In this case, we will not talk about the feeling of heat and chills in cases of infectious diseases or other purely somatic diseases. We describe situations when feelings of heat and chills appear for no reason, or rather in cases where there are no obvious somatic or infectious diseases, when doctors cannot or are confused in determining the state of the body during examination.
If you feel a feeling of heat or a feeling of chills without any obvious reasons, so-called “Hot flashes” occur, and doctors cannot establish the correct diagnosis, the treatment they prescribe is not effective, then we are talking about the presence of some kind of breakdown of nervous activity and you worth contacting us.
Brain Clinic specialists have extensive experience in treating various disorders of nervous activity that cause sensations of heat and/or chills, “hot flashes”. Our doctors will be able to correctly and safely restore the body’s functioning without any side or negative effects on it.
Call
We help in the most severe cases, even if previous treatment did not help.
| Initial consultation and examination 2,500 | Treatment and rehabilitation therapy from 5000 |
Causes of heat throughout the body without fever
Eating
Eating spicy and hot foods is the most common cause of fever.
The symptom occurs while eating or immediately after finishing a meal. First, a feeling of warmth appears in the torso area, then the heat spreads throughout the body. The person's cheeks turn red and the skin becomes hot to the touch. Sometimes, when taking too spicy foods, general sweating is observed, beads of sweat appear above the upper lip. A feeling of intense heat throughout the body occurs after drinking strong alcohol. When drinking alcohol, you feel a warmth spreading from the chest and abdomen to the extremities. The redness of the face and the shine of the eyes are noticeable. Sometimes drinking alcohol provokes redness not only of the face, but also of the neck and torso. The warming effect does not last long: if a person goes out into the cold, chills without fever quickly develop.
Emotional factors
Heat at normal temperatures is often caused by strong excitement and fear. The person feels as if the whole body is on fire, while the face turns red and the skin becomes very warm or hot. Sometimes, under stress, tremor of the fingers and interruptions in heart function appear. An unpleasant feeling of heat throughout the body persists until the person calms down. Such signs are more typical for emotionally labile young women, but can occur at any age.
Hormonal changes in women
Many cases of fever throughout the body as a component of PMS have been described. The symptom is associated both with disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone caused by changes in hormone levels, and with the increased emotionality of women during this period. Fever without temperature is observed 1-2 days before the onset of menstrual bleeding. It can appear in paroxysms for 5-10 minutes or last for several hours.
Hot flashes throughout the body sometimes occur during menopause, but with this condition, warmth is more often felt in the head and upper torso. Menopausal hot flashes are especially severe at night. Women wake up due to an unpleasant feeling of heat, increased sweating and a feeling of lack of air. Symptoms include headache and darkening of the eyes. The attacks are repeated several times a night, causing insomnia.
Heat throughout the body without fever
Vegetovascular dystonia
When the neuroregulation of vascular tone is impaired, attacks of heat throughout the body without fever are caused by any predisposing factor: stress and overwork, physical activity, cyclical hormonal changes in the female body. Sometimes hot flashes develop for no apparent reason. A person feels that warmth seems to be spreading from the depths of the body, the skin takes on a pink tint and becomes hot.
With vegetative-vascular paroxysms, fever is combined with polymorphic symptoms: dizziness, a feeling of sinking heart, tremors of the hands. As a rule, unmotivated anxiety appears. At the end of the attack, the feeling of warmth is replaced by chills, and sometimes there is cold sweat. The patient has an urge to urinate, during which a large volume of light-colored urine is released.
Allergic reactions
A feeling of heat throughout the body is more typical of pseudo-allergy. The symptom is caused by a sharp release of histamine from cells when consuming certain foods (strawberries, chocolate) and medications. In addition to fever without fever, redness of the entire surface of the skin and severe itching are noted. The clinical picture is complemented by breathing difficulties and paroxysmal headaches. Similar manifestations occur with true allergies.
