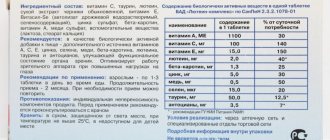
Folic acid is a water-soluble biologically active compound belonging to the B vitamins. It is produced artificially and is highly digestible. Participates in many vital processes, helps normalize the functioning of the nervous system and brain function. Useful for all age groups.
pharmachologic effect
The drug has a metabolic effect, acting as a biological compound. Helps compensate for the deficiency of vitamin B9 and is involved in erythropoiesis.
After internal use, it is quickly and completely adsorbed in the digestive tract.
There is almost 100% binding of the drug components to various proteins. Penetrates well into the placenta, blood cells and breast milk.
The maximum concentration of the drug is reached after 30-60 minutes. Excretion is carried out by the kidneys, also by hemodialysis.
Dosage
For preventive purposes, it is enough for an adult to take 400 mcg of folic acid daily. The same dose is required for adolescents during the period of active growth in order to prevent the development of anemia and retardation in physical development.
The need for folic acid in women planning pregnancy increases sharply. Six months before the expected conception, they should start taking 1 mg of the substance daily. This will contribute to the proper formation of the baby’s nervous system and help avoid the development of congenital defects.
Contraindications
The use of a biologically active substance is prohibited in the following cases:
- Individual intolerance to individual components of the drug.
- Allergic reactions to Folate.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Carbohydrate deficiency.
- Impaired adsorption of galactose and glucose.
You should take the medicine with caution if you have B9 vitamin anemia with symptoms of cyanocobalamin deficiency.
Indications for taking vitamin B9
Folic acid is prescribed to prevent a number of diseases, since people do not immediately notice a lack of the vitamin. Symptoms of B9 deficiency can easily be attributed to fatigue and high stress levels.
This substance is also used as part of complex therapy in the treatment of certain chronic diseases. It is used:
- in case of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- to prevent blood diseases, especially anemia;
- in the treatment of diabetes mellitus;
- in the complex treatment of intestinal diseases accompanied by impaired growth of normal microflora;
- with long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- with inflammatory changes in the oral mucosa and skin;
- when planning pregnancy;
- when taking antiepileptic drugs and drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia.
In addition, drugs containing B9 are indicated for women during pregnancy and menopause, and for men during puberty and in the process of planning to conceive a child. Vitamins B12, vitamins B6 and folic acid are usually taken together, since simultaneous intake with vitamin B9 and vitamin B12 reduces the risk of overdose and promotes more complete absorption of the drug, and vitamin B6 enhances the effect of folic acid on heart function. Instructions for use of vitamin B6 emphasize its importance for the functioning of this important organ.
Why is folic acid prescribed to pregnant women?
Vitamin B9 is involved in the formation of amino acid and RNA structures, which are necessary for cell division and the subsequent development of a new organism. In addition, it ensures high-quality absorption of iron and other important elements for normal activity.
Folic acid deficiency poses a significant threat to reproducing cells: without it, hematopoiesis cannot occur and the correct formation of internal organs and tissues of the fetus will not occur.
Vitamin B9 promotes the production of hydrochloric acid, is involved in the metabolism of adrenaline and serotonin, and regulates the functioning of the nervous system.
If folic acid is supplied in small quantities during pregnancy, the fetus increases the risk of hydrocephalus, spinal pathologies, heart defects and brain diseases.
Signs of a deficiency of the active substance are weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbance, apathy, depression and irritability.
Sources of vitamin B9
The human body does not synthesize such an important substance. People get it from the outside, mainly through food. Sources are:
- Green vegetables - broccoli, lettuce, asparagus, spinach, cabbage and parsley. However, during cooking, most of the substance is destroyed and goes into the water in which the vegetables were boiled or poached.
- Some types of fruits and vegetables. There is a lot of B9 in oranges, apricots and bananas, a little less in pumpkin, beets and carrots.
- Peanuts and walnuts are rich in this substance, as well as barley groats and bran bread.
- Meat and dairy products are also sources of this substance. It is mainly found in liver, chicken, eggs, real cheese and cottage cheese, some amount is found in salmon and tuna.
However, even if all these products become a daily part of your diet, you will not get the required amount of B9 - it disappears when food is cooked. That is why folic acid tablets are necessary for every person, and are especially important for women before pregnancy and during pregnancy.
How to take Folic acid during pregnancy
The optimal requirement of vitamin B9 for an adult is 50 mcg, but a pregnant woman needs much more.
The exact dosage of the drug is calculated by the doctor, according to clinical indications.
Pregnant women with the norm of the biologically active substance are prescribed 400 mcg. If necessary, the therapeutic dosage is changed from 100 to 800 mcg per day.
Vitamin B9 deficiency poses a great danger to the fetus in the early stages of its development, so many experts recommend starting to use the drug before pregnancy. It is advisable to take a course of pills at least 3 months before conception.
A regular tablet contains 1 mg of active ingredient, while a complex of vitamins designed specifically for pregnant women contains from 300 mcg. Therefore, it is enough for a woman to take a pill per day to replenish the body’s need for folate for normal functioning.
Expert opinion of a doctor
Elicheva Lyudmila Fedorovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D.
