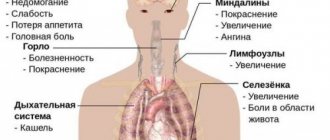
Mononucleosis is an acute infectious disease that affects the lymphatic system. With mononucleosis, the throat hurts and becomes inflamed, the patient is constantly tired, restless, and has an enlarged liver and lymph nodes. Mononucleosis is characterized by an increase in monocytes in the circulating blood.
The source of infection is an infected person. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets, often with human saliva (through kissing), and through blood transfusions.
50% of the population gets this infection in adolescence: girls at 14-16 years old, boys at 16-18 years old. People over 40 years of age are less likely to become infected with this disease. But in HIV-infected people, the disease can occur at any age.
Infectious mononucleosis (also called glandular fever, monocytic tonsillitis) is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, tonsillitis, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, and can become chronic. The causative agent of the disease is the Epstein-Barr virus, EBV (a group of herpes viruses).
In addition to an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, the disease is manifested by abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and slight impairment of the functional abilities of the liver. In the first days of the disease, changes occur in the blood, leukocytosis, and an increase in mononuclear cells: lymphocytes and monocytes. ESR increases. Atypical cells with one nucleus of medium and large size appear - atypical mononuclear cells.
1
Throat examination
2 Examination of the throat
3 Throat examination
Symptoms of mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by damage to the lymphoid tissue of the nose, pharynx, and tonsils.
Other symptoms of the disease:
- enlargement of the submandibular, axillary, elbow, inguinal, posterior cervical, tracheobronchial lymph nodes;
- a large number of wide-plasma monoculars;
- fever, swollen lymph nodes, tonsillitis;
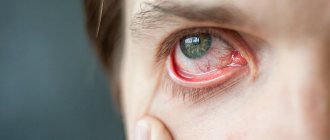
- a sore throat;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- voice with a nasal tint, etc.
The disease is accompanied by follicular, lacunar or catarrhal sore throat, an unpleasant sweetish-sweet odor from the mouth.
Atypical forms
Erased - with an incomplete, weakly expressed, quickly passing symptom complex.
Asymptomatic - there are no clinical signs of the disease. Diagnosis in this case is possible based on laboratory data, taking into account the epidemic situation.
Complications . Specific:
- asphyxia (due to supraglottic stenosis associated with a significant increase in the lymphoid formations of the Pirogov-Waldeyer pharyngeal ring);
- rupture of the spleen, which can occur spontaneously or from physical influences (for example, during palpation);
- lesions of the nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis, cranial nerve palsies, Guillain-Barré syndrome);
- hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia.
- In rare cases, bilateral interstitial pneumonia with severe hypoxia is noted.
The most common nonspecific complication is the addition of bacterial infections (otitis, sinusitis, pneumonia, etc.) caused by Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci, etc. Complications of the disease can occur at different periods, including during the period of long-term convalescence.
Pathogenesis of mononucleosis
The Epstein-Barr virus appears in the human body through the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, then spreads throughout the body and accumulates in the lymph nodes. The virus is supported by B lymphocytes that have surface receptors for the virus.
At the very peak of the disease, specific viral antigens can be detected in more than 20% of the nuclei of B lymphocytes.
When the infectious process has subsided, mononucleosis viruses are observed only in single B-lymphocytes and epithelial tissues of the nasopharynx. When some of the affected cells die and the released virus infects new cells, cellular and humoral immunity begins to malfunction. Therefore, a super-infection may form and a secondary infection may develop (most often caused by staphylococci or streptococci).
In mononucleosis, the virus affects the lymphoid and reticular tissue, this leads to enlargement of the lymph nodes, and the liver and spleen also enlarge.
Immunity against mononucleosis is stable. The infection can spread in the form of asymptomatic and erased forms; antibodies to this virus are found in 50-80% of the population.
Authorized Products
The diet for mononucleosis in children during the illness and recovery period should be gentle and include:
- Soups made with vegetable broth or water with the addition of various cereals, thin noodles and a small amount of vegetables. Frying onions and roots for seasoning soups is not allowed. Vegetables with coarse fiber are excluded, which can cause bloating and disrupt digestion - white cabbage, turnips, radishes, radishes. White cabbage is introduced no earlier than 2 months after the illness, and the rest of the listed vegetables are excluded for a long time.
- Protein food in the form of steamed cutlets, quenelles, meatballs, meatballs made from lean meat and fish.
- Boiled poultry and fish can be eaten in pieces. Cooking removes skin, visible fat and cartilage. Other options for meat and fish dishes baked in the oven are also possible - cabbage rolls with Savoy cabbage, stuffed zucchini and peppers. It is better to cook these products with milk and sour cream sauce, avoiding the use of tomato paste or tomato sauce.
- Dried wheat bread (white and grey). You should not eat fresh bread or any other yeast baked goods. For flour products, we can recommend sponge cakes and savory cookies (like “Maria”).
- Homemade eggs, soft-boiled or steamed omelet. If your child eats vegetables well, you can add them to the omelet.
- Homemade sauces based on quail eggs, lemon juice, butter, salt and 10% cream. All ingredients are well beaten and seasoned with lemon juice and salt. The value of this sauce is that the ingredients are not processed.
- Low-fat dairy products of preference: kefir, milk, acidophilus, yogurt, yogurt. All products are only natural without dyes, sweeteners or flavor enhancers. Milk can be used to prepare milk porridges. Low-fat cottage cheese in its natural form (with dried fruits) and dishes made from it (casseroles, soufflés, lazy dumplings, cheesecakes cooked in the oven). Sour cream in small quantities as a seasoning for dishes.
