04/19/2019 Article
- Diet "Table No. 7"
- Diet “Table No. 7a”
- Diet “Table No. 7b”
In medical-prophylactic and sanatorium-resort institutions, they use the traditional numbered system of diets by M. I. Pevzner for nutrition for certain diseases. The “7 table” diet is indicated for kidney diseases, such as acute and chronic nephritis (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis).
Diet No. 7, complete in energy value, is limited in the consumption of free liquid, salt (sodium chloride) and all substances that irritate the kidneys, stimulate the cardiovascular and central nervous systems, meat, dairy and mushroom broths, foods rich in essential oils and oxalic acid.
Depending on the severity and specifics of the condition, there are variations of this diet.
General rules
As you know, a therapeutic diet is prescribed for various diseases and is a prerequisite for their treatment. Nephritis is a group of kidney diseases of an inflammatory (or autoimmune) nature. This includes glomerulonephritis (the process involves the glomeruli of the kidneys), interstitial nephritis (or tubulointerstitial nephritis - the pathological process affects the interstitial tissue of the kidney), pyelonephritis (inflammation of the pelvis and calyx of the kidney). All of these diseases can be acute or occur in a chronic form, which more often causes renal failure .
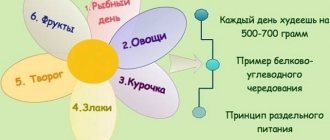
Table diet number 7 according to Pevzner is designed for patients with kidney disease in the recovery stage - usually 3 weeks after an acute illness and discharge from the hospital. The diet has several varieties, which are prescribed at different stages of the disease (exacerbation, subacute course or persistent remission) and taking into account renal function (absence or presence of renal failure). With these diseases, the kidneys are affected to varying degrees and their function is impaired, and the severity of symptoms also differs. These are increased pressure, frequent urination, changes in urine ( red blood cells , casts, protein) and edema syndrome. All this is taken into account when prescribing different types of diet.
Basic Diet 7 table provides moderate sparing of the kidneys, nutrition is aimed at reducing edema and blood pressure . In addition, it helps improve the excretion of nitrogenous metabolic products from the body. It is distinguished by the restriction of proteins, and fats and carbohydrates are contained within the physiological norm. The daily calorie content of this diet is 2700-2900 kcal. The patient is allowed 80 g of proteins per day (mainly from dairy products), 90-100 g of fats and 400-450 g of carbohydrates (in terms of sugar - 80-90 g). Food is prepared without salt.
Thus, Diet No. 7 for kidney disease has the following features:
- Limitation of salt - food is prepared without salt, but it is allowed to consume a certain amount of it (3-6 g per day) - this depends on the severity of the disease and the severity of renal failure and is provided for in the varieties of the main table. For example, in acute nephritis it is completely excluded, and in chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis in remission and without impaired renal function, up to 7-8 g per day is allowed and only in the presence of arterial hypertension makes it necessary to reduce it to 5 g.
- 80 g of protein is allowed. Milk proteins and egg whites (more easily digestible) are preferred over meat or fish. Plant proteins have less nutritional value than animal proteins.
- When preparing all dishes, meat and fish (they are allowed in quantities of 150 g) are first boiled and then baked, stewed or fried. This technological technique significantly reduces the amount of extractive substances in the finished dish.
- Avoid foods rich in essential oils (celery, fresh dill, parsley, basil, garlic and fresh onions) and sources of oxalic acid (spinach and sorrel).
- In case of kidney disease, the amount of fluid consumed is limited - from 0.9 to 1.1 liters. More accurately, it is calculated by the amount of urine excreted over the past day and should not exceed diuresis by 300–400 ml. In end-stage renal failure, fluid is significantly limited to 0.7-0.8 liters.
- Products that have a diuretic effect are required: pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini, beets, green salads, fresh apricots, raisins, dried apricots, apricots, prunes, watermelon and melon.
- 5 meals a day are provided.
- The daily diet should not exceed 3 kg by weight.
- Mandatory inclusion of vitamins A , C , B1 , B12 , K .
- Any alcoholic drinks, strong tea and coffee, cocoa, chocolate, spicy and salty snacks that irritate the kidneys are excluded.
- The intake of sodium mineral waters is prohibited.
Ten Diet Goals Number 7
- Diet table number 7 is prescribed to ensure the most gentle regime for kidney function. During the diet, the kidneys get the opportunity to restore their structure, eliminate damage caused by the disease and accumulate enough strength for subsequent work.
