It is logical to assume that increased gas formation (flatulence) is a consequence of excess gas, which begins to accumulate in the intestines. More than half of all people with various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) experience signs of increased gas formation in the intestines on an ongoing basis1.
Most people can eliminate flatulence, but you will have to make an effort and figure out which remedies are most effective. To do this, it is necessary to understand the processes of occurrence and accumulation of gases in the intestines.
Causes of flatulence
Flatulence is a fairly common phenomenon that can occur even in healthy people. For example, when consuming certain foods or having a tendency to overeat. Remember, there are situations when a long period of time passes between meals. And when you finally have the opportunity to eat, you want to eat more so that the long-awaited feeling of fullness comes sooner. It is at such moments that you may encounter a feeling of fullness in the abdomen caused by increased gas formation.
If discomfort begins to bother you regularly and it is not possible to associate it with specific situations, then a symptom such as flatulence, or bloating, may indicate a disruption in the functioning of the intestines. In this case, you should listen more carefully to your body.
Flatulence can be one of the symptoms of a problem such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). This name combines a complex of symptoms with which the body tries to attract our attention: abdominal pain, stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea or their alternation), bloating and increased gas formation1.
Irritable intestines are a consequence of a busy lifestyle with frequent stress, fatigue and emotional overload, as well as dietary errors and snacks on the go. Another reason may be previous intestinal infections when the intestines have not fully recovered3.
Thus, the cause of bloating (flatulence) in IBS is a malfunction of the intestines. With IBS, flatulence, or bloating, often occurs along with constipation. This is due to the fact that food is “locked” in the intestines, which provokes fermentation processes and, as a result, the release of gases2.
So, flatulence can occur as an independent symptom after taking certain foods or meals. However, if flatulence occurs regularly and is accompanied by abdominal pain or bowel irregularities, this may indicate that the intestines are irritated.
Symptoms of gas formation in the intestines due to a lack of enzymes
Increased gas formation in the intestines against the background of impaired digestion has clear symptoms. Many symptoms are quite obvious4:
- bloating - a distended abdomen is the most obvious sign of increased gas formation, often accompanied by heaviness after eating;
- seething and rumbling in the stomach is the “loudest” symptom that can occur at the wrong moment and can be heard by people around you;
- belching and hiccups - frequent and severe belching is a direct symptom, also applies to hiccups;
- diarrhea and constipation - due to a lack of enzymes, diarrhea is more common due to insufficient quality of fat processing;
- discomfort and pain in the abdomen.
How to treat flatulence in adults?
Treatment of flatulence is determined depending on the cause of this symptom.
If increased gas formation is the body’s response to foods, then it is important to reconsider your diet and diet.
One of the most important stages in the treatment of flatulence is diet6. In order to eliminate excess gas formation, it is worth thinking about useful habits:
- for some time, remove legumes, sweet and flour products, carbonated drinks, raw vegetables and fruits from the diet;
- give preference to fermented milk products, crumbly porridges, boiled meat, wholemeal bread;
- adhere to fractional meals (eating in small portions every 2-3 hours);
- maintain a drinking regime (drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day);
- don't overeat at night3.
If the appearance of bloating (flatulence) is associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome, then treatment of gas formation requires an integrated approach. Just following a diet to normalize work will not be enough, since the problem has been developing for a long time. Quickly accustoming yourself to a new diet is not easy. A remedy for restoring intestinal function will be a good helper.
Antifoaming drugs, which are usually used to treat flatulence, may also not be enough. Such drugs help relieve the symptom here and now, but they will not be able to restore functional impairment. In order for the problem of flatulence to be resolved naturally, time and a suitable drug are needed to train the intestines to work correctly4.
Survey
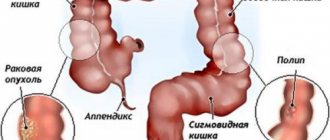
The diagnostic search is often difficult due to the variety of pathological conditions in which flatulence is observed. It is recommended that the initial treatment of this problem be with a local physician or gastroenterologist. Since bloating is detected in 80-85% of gastroenterological patients, a comprehensive examination begins with methods that allow you to quickly localize the level of gastrointestinal damage, and only after that consultations with other specialists are recommended. The most informative are:
- Endoscopic examination
. A visual examination of the digestive organs is aimed at identifying inflammation, mucosal defects, and tumors. Taking into account the probable pathology, endoscopy, colonoscopy, and capsule endoscopy are prescribed. If indicated, an endoscopic biopsy is performed for histological examination of the material. - Sonography of the abdominal organs
. A survey ultrasound of the abdominal cavity allows you to quickly assess the condition of parenchymal organs, biliary tract, spleen, blood vessels, and detect space-occupying formations and cysts. If necessary, a separate ultrasound of the liver, pancreas, and stomach is performed. - X-ray examination
. Of the x-ray methods, the most commonly used are survey x-rays of the abdominal cavity and x-rays of barium passage through the small and large intestines. To specifically identify organ damage, retrograde cholangiopancreatography and stomach radiography are often performed. - Environmental Analysis
. If there is a possible connection between flatulence and impaired gastric, pancreatic, and biliary secretion, gastric and duodenal intubation is recommended. Intraesophageal and intragastric pH-metry can help identify increased acidity and gastroesophageal reflux. - Lab tests
. Most often, biochemical tests of the liver are performed, the level of pancreatic enzymes in the blood and urine, and the content of pepsinogen in the blood are determined. In addition to the coprogram, stool tests for helminth eggs and occult blood, fecal culture for dysbacteriosis and pathogenic flora are indicated.
