The importance of proper nutrition in diabetes
If you have diabetes of any type and stage of development, you need to monitor your diet every day. A properly selected diet not only prevents the disease from progressing, but also helps to cope with it. For example, in the early stages it is enough to adjust your diet and adhere to the established rules. Then you can be completely cured even without medications.
Diet therapy involves creating a balanced diet based on the optimal amount of essential nutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, fats) and total calories.
In this case, special indicators are also taken into account, for example, bread unit (XE). This is the name for a measure that reflects the total amount of carbohydrates in a particular food product. The mass of bread taken as 20-25 g per unit (in terms of pure carbohydrates is 10-12 g, i.e. half as much).
A person suffering from diabetes should consume a maximum of 25 bread units every day, i.e. no more than 250 g net carbohydrates. The permissible value is often less - it all depends on the type, stage of development of the disease, weight, age, general condition and the presence of physical activity.
Thus, to ensure proper nutrition it is necessary:
- Make a diet according to your doctor's recommendations.
- Develop a food menu for the week.
- Select products by quantity based on calorie content, nutritional value and bread units.
- Follow these rules strictly for a significant period of time.
- Include regular physical activity, which will also help reduce glucose levels.
Product selection
When creating a diet to lower blood sugar, the main criterion is the glycemic index of foods (GI or GI). This is a digital indicator of the rate of absorption of carbohydrates into the bloodstream, measured from “0” to “100”. Products with a digital GI value of no higher than 30 units are considered ideal for a diabetic. They do not provoke sudden “glucose surges” and help reduce overall blood sugar.
The advantages of such food include:
- minimal amount of monosaccharides;
- slow absorption by the body;
- saturation for a long period of time.
A high glycemic index of foods ranges from 70 to 100. When consumed, glucose quickly penetrates into the systemic bloodstream, which leads to disruption of metabolic processes and hyperglycemia. At the same time, simple carbohydrates tend to transform into fat and are deposited in the body. This is strictly contraindicated for people with diabetes. Products that have an average GI (from 30 to 70 units) are allowed in limited quantities.
Their availability in the daily menu depends on:
- depending on the type of disease (insulin-independent patients are allowed more of this food);
- stage of diabetes (in the decompensated stage it is recommended to eliminate them);
- the general health of the patient and the doses of medications prescribed to him.
To correctly calculate the glycemic index of a dish, there are special food tables with the exact digital GI value.
Examples of a balanced breakfast, lunch and dinner
Menu planning is the main task for a diabetic. We must assume that the maximum calorie content is 1800-2000 kcal per day. Based on this, the composition and quantity of products for each meal are selected.
Breakfast
For tomorrow you can prepare dishes from the following products:
- rye bread (50 g) and butter (5-7 g);
- boiled chicken egg;
- milk glass (200 ml);
- porridge from any cereal (100 g).
Instead of porridge, you can include one of the following dishes:
cottage cheese with a moderate fat content of 4-5% (100 g);
- apple;
- plum;
- peach;
- apricot;
- any citrus (except lemon, lime).
The fruit should be of medium size - the weight in terms of pure pulp is about 100 g. Moreover, it is better to leave the fruit for an afternoon snack as a separate meal. Instead, you can use half a glass of milk (100 ml) for a snack.
Dinner
Lunch is the main meal, so it should be complete. For example, for a proper lunch you can consider the following dishes:
- fish soup or chicken soup (you can use broth with lean meat) 150 ml;
- boiled meat 100 g;
- boiled potatoes 100 g;
- black bread 50 g;
- raw or boiled vegetables 200 g;
- fruit (from those listed above) 100 g.
Dinner
A complete dinner can be prepared using the following products:
- boiled potatoes 100 g;
- any fish (low-fat) 100 g;
- fruits or vegetables 100 g;
- black bread 30 g.
Finally, as a late dinner (1-1.5 hours before bedtime), you can use a glass of low-fat kefir.
Foods prohibited for diabetes
If you have diabetes, you need to exclude or significantly limit a number of foods. These include:
- sugar, honey and sweets;
- sweet soda;
- smoked meats;
- fat meat;
- baking;
- margarine;
- fermented milk products (if they are fatty).
If you can’t give up sweets, you can use fruits and vegetables, as well as sugar substitutes, such as xylitol. Moreover, the quantities of these products should also be limited - it is better to consult a doctor first.
Can I drink coffee?
The question of drinking coffee for diabetes has not yet received a clear answer. There is an assumption that caffeine improves the sensitivity of body cells to the hormone insulin. Based on this, coffee can not only be drunk if you have diabetes, but it is also necessary. In addition, the drink improves your mood, makes you feel more alert, and stimulates brain activity.
On the other hand, there is also harm:
- increased blood pressure;
- load on the heart muscle;
- powerful diuretic effect (can be quite useful);
- weakening of bone tissue;
- increased acidity levels;
- insomnia.
Thus, diabetic patients can be advised to drink one cup of weak coffee every day. At the same time, you should not put not only sugar in it, but also cream. Cinnamon would be a useful addition as it also helps lower sugar levels.
Regulatory boundaries
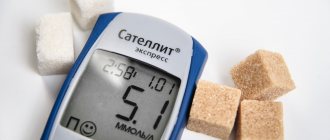
A one-time increase in digital glucose values associated with incorrect consumption of sweet foods on the eve of the test is not yet an indicator of diabetes. Objective data can be obtained by comparing the results of several tests taken on an empty stomach. Regulatory boundaries vary depending on the patient's condition and age. In the presence of infectious diseases or pregnancy, indicators may increase slightly.