Deviations in the formation and growth of the embryo occur in the first few weeks after fertilization. A woman may not know about pregnancy when she does not plan to conceive. Both parents should start taking B9 during pregnancy planning.
From about 16-20 days of embryogenesis, the process of neurulation (formation of the neural tube) occurs. With a lack of folic acid, the neural tube, which is the rudiment of the central nervous system, will not form correctly. This will lead to abnormalities in the development of the brain and spinal cord, up to anencephaly (lack of soft tissues of the head, bones of the cranial vault, and cerebral hemispheres).
Pregnant women need folacin for:
- neurulation process;
- formation of the placenta;
- construction of an extensive vascular network of the placenta;
- providing the placenta with immune protection;
- preventing miscarriage;
- reducing the risk of premature birth;
- normal gestation;
- supporting maternal health.
In early childhood, folic acid
is required for the child to grow and develop normally.
With the phenomenon of gastrulation, a trilaminar germinal disc appears with three embryonic layers, which will give rise to the remaining organs of the unborn child: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Mesoderm cells initiate the formation of the notochord, a flexible rod structure that supports the embryo until the vertebral column is formed. On the other hand, ectoderm cells give rise to the neural tube, which will form the nervous system of the fetus.
What are folates
Folate is a natural form of vitamin B9. The name folate comes from the Latin word “folium,” which means leaf. This is why leafy greens are one of the best food sources of folate. Folate is the common name for a group of related compounds. The active form of vitamin B9 is folate known as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF). Newcastle University showed in 2014 that most dietary folate is converted into 5-MTHF (methyltetrahydrofolate) before entering the blood. However, chronic consumption of folic acid rather than folate can cause saturation, which results in unmetabolized folic acid circulating in the blood that has not been converted to methyltetrahydrofolate.
Link to the study:
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24944062
Is it possible to take the drug without a prescription?
Folic acid and vitamin complexes containing it are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. The amount of the drug needed by a specific person for a lack of folic acid is calculated individually based on several indicators: gender, age, general condition of the body. Therefore, in order to choose a therapeutic dosage, you should consult a doctor.
In addition, the drug has some contraindications: hypersensitivity to folic acid, cancer, vitamin B12 deficiency. If a person has such conditions, the use of folates should be completely abandoned.
Interaction with other tools
Despite the fact that folic acid is a vitamin, before you start taking it, you should consider its compatibility with other drugs used by the patient. For example, a number of medications reduce the rate of absorption of folic acid in the intestine:
- Antacids.
- Some antibacterial agents: tetracyclines, sulfonamides, etc.
Some diuretics, for example, Triamterene, can also reduce the severity of the effect of folic acid, which should be taken into account when using them together.
Side effects
The following side effects are possible when taking folic acid:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stomach upsets;
- anorexia;
- deterioration of respiratory functions;
- feeling of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
To avoid side effects, you should carefully consider the contraindications, recommended dosage and consult a specialist.
Allergy
Folic acid is a synthetic form of B9. It is this type of vitamin derivative that can provoke an allergic reaction.
People prone to allergies are advised to take B9 in natural form. The best option is food.
Interesting to know! The foods richest in folic acid are: peanuts, sunflower seeds, parsley, cod liver and sesame.
Allergies manifest themselves in the following symptoms:
- sensation of itching of the skin, including around the eyes;
- hives.
The symptoms may also be similar to those of food poisoning.
Blood thinning
Folic acid thins the blood and is also very important for the cardiovascular system.
Interesting to know! Vitamin B9 provides more benefits when taken together with B12 and B6 (more details).
Nausea and bloating
Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain and intestinal disorders most often occur with prolonged excess of the B9 dosage. Nausea, intestinal discomfort, etc.? Stop taking supplements and consult a specialist. Loss of appetite may also occur.
Overdose is eliminated using hemodialysis.
If you feel sick during pregnancy, it is not due to a side effect from folic acid. On the contrary, B9 and B6 (when taken simultaneously) alleviate the symptoms of toxicosis.
Headache
B9 can cause headaches in the most rare cases. Typically, such disorders are associated with disorders of the nervous system. And folic acid sufficiently normalizes the functioning of the central nervous system.
Athletes can also experience headaches during overload.
Now Foods, Methyl Folate, 1,000 mcg, 90 Tablets
881 rub.
More details
Weight gain
With proper use of the supplement, obesity is almost impossible. The vitamin regulates metabolic processes, accelerating metabolism. Weight gain can only occur if the daily norm is not met. Most often, fat deposits are formed due to hormonal imbalance and the presence of certain diseases.
Female side effects: effect on periods
The side effects of taking folic acid in women are the same as in men and children. All symptoms are described in the list of side effects. Hormonal imbalances in women, problems with the cycle, etc. are not associated with B9. Judging by the reviews of many girls, if folic acid affects menstruation, it is only positive. Some female representatives, after a course of the drug, no longer even have pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation.
Did you feel a pull in your lower abdomen? Is your cycle out of whack? If problems of this kind arise, it is recommended to take hormone tests and consult a doctor.
Pimples
The appearance of acne on the face and body may well occur after a course of B9 (folin). And both for women and men. This reaction is associated with the individual characteristics of the body.
If you experience any itching or rash on your face or other areas, it is recommended that you stop taking the synthetic form of the vitamin. In this situation, it is better to switch to natural sources - products.