Common causes of hiccups
The content of the article
As a rule, hiccups appear unexpectedly and last for several minutes.
Most often it is a consequence of poor eating habits. It occurs when we eat in a hurry, greedily swallowing large, unchewed pieces of food.
In such a situation, a lot of air is swallowed and the quickly filled stomach stretches and begins to put pressure on the diaphragm, and this is the most important respiratory muscle that separates the lungs from the abdominal cavity.
Eating too cold, hot or spicy foods also contributes to the occurrence of hiccups. It is worth mentioning large volumes of carbonated drinks. When they are consumed, a significant amount of carbon dioxide accumulates in the stomach.
Often, hiccups appear after drinking alcohol. It irritates the nerve endings of the diaphragm, relaxes the muscles of the throat and stomach. Carbonated drinks can also cause a similar effect, especially when drunk quickly. If after the above types of drinking or eating on the go, frequent hiccups begin, it is worth changing bad habits.
Survey
A diagnostic search aimed at clarifying the causes of hiccups is carried out when it is combined with other symptoms, occurs frequently, and attacks last more than 60 minutes. The examination plan is drawn up taking into account the medical history and accompanying symptoms. Most often, primary diagnosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist, who, according to indications, involves other specialists in examining the patient. Depending on the suspected cause of the symptom, the following are used for express diagnostic purposes:
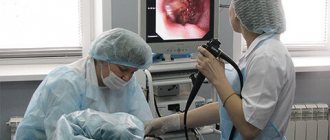
- Endoscopic studies
. Gastroscopy is the most informative method that allows you to quickly objectify pathological changes in the esophagus and stomach. If space-occupying formations, erosions and ulcers are detected during endoscopy, a biopsy is performed for histological analysis of the material. - X-ray methods
. X-ray of the abdominal cavity, X-ray examination of the chest are carried out to detect gastrointestinal pathology, relaxation of the diaphragm, pleurisy, mediastinal tumors and other possible causes of hiccups. Next, RCP and other X-ray contrast techniques are used. - Ultrasound research .
Sonography of the abdominal cavity is performed to assess the echostructure of the main parenchymal organs and identify free fluid; according to indications, it is supplemented by ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver. If pleurisy or mediastinal tumors are suspected, ultrasound of the pleural cavity and mediastinum is indicated. - Tomography
. If radiography and sonography are insufficiently informative, CT, MSCT and MRI of the abdominal or thoracic cavities and individual organs are performed. MRI of the head and spine are highly accurate in diagnosing cerebral and spinal pathologies. In difficult cases, an MRI of the whole body is performed. - Electrofunctional Research
. After excluding abdominal and thoracic causes of hiccups, electroencephalography is recommended. The method identifies foci of pathological activity in the brain. To clarify the level of damage to the nervous system, electroneurography and electromyography are also performed. - General blood analysis
. With high leukocytosis, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, and an increased ESR, further diagnostic search is aimed at identifying inflammatory and neoplastic processes. The analysis is often supplemented with the study of enzymes (ALT, AST) and determination of the level of C-reactive protein.
Upon receipt of preliminary information about a possible disease that provoked hiccups, further examination is carried out according to the appropriate protocol and may include a wide range of laboratory and instrumental methods. Differential diagnosis is carried out between various pathological processes in which hiccups may develop.
If you have hiccups, it is recommended to drink water in small sips.
Specific causes of hiccups
When we eat too much food, we feel sleepy and begin to lie down on the bed. In this case, you should not sleep on your right side. Because then the diaphragm additionally shifts, the airways work worse, and this contributes to hiccups. After a hearty lunch, it is useful to take a walk rather than doze off on the couch.
The cause of this embarrassing illness is chronic stress. When we are nervous, the heart beats faster, breathing becomes irregular, and the diaphragm does not work rhythmically. In such a situation, using infusions of sedative herbs, for example, lemon balm, valerian, and St. John's wort, can help. Sometimes a prescription anti-anxiety or anti-depressant medication may be needed.
Hiccups that recur several times a month or a week and are not relieved with home remedies may be a signal of illness.
Most often, hiccups are caused by problems with the digestive system.
Hiccups can be a symptom of inflammation of the stomach lining or gastroesophageal reflux, when stomach acids irritate not only the throat and esophagus, but also the nerves of the diaphragm.
Other diseases that hiccups may indicate are stomach ulcers or even abdominal cancer. Sometimes a symptom may indicate lesions of the lungs or mediastinum. If the doctor suspects a serious cause, he will refer the applicant for appropriate research.
