Unfortunately, many of our compatriots suffer from acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Often these accidents occur in everyday life due to negligence or failure to comply with personal safety measures. And with the beginning of the heating season, the number of acute CO intoxications increases significantly. I would like to tell the reader about carbon monoxide poisoning in more detail - in this article we will talk about the causes of poisoning, symptoms and treatment. Shall we start?
Toxicologists name 3 main reasons why carbon monoxide is so dangerous:
- lightning action;
- severe toxicity;
- high penetrating ability.
Thanks to its “invisibility” and “omnipresence,” the SO received the nickname “silent killer.”
Hypoxia in case of poisoning is due to the fact that the poison blocks the ability of red blood cells to deliver oxygen to all organs. The first symptoms of intoxication appear.
The risk of death from carbon monoxide poisoning increases with debilitating diseases - anemia, diabetes, asthma, angina. In addition, smoking and alcohol abuse aggravate intoxication.
Causes of poisoning
Man has been “dealing” with carbon monoxide since prehistoric times - as soon as he learned to make fire. It is possible that our distant ancestors also suffered from inhalation and needed help in their black-heated homes. Alas, even today, technical malfunctions of equipment, ventilation, and non-compliance with the construction technology of stoves and fireplaces are not uncommon, leading to poisoning.
Natural disasters
Perhaps, if on August 24, 79 AD, the residents of Pompeii had received emergency assistance for carbon monoxide poisoning during the famous eruption of Vesuvius, perhaps there would not have been so many tragic deaths...
Fires
Remember the summer of 2010? Due to the abnormal heat in the Moscow region, peat bogs caught fire en masse - it was then that many residents of the capital and surrounding areas felt the “delights” of the first signs of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Human activity
An undeniable “contribution” is made by airplanes, water, rail and road transport. The first symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning are often observed among representatives of a wide variety of professions: miners, pilots, firefighters, garbage disposers, cooks, traffic controllers.
There are often cases of carbon monoxide intoxication after an ordinary walk along the streets of a busy metropolis!
One of the types of air pollution in industrial centers is smog: a suspended gas contains various toxic molecules, including CO. For example, the smog that enveloped London in 1952 caused the death of 12 thousand citizens and the exacerbation of bronchial and lung diseases in 100 thousand British victims of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Symptoms and signs
The severity of the lesion depends on several factors:
- state of health and physiological characteristics of a person. Weak people, those with chronic diseases, especially those accompanied by anemia, the elderly, pregnant women and children are more sensitive to the effects of CO;
- duration of exposure of the CO compound to the body;
- concentration of carbon monoxide in inspired air;
- physical activity during poisoning. The higher the activity, the faster poisoning occurs.
How to recognize "invisibility"?
In case of mild poisoning, the face turns red and there is an irresistible drowsiness. Alas, the decision to take a nap in such a situation can be a fatal mistake!
Moderate carbon monoxide poisoning signals a mortal danger with severe shortness of breath, and the symptoms listed above are aggravated even further.
Acute severe carbon monoxide poisoning is characterized by the appearance of convulsions, suffocation, arrhythmia, pulmonary edema, and mental changes. The victim may be found unconscious.
Atypical forms
There are two of them - fainting and euphoric.
Symptoms of fainting:
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- decreased blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.
Symptoms of the euphoric form:
- psychomotor agitation;
- mental dysfunction: delirium, hallucinations, laughter, strange behavior;
- loss of consciousness;
- respiratory and heart failure.
First aid for carbon monoxide poisoning
Rescuers provide urgent evacuation of people from premises contaminated with toxic fumes. Oxygen inhalation is the first medical aid for carbon monoxide poisoning.
Ambulance doctors perform pulmonary-cardiac resuscitation, symptomatic therapy, and administer an antidote for carbon monoxide poisoning.
After providing first aid for carbon monoxide poisoning, victims are taken to toxicology or intensive care departments, where intensive detoxification therapy and symptomatic treatment are carried out: anticonvulsants, diuretics, cardiac, hormonal medications, vitamins and sorbent No. 1 - Enterosgel.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy will help avoid neurological complications.
To reduce intoxication, after carbon monoxide poisoning, physiotherapeutic treatment methods, herbal medicine and massage are used.
Physical and chemical properties of carbon dioxide
Formula – CO2. Molar mass – 44 g/mol.
