sick more often than men).
- Light eye color. Research has confirmed the connection between the development of retinal dystrophy and low intensity eye pigmentation.
- Excess sunlight. Ultraviolet light can provoke the development of pathological processes in the retina.
- Excessive content of fatty foods in food.
- Aging. Elderly people - from 60 to 90 years old - are the group at greatest risk of developing retinal dystrophy. But the disease can also occur in younger people.
- Low physical activity and excess weight. In this category, retinal dystrophy is registered twice as often as usual.
- Hypertension. The constant influence of high pressure on the ocular vessels can cause degenerative processes in the retina.
- Smoking, which negatively affects the state of the microvasculature.
- Consequences of the use of drugs, in particular antimalarials and a number of antipsychotics.
- Increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Family history of dystrophy. The increased risk of the disease is associated with the hereditary mechanism of its transmission.
Symptoms of the development of retinal dystrophy
With retinal dystrophy at an early stage, there may be a complete absence of symptoms. Moreover, if only one eye is affected, dystrophy can be asymptomatic for quite a long time.
Exudative form. Symptoms.
- Blurredness and distortion of the shape of objects in the central visual zone.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Significant drop in clarity (even with a slight lack of illumination).
- The appearance of blind spots in the field of vision.
- Difficulty recognizing faces.
Non-exudative form. Symptoms.
- Instead of a blind spot, there is a blurry spot in the field of view.
- Rapid increase in symptoms.
- Hazy vision.
- Inability to recognize small text.
Retinal dystrophy is a progressive disease, so the intensity of symptoms usually increases gradually.
The disease does not affect peripheral vision, and therefore, even at the late stage of retinal dystrophy, complete blindness does not occur.
Diagnosis of retinal dystrophy
The most effective methods are available only in the early stages of the disease. Therefore, early diagnosis of retinal dystrophy is very important.
- Routine ophthalmological examination. The most characteristic early signs for diagnosing the disease are yellow spots and thickening of eye pigment.
- Amsler grid (a kind of pattern of straight lines, similar to a chessboard). In this case, the patient will observe distortion of the lines.
- Fluorescein angiography. This method allows you to study the vessels of the eye. Angiography dye is injected intravenously, and after a short time the condition of the vessels is assessed using special equipment to identify abnormalities.
- Optical coherence tomography. It makes it possible to obtain images of cross sections of the retina and assess the condition of its structure.
- Retinal biopsy and further histological examination.
- Multifocal electroretinography.
Treatment and prevention of retinal dystrophy
Unfortunately, treatment methods that can completely eliminate retinal dystrophy have not yet been developed. However, there are therapeutic and surgical methods that can slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
Drug treatments
- Medicines that inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels. They prevent the growth of new blood vessels, alleviate symptoms and partially restore visual acuity. Used in the treatment of exudative forms of the disease.
- Vitamins and microelements. Ascorbic acid, beta-carotene, tocopherol, zinc, honey and a number of other substances have a beneficial effect on eye health and reduce the symptoms of dystrophy.
- Antioxidants.
Surgical methods of treatment
- Laser therapy. Using a laser, actively growing abnormal vessels are destroyed.
- Photodynamic laser therapy. This is a two-step method that is more effective for choroidal neovascularization.
Prevention of retinal dystrophy
- To give up smoking.
- Diets that limit fat intake, including cholesterol.
- Sufficient physical activity.
- Losing excess weight.
These preventative measures are something that everyone can take. They are especially relevant for older people, but are also recommended for younger people. These measures do not provide a 100% guarantee. However, they can play a crucial role in keeping you healthy.
To ensure timely detection of pathological changes, patients at risk are strongly advised to at least once a year .
Share on social networks!
0
Comments (0)
No comments yet
Leave your comment
- You are commenting as a guest
Dental practice ORIS
Dear readers! I invite you to a consultation with a periodontist. Today we will talk about the manifestations of dystrophy in the oral cavity. Dystrophy is a violation of trophism, that is, tissue nutrition. Osteodystrophy is characterized by a weakening of the crystalline structure of the bone tissue of the jaws, hard tissues of the teeth, a decrease in its density and volume, replacement with fibrous tissue, and, as a result, a pronounced decrease in local immunity.
In the oral cavity, clinical signs of dystrophy are exposure of roots, formation of periodontal pockets and wedge-shaped defects, increased sensitivity and pathological abrasion of teeth.