- Diet number 7 allows you to remove toxins from the organs that destroy kidney tissue, and cleanse the tubules of decay products and toxins. Thanks to the diet, the performance of not only the kidneys increases, but also those organs whose work depends on the proper functioning of the excretory systems.
- The patient's general condition improves, his performance is restored.
- Edema, which is a common accompaniment of renal failure, is reduced, and diuresis (urine excretion) is increased.
- The ability of the kidneys to clear fluids and form and excrete urine is restored.
- The load on the cardiovascular system is reduced, which, in conditions of excess fluid in the body, is forced to work at an increased rhythm.
- Blood pressure decreases and accompanying symptoms of illness disappear.
- The renal blood supply improves, and, as a result, the nutrition of the kidney cells is improved.
- Nitrogenous substances and other toxic elements are removed from the body.
- Water-salt and acid-base balance are restored.
Watch the program with Elena Malysheva, which talks about which foods are harmful to the kidneys:
Varieties
Treatment Table No. 7A is prescribed for nephritis with severe renal failure. This is a completely salt-free, plant-based diet with a significant protein limit of up to 20 g.
The amount of fluid you drink depends on your urine output in the previous day. It is usually prescribed for 20 days. When the acute process subsides and azotemia Diet 7B is recommended , in which, compared to the previous one, the amount of protein (40 g) and liquid 1-1.2 liters is doubled. It is seen as a transition to Diet No. 7.
Table 7B is recommended for nephrotic syndrome (edema, loss of protein in the urine) and is aimed at replenishing protein, so its daily content in the diet reaches 125 g. Liquid (0.8 l) and salt are significantly limited.
Table 7G is indicated for patients on hemodialysis when they have renal failure . The therapeutic diet is characterized by a protein content of up to 60 g, 2-3 g of salt and 0.7 liters of liquid are allowed.
Causes of the disease
There are local and general factors for the development of the disease.
General: decreased immunity, overwork, weakness after illness, stress, depression, vitamin deficiency and lack of microelements.
Local - a violation of the outflow of urine that occurs with urolithiasis, with the formation of a tumor, with narrowing of the ureters.
Acute pyelonephritis develops quickly, and if treatment is started in time, you can be completely cured in two to three weeks. Chronic pyelonephritis occurs as a result of an untreated acute form of the disease, when the acute inflammation has been removed, but the causative agents of the disease remain and normal urinary flow has not been restored. The chronic form is often complicated by renal failure and increased blood pressure.
Authorized Products
The dietary table provides for limiting salt, so the patient should eat only home-baked salt-free bread, pancakes or pancakes also without salt. All food is prepared without salt, but it is allowed to add salt to ready-made dishes, using 3-5 g per day.
Soups are prepared in vegetable broth with the addition of vegetables, cereals, and vermicelli. Borscht, cabbage soup and beetroot soup are allowed. Season them with sour cream, butter, dill, parsley, caraway seeds, and, if desired, citric acid. Onions can be added to first courses after preliminary boiling and sautéing.
Main courses are prepared from lean meat (chicken, beef, lamb, turkey, tongue). It must be remembered that all meat and fish products must first be boiled, and then, if you want to get a crust, lightly fried or baked.
Therefore, it is better to serve all protein dishes in pieces, and from boiled minced meat you can make cabbage rolls, stuffed vegetables, and pancakes with meat. The fish is also chosen to be low-fat, boiled in pieces and baked if desired; you can prepare a jellied dish from it. You can use sauces in dishes: tomato, sour cream, milk, any vegetable, onion (from boiled and sauteed onions), sweet gravy. Allowed dried herbs are added to them.
All cereals and pasta can be used as a side dish and in soups. Porridge is boiled in water, cereals are used to make puddings and cutlets with the addition of vegetables. Allowed are casseroles with noodles (pasta) and cottage cheese, fruit pilaf, cereals and pasta with the addition of prunes, dried apricots, raisins and jam.
The following dairy products are allowed: milk, cream, curdled milk, yogurt, cottage cheese and dishes made from it with apples, carrots and rice. Sour cream is added to dishes in limited quantities. 2 eggs per day are allowed, provided that proteins (cottage cheese, meat and fish) are reduced. Eggs are added to dishes, made into an omelet or soft-boiled.
Many vegetables are allowed (except radishes, radishes, celery, garlic, fresh onions). They can be boiled, stewed, added to casseroles and made into vegetable cutlets, salads from boiled and fresh vegetables and boiled meat. Do not add onions, sauerkraut and pickles. You can add cumin and dried dill to stewed vegetables.