- Porridge (usually buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, wheat) cooked in water and milk.
- Vegetables are mainly boiled and stewed. If the liver is in normal condition, a salad of fresh vegetables (peeled ground cucumbers and tomatoes) is allowed. It is usually difficult to get a child to eat leafy greens. Excluded from the diet: fresh onions and green onions, garlic.
- Butter and vegetable oil - 0.5 teaspoon per serving in prepared dishes.
- Fresh non-acidic fruits and berries, baked apples with honey, apple mousse, various compotes, jelly (only properly prepared - the juice of the berries is squeezed out, the squeezes are boiled, diluted starch is added, and at the end the squeezed juice).
- Rosehip infusion, still water, vegetable juices, juices from sweet fruits and berries, weak tea, viburnum infusion, bran decoction.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How does the disease progress?
The incubation period for mononucleosis is about a week. The disease begins acutely. Days 2-4 are characterized by pronounced fever and general intoxication of the body.
From the first days a person feels weakness, headache, and a little later pain appears when swallowing. The temperature rises to 38 - 40 degrees. On day 5, the patient may develop tonsillitis. It can be catarrhal, lacunar or ulcerative-necrotic. Lymph nodes are affected. A rash may appear on the body, which disappears without a trace after 1-3 days. Changes in the liver are observed.
Leukocytosis can be observed in peripheral blood. The number of lymphocytes, monocytes and atypical mononuclear cells reaches 80-90% in the first week. After mononucleosis, the mononuclear reaction can last from six months to several years.
There are several possible outcome options for the acute infectious process of EBV (mononucleosis):
- recovery;
- asymptomatic virus carriers;
- chronic recurrent infection (chronic infectious mononucleosis);
- development of the oncological process (lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, leukoplakia of the tongue and oral cavity, stomach and intestinal cancer);
- development of an autoimmune disease (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus ).
Epidemiology
The source of infection is a person with acute and chronic manifest or latent forms of EBVI. Infected individuals actively shed the virus from the last days of incubation and for 6-18 months after the initial infection. More than 90% of asymptomatic seropositive individuals harbor the virus in oropharyngeal secretions.
The main transmission mechanism is airborne, the transmission route is aerosol. EBV is mainly transmitted through direct close contact through saliva (kissing, toys with contaminated saliva) containing oropharyngeal epithelial cells. Infection is possible if sanitary and hygienic rules for handling utensils in the public catering system are not followed, as well as when using “shared” glasses, bottles, etc. Parenteral (during organ transplantation and blood transfusions) and sexual transmission are also possible. The possibility of vertical transmission of the pathogen with the development of congenital EBVI has been established. EBV is transmitted through blood transfusions and transplants. The entire non-immune population is susceptible to infection, regardless of age.
Complications after illness
Complications after infectious mononucleosis are not very common, but quite serious:
- hematological complications (autoimmune hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, granulocytopenia);
- splenic rupture;
- neurological complications (encephalitis, paralysis of facial muscles, polyneuritis, transverse myelitis, psychosis);
- hepatitis;
- cardiac complications (pericarditis, myocarditis);
- complications of the respiratory system (interstitial pneumonia, airway obstruction).
1 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
2 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
3 Consultation with an otolaryngologist in MedicCity
Fully or partially limited products
- Convenience foods, fast food, bouillon cubes, instant soups.
- Solid fats and lard, fat and meat of goose and duck, any fried foods (pancakes, cheesecakes, pancakes, pies, fried potatoes).
- Smoked meat and fish, sausages, canned food.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Fresh yeast baked goods, pastries made from puff pastry and shortcrust pastry (due to the fat and margarine content), pastries and pies.
- Legumes, white cabbage, vegetables with coarse fiber.
- Chocolate, cocoa.
- Spicy seasonings and sauces. It is not permissible for a child, even a healthy one, to consume mayonnaise and ketchup.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diagnosis of mononucleosis
Diagnosis of EBV and mononucleosis includes:
- examination by an otorhinolaryngologist, therapist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist;
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes, abdominal cavity, spleen;
- laboratory tests: clinical blood test, biochemical blood test, immunological examination to assess antiviral protection, serological tests (a criterion for the presence of the virus at the present time), DNA diagnostics using the PCR method.
1 ENT consultation in MedicCity
2 Laboratory diagnostics in MedicCity
3 Ultrasound of lymph nodes in MedicCity
Treatment of mononucleosis
Treatment of mononucleosis, if the course of the disease is uncomplicated and the patient is isolated, can be carried out at home. Treatment of patients with EBV with a complicated form of infection must be carried out in a hospital! For mononucleosis, restorative and symptomatic treatment is used. The patient is recommended to take vitamins C, P, and group B. At elevated temperatures, antipyretics are prescribed. Antibiotics for mononucleosis are prescribed in case of a secondary infection affecting the tonsils.
At the MedicCity multidisciplinary clinic, you can consult with highly qualified otolaryngologists and receive the necessary recommendations for various diseases of the ear, nose and throat. Remember that the disease is easier to cure in the early stages of development!
Menu (Power Mode)
You need to stick to proper nutrition for six months. We can say that this is the usual diet that children should have: they do not have to eat fried meat and fish, spices, hot seasonings, and sauces. Therefore, the diet is well tolerated, the only problem is the lack of confectionery products in it, which children have a fairly high tendency towards. If the diet includes a variety of protein dishes and cereals, the child’s nutrition will not be monotonous.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|