Arterial hypertension
A feeling of heat without elevated temperature occurs with changes in blood pressure. An increase in blood pressure is accompanied by a feeling of warmth throughout the body and redness of the skin. The patient experiences difficulty breathing, it begins to seem to him that there is “less air” in the room. Feeling better after taking pills that normalize blood pressure.
Thyroid diseases
The symptom is observed with increased hormonal activity of the organ. Thyroid hormones T3 and T4 stimulate basal metabolism and increase energy production, so the feeling of gift accompanies a person constantly. Manifestations do not depend on indoor temperature and emotional factors. Patients complain that they are constantly hot, wear lighter clothes that are not appropriate for the season, and cannot stay in stuffy rooms.
In addition to heat throughout the body, the skin often turns red, but there is no excessive sweating. Inhibition of the activity of the sweat glands is pathognomonic for hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. Symptoms are combined with exophthalmos, rapid heartbeat, and irritability. The appearance of fever without temperature is a typical sign of thyrotoxic goiter, thyroid tumors, and the initial stage of thyroiditis.
CNS diseases
The thermoregulation center is located in the hypothalamus; accordingly, when the brain is damaged, paroxysmal or constant sensations of heat are possible. The pathological sign is not associated with external factors and does not depend on the ambient temperature. Typically, when the hypothalamus is damaged, the fever is accompanied by general hyperthermia. This condition is typical for TBI and tumors of the pituitary-hypothalamic system.
What to do in case of a panic attack
The most important thing to do during a panic attack is to switch your attention. Any method is suitable for distraction. If an attack occurs in a public place, you can clench and unclench your fists, rub your earlobes, or shift from foot to foot. If panic takes you by surprise at home, try turning on music and starting to do household chores: washing dishes, dusting. Any activity that involves muscle work and requires attention is suitable.
Since a panic attack is accompanied by a rapid heartbeat and a feeling of stuffiness, it would be a good idea to take a couple of sips of water and concentrate on breathing. It is best to master several techniques that will quickly relieve tension. In case of an attack, start by exhaling - slow it down, and the pulse will also slow down. The ratio of the length of inhalation and exhalation should be 1:2. You can experiment and choose the technique that will help you. A smartphone can also help you take your mind off panic. Games, social networks - all this will shift attention and distract from a panic attack.
Diagnostics
When heat appears throughout the body without fever, the patient turns to a therapist, who determines the probable cause of the symptom, and then writes a referral to a specialist. The doctor is interested in how long ago the symptoms began, what, in the patient’s opinion, they are associated with, and whether any treatment was used at home. Diagnosis of the causes of illness includes the following methods:
- Instrumental Research
. To evaluate the functioning of the heart, an ECG and echocardiography are performed. To identify pathological changes in brain function, a non-invasive EEG method is prescribed. X-ray methods (scintigraphy) are indicated if a tumor process is suspected. - Laboratory methods
. Standard diagnostics include general and biochemical blood tests to exclude hidden inflammatory or metabolic disorders that occur without fever. Be sure to determine the level of thyroid hormones, adrenal hormones, ACTH and TSH. In women, the levels of estrogen, progesterone, FSH and LH are examined. - Neurological examination
. The doctor determines the activity and symmetry of reflexes, checks the initial tone of the autonomic nervous system. To study the characteristics of nervous regulation, functional tests (orthostatic, pharmacological) are used. If necessary, the examination is supplemented with a psychiatric examination.
Normalizing lifestyle and nutrition is the first step to eliminating the feeling of heat
What is a panic attack
A panic attack is an attack of sudden fear and severe anxiety for no apparent reason.
