“Congratulations, you are pregnant!” – doctors used to say these words more often; with the advent of express pregnancy tests, they can be read in the instructions for the test. In any case, most women call pregnancy and motherhood the most amazing time in their lives.
It is not without reason that they say that a pregnant woman seems to glow from within; she is especially beautiful and attractive during this period. Of course it's a miracle! The expression is a little hackneyed, but, in fact, when a new life arises from a lump of mucus during 40 weeks of pregnancy, there is no other way to call it
Pregnancy is a physiological state of the body. The changes that are taking place are programmed by Mother Nature. These changes are so significant that because of them, a woman’s whole life switches to a new rhythm: about 80% of women feel nausea, especially in the morning; the perception of odors is heightened, some of them cause unpleasant sensations, including severe nausea and vomiting; the usual diet may change - your favorite food may cause disgust, and dishes that were previously on the list of hated foods may appear in first place; increased fatigue; an incomprehensible drowsiness is annoying; frequent urge to urinate; sudden changes in mood; tearfulness.
How pregnancy begins and develops
Fertilization
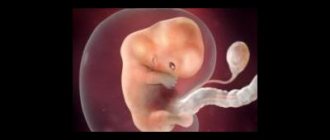
Every time in the middle of the menstrual cycle, one, rarely several, follicle matures in the ovaries. The follicle contains an egg. The moment the egg is released from the follicle is called ovulation. After release, the egg is picked up by the fallopian tubes and slowly moves towards the uterine cavity. If during this short (3-6 days) period of time a woman has sexual intercourse without means of preventing pregnancy, pregnancy may occur. The egg produces special substances that signal the sperm about where it is. If the “rendezvous” takes place, fertilization occurs. Pregnancy begins.
Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tubes, even before the egg enters the uterine cavity. After the fusion of the egg and sperm, a zygote is formed, from which the growth of the embryo begins.
What happens and what does the embryo look like? How will the size of the embryo change over the weeks? What changes will occur during the process of growth and development? What do photos of an embryo look like by week? Ultrasound is used to observe how the embryo develops over weeks and months.
Second trimester: how the baby grows in the belly
In the second trimester, further growth and development of the fetus occurs - this is what your baby is now called.
I would like to remind you that it is located in the uterine cavity, lined with the amniotic membrane and surrounded by amniotic fluid. The fetus is connected to the mother's body through the umbilical cord and placenta, through which it receives the nutrients and oxygen necessary for its development. Amniotic fluid is produced by the placenta and cells of the amniotic sac. The activity of the fetal bladder is of no small importance. In preparation for life outside the womb, the fetus swallows water, which, in turn, stimulates intestinal activity and promotes the production of original feces - meconium. Amniotic fluid also performs a protective function - it protects the baby from the effects of the external environment. During the entire second trimester, the fetus actively moves in the uterine cavity. From about 18 weeks, a woman begins to detect the movements of her baby. Now you can even communicate with him: the organ of hearing has already been formed and perceives all the sounds coming from our world.
By 20 weeks, the baby, in addition to all the organs necessary for later life, has nails, eyebrows, vellus hair, and a cheese-like lubricant appears on the skin. It weighs about 300 grams and reaches 25 cm in length. The uterus also grows with it. The fundus of the uterus can already be felt at the level of the navel.
By 24 weeks, the fetus gains the same amount and already weighs 600 grams, its length is about 30 cm. From about this time, your family can feel the baby moving by placing their hand on the stomach.
The 2nd trimester is over. What happened to the female body? Firstly, due to the addition of the uteroplacental blood flow and an increase in the volume of circulating blood (by about half a liter), the load on the heart increased. You notice that it is becoming more difficult to do your usual work, and you may experience shortness of breath after physical activity. If it doesn't go away with rest, tell your doctor. Secondly, an enlarged uterus also does not add comfort. In addition to the fact that it has become uncomfortable to sleep, you have “outgrown” your usual clothes.
Other not very pleasant symptoms also appeared. The growing uterus compresses the veins through which blood flows from the lower extremities and pelvic organs. The vascular pattern on the legs intensifies, the veins dilate - which means it’s time to wear special therapeutic compression hosiery (socks, stockings, tights), you may need to consult a specialist in vein disease - a phlebologist. For the same reason, many women develop hemorrhoids. Thirdly, due to hormones produced in large quantities that relax the muscles (primarily the uterus), the intestines begin to act up - most pregnant women suffer from constipation.