Classification
The main criteria used in systematizing the variants of hiccups are its connection with pathological conditions, development mechanisms, and duration. In most cases, hiccups are physiological in nature and are not associated with any diseases. Diaphragmatic myoclonus is called pathological, occurring against the background of various diseases and presented in such forms as:
- Central hiccups
. It is caused mainly by disturbances in the brain regulation of diaphragmatic contractions. It is observed in cases of inflammation, tumors and injuries of the brain and spinal cord. It is possible to develop hiccups with functional disorders of the central nervous system. - Peripheral hiccups
. Associated with damage to various parts of the phrenic and vagus nerves. Characteristic of volumetric processes in the mediastinum, diseases of the chest and abdominal cavity adjacent to the diaphragm. - Referred hiccups
. It is provoked by pathological conditions in organs located outside the zone of innervation of the vagus and phrenic nerve. It can be observed against the background of enteritis, colitis, helminthic infestations and diseases of the female reproductive system. - Toxic hiccups
. It becomes a consequence of poisoning of the nervous system with endo- and exotoxins. It is detected in case of poisoning with mushroom poisons, alcohol and medications (anaesthetics, drugs), uremia, diabetic coma, terminal conditions.
Physiological hiccups are usually short-lived. With pathological contractions of the diaphragm, there are episodes of transient hiccups (from several minutes to several hours), persistent hiccups lasting more than 2 days, and long-term hiccups (from a month or more). Although usually prolonged hiccups indicate the presence of pathological conditions, in rare cases it can be observed in a healthy person.
Sucking and chewing
Some people find it helpful to swallow a sugar cube without drinking water or chew the peel of bread.
Another home method is to suck on an ice cube or a slice of lemon. These actions require concentration and thereby divert attention from the hiccups. Then the breathing rhythm changes, which in turn helps to calm the diaphragm, eliminating hiccups.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Symptomatic therapy
Episodes of physiological hiccups go away on their own within 2-10 minutes. Sometimes, to relieve them faster, it is enough to be distracted, take a deep breath 2-3 times, hold your breath for a while, or drink a couple of sips of water. If the attack continues despite distracting and reflexive methods being taken, taking into account the patient’s condition, it is recommended to contact a local or family doctor, who will prescribe further examination, or call an ambulance if the patient’s condition rapidly worsens.
Before hospitalization and examination to stop hiccups, a medical professional can stimulate some reflexogenic zones in the face and exit points of the phrenic nerve, insert a catheter intranasally to a depth of 12 cm. Sometimes an intravenous infusion of calcium preparations has a relief effect. With a probable central and especially psychogenic genesis of hiccups, sedative herbal preparations, tranquilizers and antipsychotic drugs are used.
Attention (this is important)!
Intractable hiccups that last more than an hour can be a sign of intoxication or severe brain pathology. In such cases, delay in hospitalization significantly worsens the prognosis of the underlying disease, leading to the need for more complex drug regimens and emergency invasive interventions. An urgent call to an ambulance is necessary for hiccups combined with vomiting, disturbances in sensitivity, motor activity and consciousness. Repeated bouts of hiccups are also a reason for a thorough examination.
Tests and diagnostics
For diagnosis, it is important to collect an anamnesis, as a result of which illnesses suffered, the presence of head injuries, surgical interventions on the brain and spinal cord, and manipulations are revealed. Triggers that provoke hiccups, medication use, and the patient’s attitude toward smoking and alcohol are identified.
- a full examination and examination by specialists (otolaryngologist and neurologist);
- Clinical and biochemical blood test (electrolytes, C reactive protein, urea, creatinine, amylase, liver tests);
- MRI of the brain;
- CT scan of the chest;
- electroencephalography;
- esophageal manometry;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirography;
- Lumbar puncture.
Practical conclusions:
Hiccups are very common and usually completely normal.
The first and most logical action for a child’s parents when severe hiccups occur is to simply hug and reassure, and give him water to drink.
A sudden increase in hiccup episodes may also be caused by GERD, but may be associated with other, not always clear, reasons. It is necessary to clarify whether there are other signs of reflux - heartburn, belching, pain and discomfort behind the sternum.
Excessively prolonged hiccups require a doctor's examination and examination. This may include examination of the esophagus and stomach (FGDS, X-ray, CT).
2, total, today
What exactly should not be done during hiccups
Frighten.
This method rarely brings relief to an adult, and will almost certainly harm a baby. At a tender age, the baby’s nervous system is still very weak and a sudden “boo!” Not only will it not get rid of hiccups, but it can also cause anxiety in the child.
Slap on the back.