The origins of panic disorder are not completely clear. However, it is believed that the disease has a genetic predisposition and more often affects the fair sex. Women are more prone to panic attacks and suffer from this disorder 2-3 times more often than men. Panic attacks cannot lead to death, despite the fact that this is the feeling that most often accompanies them. The more often attacks occur, the worse the quality of life becomes. People who have repeatedly experienced panic attacks become increasingly anxious and subconsciously try to avoid places or situations where and when they succumbed to fear. Those who have at least once experienced an attack at night subsequently experience sleep disorders.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Most attacks of heat in the body without fever are not associated with pathological factors. To stop them, non-drug methods are sufficient. Patients need to exclude from the diet foods that are too hot and spicy, causing hot flashes. Food should be warm, but not hot. The same applies to tea, coffee and other drinks. It is necessary to limit alcohol consumption as much as possible, especially strong alcohol - with an ethanol content of more than 20%.
In order not to provoke paroxysms of heat throughout the body, you should regularly ventilate the room, avoid stuffy rooms and crowds of large numbers of people. It is important to eliminate stressful situations at home and at work as much as possible. Doctors recommend reducing the time spent surfing the Internet and watching TV shows. Frequently recurring attacks of fever without an increase in temperature are a reason to consult a doctor, as they may be a sign of serious illness.
Conservative therapy
The selection of medications for heat in the whole body without temperature is carried out after determining the cause of the ailment. If hot flashes occur against the background of menopausal syndrome, gynecologists prescribe hormone replacement therapy. Treatment helps normalize well-being, reduces the frequency of hot flashes, and eliminates other symptoms of menopause. For hypertension, rational antihypertensive therapy is prescribed, taking into account the patient’s age and the severity of the disease.
To reduce the activity of autonomic reactions, sedatives are recommended. Treatment begins with herbal remedies (St. John's wort, motherwort, valerian), and if they are ineffective, mild tranquilizers are added. To stabilize the psycho-emotional background, antidepressants are used. Neurometabolic stimulants and multivitamin complexes have a good effect.
The symptom is often provoked by emotional lability, so psychotherapy is an important component of treatment. Patients are recommended individual and family psychological correction. To normalize the state of the nervous system, physiotherapeutic techniques are used: neurosedative massage, reflexology, balneotherapy. Spa treatment is indicated.
How is normal anxiety different from a panic attack?
The mechanism that triggers a panic attack is no different from what causes ordinary anxiety - both are psychophysical reactions to danger. The difference is that a panic attack is a reaction to danger in the absence of danger. However, a false alarm triggers the same cascade of reactions as a normal alarm - the sympathetic system is activated, and adrenaline is released.
A panic attack can occur due to excessive physical activity, fatigue and exhaustion, as well as due to the abuse of stimulants and alcohol. In addition, stress and unresolved conflict situations can trigger an attack. A lack of understanding of one's own experiences and feelings, a tendency to avoid and ignore negative emotions also increase vulnerability to panic disorder.
How to treat panic attacks and when to see a specialist
It is necessary to contact a specialist if you have recurring panic attacks. Therapy is selected individually and, as a rule, includes psychotherapeutic work and drug therapy. Psychotherapy involves various techniques aimed at recognizing and understanding the causes of problems, teaching ways to deal with the symptoms of the disease, and relaxation methods. Psychotherapy can take place in the form of individual meetings with a psychotherapist or in the form of group sessions with other patients. Drug therapy for panic disorder is carried out with various drugs that help reduce the level of anxiety and fear. Prescription, dosage adjustment and discontinuation of treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Modern neurotechnologies can also help in the treatment of panic attacks. Methods of neurofeedback training have been developed for patients with panic disorder. During the trainings, patients learn to manage their emotional state, they form new neural connections, and their anxiety level decreases. In addition to professional help, lifestyle plays a significant role in the treatment and prevention of panic attacks. Try not to abuse alcohol and caffeine, get more rest, go in for sports, preferably yoga.
Source: https://www.wmj.ru/krasota/telo/golovokruzhenie-zhar-i-dazhe-udushe-simptomy-panicheskikh-atak-i-kak-s-nimi-borotsya-razbiraem-s-vrachom.htm
Back to list
Discharge during menopause
During premenopause, menstruation gradually loses its former regularity: it may occur later or earlier than expected. Their intensity changes - and it can either decrease or increase. Occasional intermenstrual discharge is possible - light, “spotting”, brownish in color.