Embryo 1 week
The zygote is still in the fallopian tube on its way to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are lined with villi, which move the egg towards the uterus. If the zygote does not enter the uterus within a certain time, it may attach to the wall of the fallopian tube. In this case, they talk about ectopic pregnancy - a condition dangerous to health and life.
During fertilization, the sperm brings in its 23 chromosomes, which combine with the 23 chromosomes in the egg. Moreover, depending on whether the sperm contains an X or Y chromosome, the gender of the unborn child depends.
After fertilization and the formation of a zygote, about 30 hours pass. The fertilized egg begins to divide. This process is called fragmentation, since with a slight increase in volume, the number of cells grows exponentially and their size decreases. From 1 you get 2, from 2 you get 4, etc. With an increase in cell mass, the gastrula turns into a morula. The morula looks like a spherical collection of cells. By day 7 after fertilization, the morula turns into a blastula. A fluid-filled cavity, or blastocoel, appears in the center of the embryo. The blastula enters the uterine cavity and is immersed in the mucous layer. This process is called implantation and involves the outer shell of the blastula, called the trophoblast. After implantation, trophoblast cells begin to produce human chorionic gonadotropin, an important hormone that supports pregnancy. Human chorionic gonadotropin can be detected in urine, where its presence is determined using a rapid pregnancy test. By the end of the first week, the size of the embryo is only 0.3 mm.
Fetal development by week in the first trimester
The conception of a child occurs during the period of ovulation, after the fertilization of the egg by the sperm. As a rule, ovulation coincides with days 10-16 of the menstrual cycle.
Human intrauterine development is divided into two stages: embryonic and fetal. The first stage is the period from the moment of fertilization of the egg to the tenth week of pregnancy.
During the embryonic stage, important processes occur: crushing and implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity, the formation of the neural plate (the rudiment of the central nervous system) and its closure into the neural tube, the formation of organs and the placenta.
It is worth distinguishing between embryonic and obstetric stages of pregnancy. The first is counted from the moment of conception, the second - from the beginning of the last menstruation. As a rule, the difference between these periods is two weeks.
It turns out that the formation and ontogenesis of the embryo begins only in the third week of pregnancy. Let's take a closer look at how the fetus develops week by week during the first trimester.
3rd week of gestation
After the sperm penetrates the egg, a zygote is formed - a diploid cell with a set of chromosomes equally obtained from female and male gametes. The duration of formation of a diploid cell is 25-30 hours.
The zygote begins dividing and moving towards the uterus. At the beginning of division, the zygote splits into 2-4 blastomeres (round-shaped cells that form the embryo). The number of blastomeres increases every day.
On the fourth day after conception, the zygote consists of 12-14 blastomeres. The density of embryonic cells increases, and they are closely connected with each other. The embryo enters the uterine cavity.
A blastocyst is formed (an early stage of embryo development), which is implanted into the endometrium of the uterus. During implantation, a pregnant woman may experience uterine contractions and spotting, which is often mistaken for menstruation. However, unlike menstruation, bleeding during implantation is mild and short-lived.
4 week
Implantation accelerates the development of the embryoblast (internal cells of the embryo), resulting in the formation of extra-embryonic organs:
- chorion is a membrane that performs excretory, respiratory and protective functions. After implantation of the embryo, the first chorionic villi begin to appear on its surface. Subsequently, some of the chorion cells destroy the uterine wall and participate in the formation of the placenta;
- amnion is a water membrane that provides the fetus with optimal development conditions and protects it from mechanical stress. Amnion fluid consists of proteins, sugars, mineral salts and other substances;
- the yolk sac, which performs a hematopoietic function. At first, its size exceeds the size of the embryo. After the 12th week of gestation, this temporary organ decreases in size and completely disappears.
The formation of the primary intestine occurs. The organs of the digestive system will subsequently develop from its departments. In the fourth week of gestation, the formation of the liver and pancreas occurs.
After implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity, placenta rudiments form at the site of attachment of the embryo. The process of its formation will be completed by the 16th week of gestation. The placenta provides the fetus with the necessary oxygen and nutrients, protects against infections, and removes metabolic products.
By the end of the fourth week of gestation, a woman notices that the expected menstruation does not occur. During this period, mood swings, fatigue, and increased sensitivity of the mammary glands may occur.