If you have flatulence, you should avoid foods that cause gas.
Flatulence Remedy for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The drug Duspatalin® 135 mg was created specifically for the treatment of irritable bowels. Thanks to a special mechanism of action, the drug helps not only relieve pain, but also restore its function5. This allows you to control symptoms such as pain and spasms, bloating, gas formation and stool disorders: diarrhea or constipation when taking a course of 28 days7.
You can read more about Duspatalin® 135 mg tablets here5.
Co-author of articles, editor - Shimbaretsky Georgy Alekseevich.
When to see a doctor
By itself, intestinal gas rarely indicates the presence of a serious illness. They can cause discomfort and embarrassment, but are usually just a sign of a normally functioning digestive system. If you experience frequent attacks of flatulence, you should work with a nutritionist to find a more suitable diet.
However, you should see a doctor if flatulence is persistent or severe, or if the flatulence is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, unintentional weight loss, blood in the stool, or heartburn.
At first glance, flatulence may not cause serious discomfort in everyday life, but increased gas production may indicate the development of a dangerous disease.
Diet
First of all, you need to exclude foods that increase gas formation from your usual diet. For some patients, these include flour products, and for others, meat and fatty foods. Particular attention should be paid to foods high in fiber (cabbage, various fruits, brown bread, tomatoes, berries, legumes). It is better not to eat vegetables raw, but try to bake or stew them. There is no need to completely exclude them from the diet.
Doctors advise stopping eating ice cream and whole milk for 2 weeks. If, after this time, intestinal motility returns to normal, then the cause of the dysfunction is lactose intolerance. If there are no changes, it is useful to eat kefir and cottage cheese every day.
For a while, it is necessary to exclude carbonated drinks and beer, because they cause fermentation. Chewing gum is also prohibited. During the chewing process, a person swallows excess air.
To get rid of constipation, you need to include indigestible fiber in your diet. It is found in large quantities in wheat bran. Exotic dishes can also pose a danger. Therefore, you need to give up Asian or Chinese cuisine for a while.
Sources
- Management of common gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population. A global view of heartburn, constipation, flatulence and abdominal pain/discomfort // Global practical recommendations of the World Gastroenterological Organization. - May, 2013.
- Hyun Jik Lee, Kyung Sik Park. Bloating [Electronic resource] // Korean Journal of Gastroenterology, December 2021.
- Max Schmulson. Understanding Bloating and Distension [Electronic resource] // International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, 2013.
- Nayoung Kim, Dong Hyun Oh. Abdominal Bloating: Pathophysiology and Treatment [Electronic resource] // Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility, October 2013.
- Carly Gennaro, Helaine Larsen. Symptomatic Approach to Gas, Belching and Bloating with OMT Treatment Options [Electronic resource] // Osteopathic Family Physician, 2021.
Unpleasant odor due to gas formation
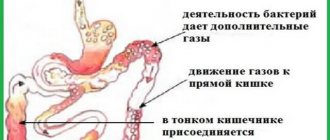
Normally, approximately 0.1-0.5 liters of gases are excreted during the day. For problems with digestion and severe flatulence, this volume increases to 3 liters. The process of involuntary release of gases, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, is called flatus in medical practice. This indicates disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal gases are continuously produced and consist of 5 components:
- nitrogen;
- oxygen;
- hydrogen;
- carbon dioxide;
- methane.
Sulfur-containing components give gases a specific odor. They are produced by bacteria living in the intestines. You can cope with flatulence and foul odor if you know the root cause of the problem.
Where is an MRI of the intestine done?
Remote screening using a hardware installation is available in specialized medical institutions that contain diagnostic rooms with high-precision equipment. In St. Petersburg, both state and private organizations, distributed throughout all districts of the city, receive admissions. Before registering for a study, you must make sure that the clinic uses tomographs with a field generation frequency of 1.5 Tesla or more. Only high-field machines guarantee the correct scanning result.