The baby's skeleton is still very fragile, so any sudden movements can lead to serious damage. Instead of patting, you can gently give a light, pleasant massage to relax the baby's muscles.
Use medications and other means without a doctor’s prescription.
Caring grandmothers often recommend remedies that “in better times” helped their children from all ailments. But all medications should be prescribed only by a pediatrician.
There is no need to become a doctor for a child and look for drugs or grandmother’s advice on how to get rid of hiccups in a baby. It is better to be a caring parent, feeding him with your calmness. If hiccups are frequent and persistent, you should definitely show your baby to the doctor so as not to miss its pathological causes.
List of sources
1. Event-related potentials following contraction of respiratory muscles in pre-term and full-term infants, Clinical Neurophysiology
Risk of hiccups when drinking alcohol
Usually this phenomenon occurs due to involuntary contractions of the diaphragm and larynx. During normal flow, it helps remove air accumulated there from the stomach. It occurs suddenly and passes just as quickly, causing virtually no inconvenience .
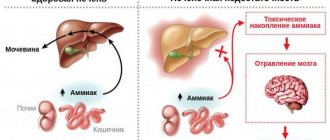
But hiccups when drinking alcohol, caused by its toxic effects , are a phenomenon of a completely different kind. Its appearance indicates an increase in the size of the liver and intoxication. It may also be a signal of central nervous system dysfunction. Processes begin in the body that lead to irreversible consequences. Observed:
- uncontrolled urination;
- nervous exhaustion;
- disturbance of sleep and wakefulness;
- partial memory loss;
- sensory disturbance;
- amyotrophy.
You should contact a narcologist immediately if these symptoms and hiccups appear. It may also indicate the possible development of a heart attack . Hiccups should be perceived as a signal of dysfunction of the cardiovascular, reproductive, immune, nervous and digestive systems, aging and wear and tear of vital internal organs, and not as a common occurrence.
Among other things, hiccups after alcohol can be a manifestation of a very dangerous disease - alcoholic polyneuritis, which accompanies all alcohol addicts. Therefore, when it appears, it is recommended to pay attention to the following symptoms :
- fatigue;
- painful sensations in the muscles of the lower leg;
- disturbance of sleep and wakefulness;
- loss of sensation in the arms and legs.
If medical assistance is not provided in the near future, it is very likely that alcoholic polyneuritis will end in the death of the patient. Uncontrolled hiccups threaten the life of the drinker . He may choke on food or choke on vomit. Also, during contractions of the diaphragm, a microinfarction is possible.
List of sources
- Ivashkin V.T., Trukhmanov A.S. Evolution of ideas about the role of disorders of the motor function of the esophagus in the pathogenesis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology 2010; 20(2):13-9
- Cherkasov M.A., Mokhanna M.I., Ibragimov Z.A., Rabadanov R.Sh., Kovalenko A.N., Aliev A.G. Persistent hiccups after epidural anesthesia for revision hip replacement // International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research. – 2021. – No. 9. – P. 86-90.
- Shtulman D.R., Levin O.S. Neurology: A Practitioner's Handbook. 6th ed. 2008, 1024 p.
Diet
There is no special diet for central hiccups, since it is impossible to influence this process with therapeutic nutrition. For food-related hiccups, it is important to monitor the amount of food you eat and the speed at which you eat it, as both of these factors can trigger hiccups. For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, therapeutic nutrition should be used in accordance with the underlying disease. The general principles are fractional meals, exclusion of fatty, spicy, fried foods, foods that cause bloating (legumes, baked goods, kvass, an abundance of simple carbohydrates).
Proven methods for getting rid of hiccups after drinking alcohol
Often, neither the drinker himself nor his relatives take this phenomenon seriously, but this is a fundamentally erroneous opinion , because it is one of the main signs of severe poisoning of the body. Therefore, you need to know methods on how to get rid of hiccups after drinking alcohol.
The first action that needs to be taken is to induce vomiting to clear the stomach of alcohol. This will prevent an increase in the concentration of ethanol in the blood and eliminate discomfort by switching the nervous system to the gag reflex.
For hiccups caused by drinking alcohol, it is recommended to take foods with a strong taste: mustard, horseradish, citrus fruits, garlic, onions, pickled apples and cabbage. The latter contain succinic acid, which promotes the oxidation of toxic breakdown products of ethanol and their removal from the body, sobering up.