5 week
By the fifth week, the neural tube appears - the basis of the spinal cord and brain. The heart forms from the bulge in the central part of the fruit. During this same period, hemoglobin begins to form, so the rate of iron consumption by the embryo increases.
The umbilical cord begins to form, which will become the connecting link between the embryo and the placenta. As the fetus grows, the umbilical cord also increases in size.
During this period, a woman may experience the first signs of toxicosis: nausea, vomiting, intolerance to certain foods and odors.
week 6
The embryo’s heart begins to beat, and the thymus gland, which is responsible for immunity, is formed. Formed:
- rudiments of arms and legs;
- cerebral hemispheres;
- eye sockets and ear canals;
- organs of the excretory system.
Vessels are actively growing, blood circulation is established.
week 7
Nerve fibers, esophagus, stomach, and pharynx develop. The embryo develops semblances of hands and primary germ cells. The pancreas begins to produce insulin. The respiratory system is currently represented only by the trachea.
A woman may experience increased signs of toxicosis, so it is important to drink plenty of fluids.
8 week
This period is characterized by the formation of facial features in the embryo, as well as the development of the lower and upper limbs. The retina forms in the eyes, the upper limbs are able to bend at the elbows, and the lower limbs at the knees.
The genitals acquire a characteristic appearance, but this is still not enough to determine the sex of the unborn child.
Week 9
Left and right atria and ventricles appear in the heart. Large blood vessels and endocrine glands develop. The placenta begins to produce hormones. The fingers on the lower and upper extremities are fully formed.
10 week
If the genotype of the embryo contains a gene that initiates the development of the male body, then in the tenth week of gestation the testicles actively develop and they begin to produce the hormone testosterone.
At the same time, the fetus develops the optic nerve, and urine begins to form in the kidneys. The strength of bone tissue increases. The diaphragm forms between the abdominal and thoracic cavities.
11 week
From the 11th week the fetal period of intrauterine development begins. The state of health of most pregnant women stabilizes: the symptoms of toxicosis, irritability, and fatigue disappear.
The fetus has formed the most important organs, the face, and the hemispheres of the brain. Muscle tissue develops. The fetus begins to make movements, but the woman does not feel them yet.
12 week
Taste buds on the tongue are formed. The cerebellum is actively developing - the part of the brain that is responsible for performing targeted movements, their speed and maintaining muscle tone. The rudiments of nails and teeth appear.
The thymus gland is a full-fledged organ in which T-lymphocyte differentiation occurs. The body proportions of the fetus are still incorrect: the head is large, the arms are long, and the legs are short and bent at the knees.
The intestines enlarge and begin to fold into loops. Leukocytes appear in the blood, which protect the body from external and internal pathogenic agents.
The formation of the gonads continues. By the end of the 12-13th week of pregnancy, it becomes possible to determine the sex of the fetus.
Embryo 2 weeks
On days 8-9 after fertilization, the blastula turns into a gastrula. In this case, the internal cells of the blastula are divided into 3 layers. The outer layer, or ectoderm, will develop into the nervous system and skin. The internal (endoderm) will turn into the cavity of the gastrointestinal tract. The mesoderm, the middle layer, will give rise to the musculoskeletal system (bones, ligaments and cartilage), muscles, kidneys, blood vessels and other internal organs. 10 days after fertilization it is already possible to get a positive pregnancy test result.
Embryo 3 weeks
At week 3, the embryo moves from the gastrula stage to the neurula stage. The ectoderm in the area of the future spine forms a groove that gradually goes deep into the embryo. The edges of the groove are closed. A neural tube has formed that will become the brain and spinal cord. An embryo is formed that will become the baby’s heart.
At week 3, the placenta begins to form - the life support system of the embryo. The trophoblast and part of the ectoderm form the amnion and chorion. The amnion is popularly called the “shirt”. Amniotic fluid collects in the amniotic cavity. The chorion is a villous formation that also produces human chorionic gonadotropin. After some time, with the participation of the mesoderm, the placenta is formed from the chorion. By the end of 3 weeks, the embryo grows to a size of 4 mm.
Embryo 4 weeks
At week 4, the brain and spinal cord begin to form from the neural tube. At the same time, the heart makes its first contraction. Now it will not stop until the very end of life.