All ripe fruits and berries are allowed in fresh and processed form: puree, jelly, jelly, baked, compotes, jam. You can add cinnamon to desserts. Candies (except chocolate), honey and fruit ice cream are also allowed as desserts. Drinks include any juices, weak coffee, tea with lemon, rosehip infusion.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| cinnamon | 3,9 | 3,2 | 79,8 | 261 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| dried parsley | 22,4 | 4,4 | 21,2 | 276 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
| sour cream sauce | 1,9 | 5,7 | 5,2 | 78 |
| tomato sauce | 1,7 | 7,8 | 4,5 | 80 |
| caraway | 19,8 | 14,6 | 11,9 | 333 |
| dried dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled beef tongue | 23,9 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 231 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| ghee | 0,2 | 99,0 | 0,0 | 892 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| coffee with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 1,0 | 11,2 | 58 |
| black tea with milk and sugar | 0,7 | 0,8 | 8,2 | 43 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Table of composition of diet number 7 for a day
| Name of substance | Quantity in grams | Notes |
| Squirrels | 80 | 50% plant origin |
| Fats | 80-90 | 30% plant origin |
| Carbohydrates | 350-400 | mostly fruits and vegetables |
| Phosphorus | 1,6 | |
| Sodium | 2,3 | |
| Iron | 0,06 | |
| Calcium | 1,0 | |
| Magnesium | 0,4 | |
| Potassium | 4,4 | |
| Vitamin A | 0.3 mg | retinol |
| Carotene | 8.5 mg | |
| Vitamin B1 | 1.7 mg | thiamine |
| A nicotinic acid | 20mg | |
| Vitamin C | 150mg | ascorbic acid |
| Riboflavin | 2.5 mg |
Daily calorie content should not exceed 2500 kcal. The amount of table salt is no more than 5g.
How to get used to eating without salt
A diet without salt makes many people despondent, because unsalted foods seem tasteless and food literally “doesn’t fit into your mouth.” But a person can get used to anything, especially if he knows some tricks.
Some dishes actually taste even better when prepared without salt. It's all about habit and your attitude. Try replacing salt with some seasonings that are acceptable on diet No. 7. You can season dishes with lemon juice, coriander, cinnamon, herbs, vinegar, etc.
- buckwheat without salt tastes very pleasant if seasoned with oil without salt;
- You can eat rice without salt; you can eat it in the form of milk porridge or fruit pilaf;
- cabbage without salt is also tasty if supplemented with grated carrots or cranberries;
- any porridge without salt can be prepared with the addition of berries or dried fruits.
It is worth remembering that every day without salt helps your kidneys recover, improves overall well-being, helps remove excess fluid and facilitates the functioning of many other organs and systems.
Tip: if you absolutely cannot do without salt, try adding chopped seaweed, which has a salty taste, to your dishes.
Fully or partially limited products
You cannot salt food. It is also not allowed to eat regular bread, and add salt to homemade flour products. Meat, fish, and mushroom broths, legume broths, pea and bean soups are excluded. Fatty varieties (pork, duck and goose), sausages, smoked meats, and canned food are excluded from meat products. You should not eat fried foods or stewed meats without first boiling them.
Fatty types of fish, salted and smoked, canned fish and fish caviar are not allowed. Any cheese should be excluded due to its high salt content. It is expected to exclude legumes, onions, garlic, radishes, sorrel, spinach, radishes, as well as all salted and pickled vegetables and mushrooms from the diet. Pepper, mustard, and horseradish should be excluded from seasonings and sauces. Any pickled or pickled vegetables are not allowed. Animal fats are prohibited. Strong coffee, mineral waters with sodium, and cocoa should be excluded from drinks.
Cream, sour cream, milk soups, lard are limited.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
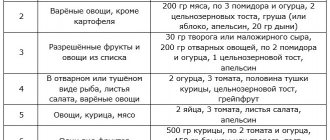
Menu (Power Mode)
Now that we have found out the main points and products that the therapeutic Diet No. 7 includes, the menu for the week can be developed without much difficulty. You need to try to make your diet varied, since all cereals, cottage cheese, meat and all (with minor exceptions) vegetables are allowed. Dried herbs can be added to dishes, and all sauces can be prepared.