Carbon dioxide belongs to the class of acidic oxides, i.e. When interacting with water, it forms an acid called carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is chemically unstable and at the moment of formation it immediately breaks down into its components, i.e. The reaction between carbon dioxide and water is reversible:
CO2 + H2O ↔ CO2×H2O(solution) ↔ H2CO3.
When heated, carbon dioxide breaks down into carbon monoxide and oxygen:
2CO2 = 2CO + O2.
Like all acidic oxides, carbon dioxide is characterized by reactions of interaction with basic oxides (formed only by active metals) and bases:
CaO + CO2 = CaCO3;
Al2O3 + 3CO2 = Al2(CO3)3;
CO2 + NaOH(dilute) = NaHCO3;
CO2 + 2NaOH(conc) = Na2CO3 + H2O.
Carbon dioxide does not support combustion; only active metals burn in it:
CO2 + 2Mg = C + 2MgO (t);
CO2 + 2Ca = C + 2CaO (t).
Carbon dioxide reacts with simple substances such as hydrogen and carbon:
CO2 + 4H2 = CH4 + 2H2O (t, kat = Cu2O);
CO2 + C = 2CO (t).
Note! When carbon dioxide reacts with peroxides of active metals, carbonates are formed and oxygen is released:
2CO2 + 2Na2O2 = 2Na2CO3 + O2↑.
A qualitative reaction to carbon dioxide is the reaction of its interaction with lime water (milk), i.e. with calcium hydroxide, in which a white precipitate is formed - calcium carbonate:
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 = CaCO3↓ + H2O.
Carbon dioxide is a gaseous substance without color or odor. Heavier than air. Thermally stable. When compressed and cooled, it easily transforms into liquid and solid states. Carbon dioxide in a solid aggregate state is called “dry ice” and easily sublimes at room temperature. Carbon dioxide is poorly soluble in water and partially reacts with it. Density – 1.977 g/l.
Preventing carbon monoxide poisoning
To prevent an accident, you must:
- ventilate the premises, do not use faulty gas equipment, check the permeability of the chimney;
- comply with safety regulations at the enterprise;
- properly operate baths and saunas;
- Avoid long stays near busy highways.
Remember that timely first aid for carbon monoxide poisoning gives the victim a chance to survive and prevent the sad consequences of intoxication!
Operating principle
When a person inhales air that contains a high content of carbon monoxide, it is transported to the respiratory part of the body, where it is absorbed by the blood cells. The chemical component is quite similar to hemoglobin, myoglobin and enzymes that contain iron. Carbon dioxide freely enters into a process with these elements, during which a type of oxygen is formed that is unable to be transported into carboxyhemoglobin tissues. A patient with this diagnosis develops hypoxia. Slow dissolution of compounds has an adverse effect on the nutritional properties of internal organs and tissues. In combination with this, a process of unstable operation of biochemical phenomena occurs, which is based on the functioning of iron-containing enzymes. With the accumulative activity of under-oxidized metabolic products, additional poisoning occurs, spreading to the central nervous system and other organs.
Industrial use
In the metallurgical industry, carbon monoxide is often used for the reduction of metals from their oxides or salts. The formula of the resulting compound is CO2. A pure substance, metal, is also formed.
In addition, carbon monoxide is used:
- for processing meat and fish products, which allows you to give them a fresh look;
- for the synthesis of certain organic compounds;
- as a component of generator gas.
Therefore, this substance is not only harmful and dangerous, but also very useful for humans and their economic activities.
Sources
- https://www.gasdetecto.ru/podderzhka/stati/ugarnyj-gaz-vozdejstvie-na-cheloveka-i-pribory-ego-kontroliruyuschie/
- https://istra-gaz.ru/raschety/ugarnyj-gaz-primenenie.html
- https://bouw.ru/article/ugarnyy-gaz
- https://nauka.club/khimiya/oksid-ugleroda.html
- https://FB.ru/article/184533/ugarnyiy-gaz-formula-i-svoystva
- https://kidschemistry.ru/ximicheskie-i-fizicheskie-svojstva-ugarnogo-gaza.html
- https://www.schoolchemistry.ru/katalog/uggaz.htm
- https://www.med24.online/articles/otravlenie_ugarnym_gazom_priznaki_simptomy_pervaya_pomosch/
- https://medicina.dobro-est.com/otravlenie-ugarnyim-gazom-simptomyi-i-pervaya-pomoshh-lechenie.html
Conditions for the appearance of fumes in the room
Carbon monoxide can be produced using dozens of chemical reactions, but this requires specific reagents and conditions for their interaction. The risk of gas poisoning in this way is practically zero. The main reasons for the appearance of carbon monoxide in a boiler room or kitchen area remain two factors:
- Poor draft and partial flow of combustion products from the combustion source into the kitchen area;
- Improper operation of boiler, gas and furnace equipment;
- Fires and local fires of plastic, wiring, polymer coatings and materials;
- Waste gases from sewer lines.