The rudiments of arms, legs, eyes, and internal organs are formed. Blood begins to flow in the blood vessels. Before this, the embryo received nutrients from the yolk sac, which, like in birds, contains reserves necessary for the initial stage of development. In addition, the yolk sac in mammals plays the role of the liver, bone marrow, and kidneys. It is the yolk sac that contains future germ cells, which migrate from it to the primordia of the gonads. After the appearance of the corresponding organs in the baby, it gradually disappears by the end of the first trimester.
Why does bleeding appear?
They can occur on the days of expected menstruation and more often in women who, even before pregnancy, had problems with the menstrual cycle (when ovulation occurred not in the middle of the cycle, but before menstruation). Call an ambulance quickly: the appearance of such discharge is a reason for a trip to the hospital.
If it turns out that the cause of the events lies in hormonal deficiency, you will need to undergo an examination, and a pregnancy loss specialist will prescribe the necessary therapy for you. If this is due to the incorrect location of the branched chorion, which can be determined during an ultrasound examination, you will be advised to lie down more and take sedatives.
Embryo 5 - 6 weeks
Embryo. 5 weeks from the moment of fertilization.
At 5 weeks, the umbilical cord is formed, which will connect the baby to the placenta. The umbilical cord contains arteries and veins. The length of the umbilical cord by the end of childbirth can reach 70 cm. At the 5th week, the arms and legs look like flippers, but individual details can already be distinguished. The first impulses begin to be generated in the nervous system - the basis of nervous activity. The head of the embryo is formed, and holes for the ears, eyes, mouth and nose appear in it. The length of the embryo reaches 1 cm.
Embryo. 6 weeks from the moment of fertilization.
At week 6, it is already possible to distinguish the features of the future face. Limbs and fingers are developing. The baby begins to make his first movements. The pigment that determines the color of the eyes is formed on the iris. At week 6, the embryo's heartbeat can be seen and heard using an ultrasound scanner or ultrasound. The placenta is fully formed. The rudiments of the lungs, kidneys, gonads, stomach and intestines are formed. Amniotic fluid already surrounds the embryo. The 6th week of pregnancy in Western countries is considered the optimal time for the first visit to a gynecologist. It is necessary to do an ultrasound, undergo a series of tests, and undergo an examination by specialized specialists.
29-32 weeks
The third trimester of pregnancy has arrived.
During this last trimester of pregnancy, your baby is growing, storing fat, and his organs are slowly maturing. By 32 weeks of pregnancy, your baby will be about 40 centimeters long and will weigh up to 2 kg.
At this time, the child may exhibit high motor activity and even “hiccup” (so-called hiccup-like movements)! This is how the child practices breathing and trains the respiratory muscles.
Read about 29-32 weeks of pregnancy...
Embryo 8 weeks
The kidneys begin to produce urine. Hair follicles form in the skin. Almost all vital organs have already been formed. Reflexes and feelings are triggered. Ears form, the face no longer looks like an alien from a science fiction movie. It is clearly visible that a person is growing. The bones are still made of cartilage, but later they will be saturated with calcium and turn into real bone tissue. This process will be completely completed only by the age of 25, long after birth. The size of the embryo is almost 2 cm.
Diagnosis of pregnancy
Before performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, a gynecologist may suspect a short-term pregnancy based on subjective signs. These include the woman’s report of the absence of menstruation and examination data:
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- bluish tint of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix;
- an increase in the size of the uterus from 5-6 weeks, a change in its consistency;
- asymmetry of the uterus with protrusion of the angle in which the embryo is implanted;
- mobility of the uterine body.
To confirm the fact of pregnancy and determine the location of the ovum, an ultrasound examination is performed at a period of 5-8 weeks. If necessary, this diagnostic procedure can be performed repeatedly over short periods of time. One of the indications is a suspicion of late ovulation, when the ultrasound picture does not correspond to the expected gestational age. Changes in the type and size of the embryo over time are correlated with the rate of growth of hCG concentration.
The processes occurring in a woman’s body after conception cause changes in appearance and the appearance of new and unusual symptoms. The first signs of pregnancy are divided into probable, doubtful and reliable. Ultrasound is considered the most reliable method for early diagnosis of pregnancy.