The only limitation is salt. The amount of it in ready-made dishes is discussed with the doctor. To diversify the menu, try to master bread baking - bake unsalted bread with different seasonings (carrots, pumpkin, cumin, dried dill, parsley) and sweet bread (muffin) with raisins, dried apricots, prunes, apples, enhancing the taste with cinnamon. Any homemade pastry is also available, but not salty.
Monday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Tuesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Wednesday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Thursday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Friday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Saturday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Sunday
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Diet 7A is the strictest of all varieties. It is prescribed to a patient in a hospital with acute severe kidney disease. Meals are 5-6 times a day and consist mainly of vegetables, fruits and cereals. Proteins are allowed in quantities of only 20 g-25 g - this means that a piece of meat or chicken is allowed only for lunch and a little milk with cereals. An approximate calculation of the amount of protein in products is carried out by protein “units”. One unit corresponds to 6 g of protein and is contained in: 25 g of cooked meat (or poultry), 30 g of boiled fish, 45 g of cutlets (meat or chicken), 1 egg, 25 g of hard cheese, 1 cup of milk, 30 g of cottage cheese , 200 g sour cream.
Specialized products containing little protein (artificial sago, protein-free bread, salt-free bread made from maize starch, amylopectin starch) are widely used. You can consume 300-400 g of such bread per day, in the absence of bran bread - 200 g. The amount of fats and carbohydrates is moderately reduced. Sugar - 75 g for the whole day. Salt is completely excluded, the amount of liquid is with the doctor's permission.
Table 7A diet menu looks like this:
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Recipes
First meal
Brussels sprouts soup
Potatoes, carrots, onions, tomatoes, vegetable oil, Brussels sprouts (or broccoli).
Place the chopped potatoes into boiling water. Lightly saute chopped carrots, tomatoes and onions in vegetable oil (they must first be boiled for 1 minute). When the potatoes are almost done, add the dressing and cabbage. Boil for another five minutes.
Vegetarian borscht with prunes and sour cream
Beets, white cabbage, potatoes, tomato paste, onions, prunes, vegetable oil, sour cream.
Place the chopped potatoes in a saucepan with water. Finely chopped beets and onions simmer over low heat under a lid. Add vegetable oil and tomato paste. Boil prunes separately in a small amount of water. When the potatoes are almost ready, add the dressing to it, add the prune broth and at the end add shredded cabbage and boil. Add prunes to the prepared borscht and serve with sour cream.
Second courses
Pilaf with fruits
Pilaf with fruits
A glass of rice, carrots, 7 pcs. dried apricots and prunes, 50 g raisins, dried apples, apple (grape) juice 2 cups, vegetable oil.
Cut the carrots into strips and fry in vegetable oil. Wash the rice, cut the dried fruits. Place carrots, rice and dried fruits in a thick-bottomed cauldron. Pour the juice over everything and cook over low heat for 30-40 minutes with the lid closed until the rice is cooked. You can add walnut oil to the finished pilaf and mix.
Lapshevnik with cottage cheese
200 g noodles, 200 g cottage cheese, one egg, 1 tbsp. l. sugar, 50 g butter, 2-3 tbsp. l. sour cream.
Boil the noodles, grate the cottage cheese and add to the noodles. Add melted butter and egg, mashed with sugar. Place the mixture in the mold and brush with sour cream. Bake until golden brown. Serve with sour cream, honey or jam.
Dessert
Pumpkin with apples, cinnamon and nuts
0.5 kg pumpkin, 2-3 apples, 40 g butter, cinnamon, 1 tbsp. l. honey, any nuts.
Cut the peeled pumpkin and apples into pieces. They can be baked in the oven in a suitable form with a little water or stewed in a pan. Sprinkle the finished dish with cinnamon, add butter and honey. Decorate with nuts.
Carrot-apple cutlets
200 g apples, 200 g carrots, 1 tbsp. l. butter, 2 chicken whites, 1-2 tbsp. l. semolina, sugar, sour cream or honey for serving.
Stew the grated carrots in butter, add grated apples, and a little water if necessary. Add whipped egg whites, sugar and semolina to the warm carrot-apple mixture. Mix well, form into cutlets, fry in a pan or bake in the oven. Serve with honey or sour cream.
During pregnancy and lactation
A form of late toxicosis is nephropathy of pregnancy. It includes characteristic symptoms that appear in the third trimester of pregnancy : edema , hypertension and the presence of protein. Primary nephropathy develops in healthy women with no history, and secondary nephropathy develops against the background of pre-existing diseases ( glomerulonephritis , pyelonephritis , heart defects, diabetes mellitus ). A constant sign of it is progressive hypertension , after a while proteinuria (protein in the urine) joins and increases. The severity of edema can vary - from mild pastiness of the hands and face to swelling of the entire body.