You can find and compare MRI medical centers on the service of the “Unified Recording Center” in St. Petersburg. At the top of the page is the number of the consultation service, whose operators will not only answer your questions in detail, but will also suggest the addresses of conveniently located clinics and make an appointment for your free time. Institutions are distributed by location, ratings, prices for services and technical indicators of equipment, which makes comparison and selection easier. Book the procedure through the portal and receive a special discount from the service.
Diagnostics
Since flatulence can occur as a result of normal body function, attempting to diagnose causes may not be practical. Diagnosis is required for prolonged, intense flatus with a strong unpleasant odor and constant bloating.
Due to the fact that flatulence is a symptom of many diseases, it becomes difficult to diagnose its origin. First of all, you need to consult a gastroenterologist, since flatulence, in most cases, occurs as a result of damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Only after this, if necessary, the patient can be referred to other specialists.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Photo: peoplecreations/freepik.com
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Physical examination. An external examination of the patient is carried out, a medical history is examined, an anamnesis is collected from close relatives for the presence of possible hereditary diseases. The doctor will also carefully examine your diet and lifestyle.
- Laboratory research. In this case, the patient undergoes a blood test (for the content of enzymes), feces (for the presence of blood and helminth eggs), microflora of the stomach and intestines, and urine. Additionally, a biochemical study of the liver is performed.
- Instrumental research. Common methods in gastroenterology are colonoscopy, ultrasound and abdominal radiography.
Diagnostic measures
If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should contact a therapist or gastroenterologist, who will conduct an initial history taking, examination and interview of the patient. If necessary, other highly specialized specialists will be involved in the examination: neurologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists or infectious disease specialists. At the primary stage, laboratory test data is collected and assessed. The presence or absence of inflammatory processes, parasitic lesions, and pathogenic microflora is determined.
Next, hardware research methods are assigned, the list of which is as follows:
- non-invasive examination of the rectum;
- probing imaging methods (endoscopy, colonoscopy);
- ultrasonography;
- ultrasound examination (adjacent organs are studied);
- contrast radiography or MSCT;
- irrigoscopy;
- MRI of the intestines.
Instrumentally penetrating research methods are not always applicable in individual cases. There is a risk of additional injury when inserting a probe rectally, and traditional methods such as ultrasound or radiography are sometimes unable to provide correct results due to layers of intestinal structures. The most informative, safe and painless method is magnetic resonance screening, which allows you to study even distant canal loops that are inaccessible to colonoscopy.
Drug treatment
Treatment of flatulence in adults may include a number of medications:
- enzyme preparations;
- choleretic drugs;
- probiotics and prebiotics;
- antispasmodics and prokinetics, etc.
Enzyme replacement therapy can help reduce symptoms if they are caused by enzyme deficiency or pancreatic disease. Choleretic agents increase the volume of bile in the intestine, which promotes normal motility in diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
Restoring the normal balance of microflora is an important factor in the treatment and prevention of flatulence. The doctor may prescribe prebiotics, probiotics or synbiotics containing lactobacilli. They have been proven to suppress excess gas formation.
Intestinal motor disorders can be eliminated with the help of prokinetics or antispasmodics. Such prescriptions require careful examination; drugs have certain restrictions and are prescribed according to indications.
Treatment of flatulence that develops as a result of poor nutrition may involve only symptomatic therapy. Adsorbents are able to bind gases in the intestines and reduce their volume, relieving unpleasant symptoms. It is important to understand that some sorbents can cause stool retention, so you should be careful when choosing a drug.
"Fitomucil Sorbent Forte" is a drug that can be recommended for flatulence. This is a natural sorbent, the action of which is complemented by a complex of probiotics in the composition. The product works due to dietary fiber - the shell of plantain seeds: it absorbs toxins, excess liquid and gases, and helps reduce gas formation in the intestines. Inulin in Fitomucil Sorbent has a probiotic effect and stimulates the growth of beneficial microflora. A complex of living probiotic bacteria has a beneficial effect on digestion. One of the indications for the use of the drug is post-infectious digestive disorders in the form of diarrhea, flatulence, and unstable stool.
Symptoms
Flatulence is manifested by bloating or attacks of cramping pain, and may be accompanied by nausea, belching, loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea, problems with sleep, headache and general weakness. Bloating during flatulence is one of the most striking manifestations of an increase in the amount of gases in the intestines. It is impossible not to notice it, since bloating is accompanied by pain and a feeling of severe discomfort. The abdomen increases in size due to the overflow of the intestines with gases. However, their passage does not occur, since the large intestine is spasmed.