When I, the periodontist ORIS, proceed to reveal the causes of these diseases, patients perceive my words with doubt: is everything really that big? Is everything really so closely connected? And can all problems really be “read” by their teeth? To understand the cause-and-effect relationships, let's step back and consider any work team. If the cleaner did the cleaning improperly or completely ignored it, the workers’ mood at the sight of dust and debris will be spoiled and depressed, and this will affect their performance and productivity. From dust and compressed air, oxygen starvation will develop, your head will hurt, and with it all problem areas (teeth, gums, joints, spine). Another example: your boss is angry! It's not good for anyone, is it? Increased nervous tension will lead to a powerful surge of adrenaline, a rise in blood pressure and will manifest itself as pain in the wisdom tooth, itching in the gums, and “threading” in multi-rooted teeth, because the oral cavity has a monosynaptic connection with the brain. That is, electrical impulses during periods of brain and nervous tension directly enter the nerve plexuses of the oral cavity, causing pain and discomfort. This is the body's protective reaction to stress. The principle is simple: if a person is in pain, he strives to eliminate and block all irritating factors - this is the instinct of self-preservation. EVERYTHING in the world is interconnected! And in the body, all organs and systems depend on each other and always act together. Remember the article “Immunity” .
Well, the reasons for the clinical manifestations of dystrophy in the oral cavity
lie in poor nutrition, physical inactivity, unbalanced physical activity, unbalanced bite, circulatory disorders, innervation, hormonal changes and disruptions, taking “dopings” and medications, and general diseases.
In each specific case, you need to understand and look for ways to solve the problem. Finding out the reasons requires time, the interest of the doctor and the patient in the final result, professional knowledge and strength, and restructuring the initial conditions will take years, dedication, discipline and motivation of patients.
You have severe periodontitis,
with pronounced atrophy (loss) of the bone tissue of the jaws (in the area of individual teeth the bone tissue is almost completely lost), with severe exposure (2/3 or more) of the roots, the presence of wedge-shaped defects, increased sensitivity and mobility of the teeth, an unbalanced bite, poor circulation and tissue trophism. Complex treatment of such a patient will be quite complex and lengthy, because it is vital to change the destructive, pathological “scenario” of oral cavity degradation! We must act actively and immediately - this is obvious, isn’t it?!
Here is another example of severe periodontitis with pronounced atrophy of the bone tissue of the jaws, exposure of the roots of the upper teeth - 2/3, lower - 1/3 of the length, wedge-shaped defects, unbalanced bite, mobility of all teeth of varying degrees, with impaired blood circulation and tissue trophism .
This clinical case is also not easy. In addition to professional difficulties, one has to overcome “pathological” principles of consciousness and worldview, prejudices and misconceptions, and previous negative experiences of patients. The more confused and neglected everything is, the more difficult it is to “restore order” to the oral cavity and give the patient a completely new quality of life! Don't let yourself go! Listen to our advice!
Today we will look at the common causes of dystrophy in the oral cavity, which you can eliminate.
The NUTRITION of modern people is depleted in proteins, microelements and vitamins; in most cases it cannot be called balanced. We informed you about the principles of proper nutrition in the article “Food Hygiene”. Remember it and pay attention to the weekly diet of families from different parts of the world and compare it with yours. Nutrition needs to be reviewed every new season of the year, making significant adjustments. It is necessary to carefully plan your diet every week and keep a food diary for analysis and control. Most often I hear: “My wife cooks deliciously, but it’s not healthy” or “Everyone has gastritis!”, “I’m already 50, and I don’t want to eat only grass!”, “My mother didn’t teach me to eat differently,” “Mom didn’t teach me to cook differently.”
My friends, your mother cannot teach you everything, but she gave you life and the opportunity to improve
non stop !!!
I dedicated an entire section of the Dental Health blog to PHYSICAL ACTIVITY . I will briefly express fundamental thoughts: your physical exercises will be effective, that is, healthy, only if: preliminary stress relief - alignment - according to the principles of Pilates; proper warm-up, with the preparation of all major joints; systematic progressive training methodology (from simple to complex); varied weekly physical activity (Pilates, cardio, strength training), cool-down with elements of stretching and yoga breathing practices. Don't allow physical inactivity into your happy life! Take walks in the fresh air every day and don’t forget to chew properly, as I taught and teach you! Remember my article “Experiment”.
GENERAL HEALTH
we must preserve and strengthen all life. This is our duty to the Motherland and duty to our family!
And the prevention of all diseases lies in nutrition, physical activity, and timely elimination of functional disorders so that they do not become organic. For example, sedentary work must be compensated by walking, swimming, fitness, otherwise osteochondrosis will develop, compression of the neurovascular bundles of the neck will occur and will lead to impaired blood circulation and trophism of the oral cavity, periodontitis, atrophy of the bone tissue of the jaws and, ultimately, loss of teeth! Bleeding gums and bad breath must be eliminated in time, before the inflammatory process affects the bone tissue of the jaws and weakens your immunity! Dental health reflects the real state of functioning of the organs and systems of the body, their balance and interaction. Don’t be like the bureaucratic management system: “I don’t see anything, I don’t hear anything, I won’t tell anyone anything.”
Change behavioral stereotypes, think, delve into it, help yourself under the strict guidance of a dentist.
Be active and proactive, understanding and hardworking!
DEFEND YOUR RIGHT TO A HAPPY LIFE!