When assessing blood sugar levels, the patient's age category should be taken into account
In addition to plasma glucose levels, diabetes mellitus is differentiated by the type of disease:
- Insulin dependent or type 1. It is characterized by a malfunction of the pancreas in the production of the hormone insulin, which is responsible for delivering sugar to tissues and providing them with energy.
- Insulin-independent or type 2. It occurs due to the inability of body cells to use a hormone (insulin), which causes excess glucose to accumulate in the blood.
To diagnose a specific type of disease, not only an analysis for the amount of mmol/l glucose is performed, but also a test for the determination of antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase (GAD antibodies). Only an endocrinologist can diagnose diabetes and determine treatment tactics. To avoid complications, self-diagnosis and self-medication are prohibited.
Why don't my sugar levels go down?
If the diet is balanced and takes into account prohibited foods, total calories and nutrient content, sugar levels can at least be maintained within acceptable limits. But sometimes even proper nutrition doesn’t really help. This is due to various reasons:
- no or very little physical activity;
- severe, ongoing emotional stress;
- violation of the dosage of administered insulin;
- consequences of a stroke or heart attack.
It is quite possible to control and even reduce blood glucose levels with proper nutrition. But it is important to understand that this is not the only way, so with diabetes you need to adjust your entire lifestyle, not just your diet. In addition, the patient should monitor glucose fluctuations and periodically consult a doctor for advice.
Diabetic food basket
Products that lower blood sugar are more correctly called stabilizing this indicator. Not a single dish can replace a diabetic with the first type of disease, a timely injection of insulin. The complex process of forming glucose molecules from the amino acids of eaten proteins (gluconeogenesis) can affect sugar levels, even hours after eating.
Foods with low glycemic activity help maintain glucose levels at a minimum level for a particular stage of diabetes. A diabetic diet to lower blood sugar is based on regular consumption of foods whose GI does not exceed 35 units. With this diet, it becomes possible to control glucose and reduce the dose of medications.
Healthy vegetables, fruits and berries
Products from this category form the basis of dietary nutrition. They not only curb glycemic levels, but also enrich the body with vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Helps improve the general condition of blood vessels and eliminate “bad” cholesterol. In addition, vegetables and fruits are low in calories, which helps control body weight.
List of products approved by endocrinologists:
What fruits can you eat if you have diabetes?
- Apples. They are a source of: pectin, fiber, iron, vitamins A, C, E, manganese, potassium. Stabilizes digestion processes.
- Pomegranate. Due to the content of tannins and fiber, they stimulate intestinal functions, which have a beneficial effect on the process of hematopoiesis. Helps improve the performance of the pancreas.
- Pears. They have a diuretic and bactericidal effect. Helps cope with fluid retention in the body.
- Pomelo. Along with low GI, it is enriched with potassium, which contributes to the smooth functioning of the heart.
- Jerusalem artichoke or earthen pear. Activates the endocrine function of the pancreas to produce insulin. It is an indispensable vegetable in the menu of diabetics.
- Momordica or bitter gourd. A dietary product that helps reduce body weight, stimulates insulin synthesis and improves metabolic processes.
- Cabbage: white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli. Contains B vitamins, strengthens the immune system and the vascular system of the body.
- Cucurbitaceae family: pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini, squash. Combination with protein foods slows down gluconeogenesis. The high water content replenishes fluid deficiency. Zucchini and pumpkin have a higher GI, so they should be used with caution, despite the benefits for the body.
- Cowberry. Acts as a diuretic and insulin catalyst, allowing you to control glucose.
- Kalina. Contains invert sugar, which does not require insulin for transport to body tissues.
- Blueberry. Maintains the health of the pancreas, effectively fights edema, regulates glucose absorption, and has a beneficial effect on the vascular system of the visual organs.
- Black currant. Stimulates metabolic and immune processes, saturates the body with vitamins.
Most vegetables have low calorie and GI content and are optimal foods for diabetes
Legumes and cereals
Not all cereals have a low glycemic index, but when cooked (cooking), the GI decreases. Therefore, porridge must be included in the menu of people with diabetes. Legumes help enrich the diet with minerals and vitamins; when consumed regularly, they can inhibit the breakdown of nutrients. Green beans are used in folk medicine as a product that reduces sugar levels.
Cereals: oats, pearl barley, wheat improve metabolism, normalize digestive processes, and replenish micro- and macroelements. In addition, porridge allows you to maintain a feeling of fullness for a long time and reduce the risk of blood sugar changes. Legumes: beans, peas, chickpeas. They have low glycemic activity. The process of absorption of complex carbohydrates does not require insulin. Rich in minerals and vitamins.
Spices
Spices are believed to lower sugar. They do not have a direct effect on the quantitative composition of glucose, but due to their active participation in the process of gluconeogenesis, glucose absorption slows down, so sugar levels remain at the same level. Spices allowed for diabetes include oregano (oregano), cinnamon, cloves, ground pepper (black, red, white), ginger and garlic.
Protein products
Protein foods do not lower sugar, but their correct combination with permitted vegetables helps maintain glucose balance and prevent sudden “jumps” in glycemia. The sources of protein in the diabetic menu are:
- Dietary poultry meat (chicken, turkey). When cooking, it is necessary to remove oily skin from poultry.
- Nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts). It should be consumed in small quantities so as not to put stress on the weakened pancreas.
- Mushrooms. Despite the low GI, they are considered a heavy, filling food. Allowed for limited use.
- Seafood (mussels, shrimp, crabs) and lean fish. Have minimal effect on blood glucose levels. Enrich the body with protein and minerals (zinc, selenium, calcium, etc.).