In such cases, in addition to medication prescriptions for pregnant women, therapeutic nutrition is simply necessary. Inpatient treatment is required for constant monitoring of blood pressure, renal function and blood electrolytes. The diet consists of limiting salt consumption to 1.5-2.5 g, as well as liquid to 1 liter. A sufficient amount of protein, plenty of vegetables, fruits and foods high in potassium are recommended. Fasting days (curd, kefir, fruit) are prescribed weekly.
After discharge from the hospital, a pregnant woman is recommended to take the main Table No. 7, which has an increased salt content, before giving birth. Women who have kidney disease should follow this diet after childbirth.
Table No. 7v
After a cycle of seventh diets, the patient often loses most of the proteins in the urine. Considering that the diet greatly limits this component, the body feels its deficiency - nephropathy. Table No. 7b can be used in complex treatment in pregnant women with the development of late gestosis and the appearance of nephropathy (detection of protein in the urine). Diet 7c is prescribed to replenish missing nutritional components. As a result of this treatment, the patient (or pregnant woman) improves protein metabolism, swelling goes away, and kidney function normalizes.
The expansion of the diet of table No. 7b will occur due to an increase in protein. The basis of nutrition is plant foods (except for prohibited types), without the use of salt, 125 g of dairy or meat products per day. Liquids, including first courses and drinks, should be approximately 800 ml. Sugar consumption is limited (50 g per day).
The rules of the diet remain unchanged: small meals, less liquid, minimum salt, no alcohol. Several times a week you can drink weak natural coffee with milk. Pasta and cereals (as in No. 7), and seafood are added to the menu. For pregnant women, the diet may vary slightly depending on the condition of the patient and the fetus.
When the general well-being improves and the patient’s laboratory and instrumental tests return to normal, diet No. 7 or other proper nutrition is prescribed.
Reviews and results
This therapeutic food cannot be called monotonous, since almost all products and various technological methods of cooking are allowed. You can diversify it with many new dishes. The only drawback, according to many patients, is the unsalted and tasteless dishes. It is very difficult for some to get used to this, but high blood pressure and the presence of edema require salt restriction. Reviews note the effectiveness of this therapeutic nutrition: after 3-5 days, swelling of the face and hands decreases, blood pressure normalizes, and general condition improves.
- “... I was prescribed a kidney test during pregnancy because edema appeared and protein was found in the urine. The pressure was normal. I kept a diet with limited salt until the birth. It was hard, but for the sake of the child, anything can be endured. The doctor said that there could be premature birth, placental abruption and even eclampsia during childbirth. I followed all the recommendations and was hospitalized twice”;
- “... After acute glomerulonephritis (there was a severe sore throat), this diet was prescribed for six months. I checked my tests all the time. Only six months later, the doctor allowed me to increase the amount of salt and slightly expand my diet. The hardest thing is to get used to eating without salt. This was difficult for me, sometimes I just took a crystal of salt and dissolved it”;
- “... There was swelling and high blood pressure with acute glomerulonephritis. Allowed 5 g of salt - this is a level teaspoon. It was hard to bear, but I strictly measured the prescribed amount and did not violate the recommendations. Of course, it was impossible to eat ready-made store-bought products that contain salt. I excluded sausages, pickles, and smoked foods for almost a year. It was difficult, since I had to cook myself and take lunch to work - I canceled snacks in a cafe with my girlfriends.”
Signs of illness
The disease is manifested by a sharp increase in temperature to 39-40 degrees, weakness occurs, sweating increases, headaches appear, sometimes nausea and vomiting, and lower back pain occurs, usually on one side.
Most often, a dull pain of varying strength occurs. If the disease occurs in the presence of urolithiasis, then an attack of renal colic may occur. If the disease proceeds without complications, then the outflow of urine is usually not impaired.
If not treated in a timely manner, acute pyelonephritis will become chronic, and the patient will regularly suffer from aching lower back pain, more often in damp, cool weather. Exacerbations of the chronic form of pyelonephritis occur occasionally.
A process of suppuration may develop, which will sharply worsen the patient’s condition. The temperature during the day can be normal, but in the evening it can rise sharply to 40-41°C. There may be painful urination, a need to frequently visit the toilet, and the urine becomes dark and may even contain blood.
With this disease, proper nutrition is of great importance, since it is necessary to reduce the load on diseased kidneys.