So-called menopausal bleeding, associated with impaired production of sex hormones, develops in women aged 40-50 years, before menopause. Typically, such bleeding begins after a missed period, but it may coincide with the expected period or even begin a little earlier. It differs from regular menstruation in its long duration - up to several weeks.
The intensity of such bleeding may vary and may be repeated. Sometimes they are quite abundant, even threatening health and life.
Menopausal bleeding requires treatment in a hospital, usually responds to hormone therapy, but surgery may also be required. As a rule, diagnostic curettage is required to clarify the diagnosis in such cases. This is necessary in order not to miss possible hyperplasia (overgrowth) of the endometrium, its polyps and other conditions that are also manifested by uterine bleeding. Treatment tactics will depend on the correct diagnosis.
Uterine bleeding that occurs in postmenopause is much more dangerous, as it often indicates a serious illness. For example, spotting in a woman not receiving hormone replacement therapy that occurs several years after menopause can be caused by uterine cancer or ovarian tumors. In this case, it is necessary to undergo a thorough medical examination as quickly as possible with mandatory separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervix and body of the uterus. Early diagnosis allows for timely successful treatment.
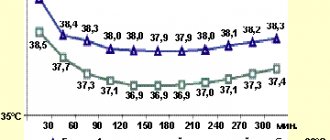
Types of fever
Fever can be classified depending on how long the condition lasts and what temperature range it is associated with.
Temperature can be classified according to the following phenomena:
- hypothermia – up to 35 degrees Celsius;
- normal – from 35 to 37 degrees Celsius;
- hyperthermia - an increase in temperature above 37 degrees Celsius;
- fever – an increase in body temperature above 38 degrees Celsius with preservation of thermoregulation.
The height of the temperature can help indicate what type of problem is causing it. Temperature varies over time:
- acute type – duration up to 7 days;
- sub-acute – duration up to 14 days;
- chronic or permanent – lasting more than 14 days.
Fevers that persist for days or weeks without explanation are called “of unknown origin.”
Senestopathies
Burning, itchy feelings provoked by mental disorders are classified as simple thermal senestopathies.
Senestopathies are a variety of unpleasant, intrusive and exhausting impressions that are concentrated on the surface or inside the body. This concept was first learned about in 1907 thanks to the scientists P. Camus and Dupre.
The peculiarity of this condition from true burning and itching is the rich and elaborate way of describing them. For example, “there is a fire in the head”, “the chest is on fire”. The localization is characterized by an unusual presentation: “itching in the stomach area”, “a vessel in the abdomen is pulsating”.
Such episodes can be isolated, constant or paroxysmal. Sometimes they are so intrusive that they literally drive the patient crazy.
Their characteristic feature is tactile hallucinations. They often manifest themselves in terms of itching and tingling. A person claims that bugs or mites are crawling under his skin. In some cases, he even sees them, or it seems to him that crumbs or sand are stuck to his body.
Such hallucinations provoke obsessive actions. The patient persistently visits doctors or tries to get rid of intrusive parasites on his own: he constantly washes himself and disinfects his body.
Mental disorders that lead to similar senestopathies:
- hypochondria;
- neuroses and depression;
- psychoses and psychopathy;
- oneiroid;
- paranoia;
- affective and delusional disorders, etc.
Symptoms in adults
Seek medical help when your body temperature reaches 39.4°C or higher. Seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms accompany a fever:
- Strong headache;
- unusual skin rash, especially if the rash progresses quickly;
- unusual sensitivity to bright light;
- stiff neck and pain when tilting the head;
- mental confusion;
- constant vomiting;
- difficulty breathing or chest pain;
- abdominal pain or pain when urinating;
- convulsions.