You can eliminate discomfort through breathing exercises. The simplest exercises are pulling up with your arms and bending down while holding your breath. You need to do 10-15 repetitions. Gymnastics will not only relieve discomfort, but also improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system and, accordingly, overall well-being. It is better to do gymnastics in the fresh air or in a well-ventilated area . You can improve your well-being by walking, which promotes:
- improving blood circulation;
- eliminating oxygen starvation of cells;
- normalization of metabolic processes;
- improving the functioning of the bronchopulmonary system;
- sobering up;
- normalization of sleep and wakefulness.
In the question “how to get rid of hiccups from alcohol,” the use of unconventional, extraordinary methods can help, such as distracting attention through conversation, an interesting movie, a computer game, or communication on social networks. You can eliminate discomfort and improve your overall well-being by drinking good quality water or green tea without sugar. However, all of the above makes sense if you stop drinking alcohol immediately after discomfort occurs.
Treatment
Non-drug
It is recommended for use before the use of medications; it is prescribed purely individually. The most common types of non-drug therapy are the following.
Changing the diet : reduce the single volume of food taken with an increase in the frequency of intake.
Use of mint infusion : helps relax the sphincters, should be freshly prepared, not used together with prokinetics that increase the tone of the muscles of the stomach and intestines and the lower esophageal sphincter.
Nasopharyngeal stimulation techniques:
- rinse your nose with cold water;
- suck cold water through a straw, swallow or suck small pieces of ice;
- swallow 1 teaspoon of dry granulated sugar;
- quickly drink two glasses of water;
- gargle with water;
- suck on lemon slices;
- swallow pieces of dry bread;
- inhale saline solution through a nebulizer;
- stretch your neck;
- massage the soft palate for 1 minute;
- stretch out your tongue with your fingers;
- press hard on your tongue.
Preventing irritation of the diaphragm : bend forward, pressing your knees to your stomach.
Stimulation of the C5 dermatome (interrupts stimulation of the hiccup neural arch):
- patting or scratching the back of the neck;
- placing a cold, safe metal object behind the collar (for example, a key);
- cold compress on the face.
Breathing manipulations:
- holding your breath;
- causing sneezing or coughing;
- frequent deep breathing (hyperventilation);
- breathing into a paper bag (hypoventilation);
- “Valsalva maneuver” (forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed). Should not be carried out if you have a cold, because... the infection can penetrate into the middle ear cavity, and in patients with heart disease (increases blood pressure). Use caution in patients with pulmonary emphysema, primary/secondary tumor lesions of the lungs, so as not to provoke pulmonary hemorrhage.
Medication
Treatment for hiccups is determined by the cause of its occurrence. In palliative care, hiccups are most often caused by several causes; as a rule, an integrated symptomatic approach is used for treatment (see Diagram 1, Appendix 1).
Table 1 shows the medications and dosages used in the treatment of hiccups. The route of administration of drugs is oral (inside), unless otherwise indicated.
How to treat hiccups, including prolonged ones?
There are so many treatment methods that it seems to hint that none of them works one hundred percent.
Always start with household methods :
Calm down.
Drink water - plain, with lemon, with ice. Gargle with water. Touch the uvula or the wall of the pharynx with a spatula or spoon. All this is needed to create a new impulse from the throat receptors to the vagus nerve network.
In the hospital, the stomach is sometimes washed with ice water.
This is also a reflex effect. This also removes pressure on the walls of the stomach from the inside. At home, you can simply provoke vomiting in yourself or your child, for example, in a “restaurant” way.
Holding air while inhaling, simulating straining, hyperventilation - consciously increasing breathing, light massage of the eyeballs through closed eyelids can help.
If simple methods don’t work, they use medications.
Most often, persistent hiccups are treated with the following drugs:
Gabapentin is a drug for the treatment of neuropathies and seizures.
Baclofen is a muscle relaxant.
Interestingly, baclofen is also used to treat persistent esophageal reflux that does not respond to other treatments.
Second stage treatment:
Metoclopramide (cerucal) is a well-known antiemetic and prokinetic agent. We recently discussed the role of prokinetics in the treatment of GERD.
Chlorpromazine (aminazine) is an antipsychotic.
Proton pump inhibitors are the main drugs for the treatment of GERD and can also be used in the complex treatment of prolonged hiccups.
Tips on how to avoid hiccups after drinking alcohol
It is recommended to monitor your breathing so that it is even, try not to mix carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks. You should not take the latter on an empty stomach. It’s better to have a good snack, but without haste. Controlling the amount you drink is the key to good health in the morning and eliminating the risk of intoxication.
For a “civilized” feast, following these recommendations is realistic. However, a dependent person in the company of his own kind is unlikely to think about such “little things”, and also why hiccups after alcohol are considered not a very good thing. Relatives should take care of his health and well-being.