The source of carbon monoxide can be secondary combustion of ash, loose soot deposits in chimneys, soot and resin embedded in the brickwork of fireplace mantels and soot extinguishers.
Most often, the source of gas CO is smoldering coals that burn out in the firebox when the valve is closed. Especially a lot of gas is released during the thermal decomposition of firewood in the absence of air; approximately half of the gas cloud is occupied by carbon monoxide. Therefore, any experiments with smoking meat and fish using the haze obtained from smoldering shavings should be carried out only in the open air.
A small amount of carbon monoxide may also appear during cooking. For example, anyone who has encountered the installation of gas heating boilers with a closed firebox in the kitchen knows how carbon monoxide sensors react to fried potatoes or any food cooked in boiling oil.
Properties of a toxic substance
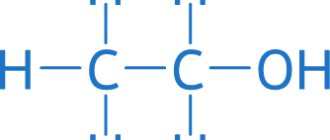
There is nothing unusual in the nature and properties of carbon monoxide. Essentially, it is a product of partial oxidation of coal or coal-containing fuels. The formula of carbon monoxide is simple and straightforward - CO, in chemical terms - carbon monoxide. One carbon atom is connected to an oxygen atom. The nature of the combustion processes of organic fuel is such that carbon monoxide is an integral part of any flame.
When heated in the firebox, coals, related fuels, peat, and firewood are gasified into carbon monoxide, and only then are burned with an influx of air. If carbon dioxide has leaked from the combustion chamber into the room, it will remain in a stable state until the moment when the carbon flow is removed from the room by ventilation or accumulates, filling the entire space, from floor to ceiling. In the latter case, only an electronic carbon monoxide sensor can save the situation, responding to the slightest increase in the concentration of toxic fumes in the atmosphere of the room.
What you need to know about carbon monoxide:
- Under standard conditions, the density of carbon monoxide is 1.25 kg/m3, which is very close to the specific gravity of air 1.25 kg/m3. Hot and even warm monoxide easily rises to the ceiling, and as it cools, it settles and mixes with air;
- Carbon monoxide is tasteless, colorless and odorless, even in high concentrations;
- To start the formation of carbon monoxide, it is enough to heat the metal in contact with carbon to a temperature of 400-500 ° C;
- The gas is capable of burning in air, releasing a large amount of heat, approximately 111 kJ/mol.
Not only is inhalation of carbon monoxide dangerous, the gas-air mixture can explode when the volume concentration reaches from 12.5% to 74%. In this sense, the gas mixture is similar to household methane, but much more dangerous than network gas.
Methane is lighter than air and less toxic when inhaled; in addition, thanks to the addition of a special additive - mercaptan - to the gas flow, its presence in the room can be easily detected by smell. If the kitchen is slightly gassed, you can enter the room and ventilate it without any health consequences.
With carbon monoxide everything is more complicated. The close relationship between CO and air prevents the effective removal of the toxic gas cloud. As it cools, the gas cloud will gradually settle in the floor area. If a carbon monoxide detector is triggered, or a leak of combustion products is detected from a stove or solid fuel boiler, it is necessary to immediately take measures for ventilation, otherwise children and pets will be the first to suffer.
This property of a carbon monoxide cloud was previously widely used to fight rodents and cockroaches, but the effectiveness of a gas attack is significantly lower than modern means, and the risk of poisoning is disproportionately higher.
For your information! A CO gas cloud, in the absence of ventilation, can retain its properties unchanged for a long time.
If there is a suspicion of carbon monoxide accumulation in basements, utility rooms, boiler rooms, cellars, the first step is to ensure maximum ventilation with a gas exchange rate of 3-4 units per hour.