Embryo 10 weeks
The baby's eyelids close. He will open them himself at 28 weeks. The respiratory system is almost completely formed. The skeleton and its structure fully correspond to a person. The arms and legs are lengthened to normal proportions. But the head occupies almost half the length of the body. This is due to the active development of the cerebral hemispheres, the cerebellum is growing. The external genitalia develop according to gender. You will soon find out if he or she is growing in your belly. The baby's blood acquires its own group and Rh factor. Height can reach 7-8 cm.
What examinations are performed during pregnancy?
The word “pregnancy” comes from the word “burden.” Pregnancy is a significant burden on a woman’s entire body. Therefore, if the pregnancy is planned, try to cure your chronic diseases first. If you did not expect pregnancy, but, nevertheless, it turned out to be desired, consult a doctor as soon as possible. You will be examined, treatment will be selected and all necessary recommendations will be given for further pregnancy.
If you are healthy, you will just need to get tested.
- Analysis for syphilis, HIV infection, hepatitis B and C. The first time this test is taken is at the first visit to the antenatal clinic. You will have to retake it once every 3 months (3 times during the entire pregnancy).
- A general blood test will have to be taken monthly. The doctor will be interested in the level of hemoglobin, the number of leukocytes, platelets, and ESR.
- A biochemical blood test is also taken once a month. It can be used to judge how the internal organs function, primarily the liver and kidneys.
- A general urine test in the first and second trimesters is taken once a month, then once every 2 weeks, and after 36 weeks - weekly.
- Analysis to determine blood type and Rh factor. Rent once. However, if you have Rh negative blood and your husband has positive blood, you will have to determine the amount of Rh antibodies in your blood monthly, and more often if necessary. This is very important for identifying Rh conflict between the organisms of the mother and fetus.
- Coagulogram. Changes in the blood coagulation system are determined monthly. This is very important, because the mother’s blood provides nutrition to the baby.
- Testing for sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, viral infection) is done either before pregnancy or in the early stages. If necessary, for example, if there are signs of intrauterine infection, the tests will have to be repeated.
- Ultrasound for uncomplicated pregnancy is performed at 20-24 and 36 weeks. According to indications, this study can be performed more often, since it does not have a negative effect on the mother and fetus.
- At 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, it is necessary to take an analysis for possible fetal malformations - determine the level of alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin and unconjugated estriol in the blood.
- After 34 weeks of pregnancy, fetal cardiotocography (CTG) is indicated once every 2 weeks to assess its intrauterine condition.
- Pregnant women are required to be examined by a therapist, ophthalmologist, ENT doctor, or dentist.
- The need for other studies is discussed individually with the doctor leading the pregnancy.
Embryo 11 weeks
The baby has a hairstyle. The fine hair on the head and body is called lanugo. They usually fall out by the time of birth. The skin is almost transparent, blood vessels are visible. The first foci of ossification form in the bones. White blood cells - leukocytes - appear in the blood. The arms are pulled up to the face, the baby can put a finger in the mouth. We begin to do exercises - the baby can actively move in the womb, but its size (10-15 cm) and low weight (30 g) do not yet allow the mother to properly feel these movements.
Embryo 12 weeks - 13 weeks
Embryo 12 weeks. Photo
During this period, you can visit a doctor and have an ultrasound examination done in 3D reconstruction mode. Here is your baby's first portrait. Ultrasound can determine the sex of the child with almost 100% accuracy. During an ultrasound, screening for developmental pathologies is carried out. The finger can now be sucked - the sucking reflex has appeared. The liver and pancreas produce secretions. Meconium is formed in the intestines - original feces. The formation of the genital organs is completed. The baby's height is about 15 cm, weight 40-50 g. Despite the fact that the child is so small, he is already a person. All organs are in their places, now his body will be more resistant to negative influences. All that remains is to grow. The first trimester is over.
Embryo 16 weeks -19 weeks
Marigolds appeared on my fingers. Taste buds on the tongue can sense taste, and receptors in the nose can sense smell. Mom may or may not like the foods she eats. Fully formed ears make it possible to hear sounds. Including mom's heartbeat. Recent research has led to an original practical application - soft toys are made for newborn children that reproduce the mother's heartbeat. It is believed that a calm, measured heartbeat calms the baby. Try not to be nervous. The eyes begin to discern light.
And of course, during this period, mothers begin to feel the baby’s movements inside them. There is feedback from the mother. The baby can sleep and be awake, this is noticeable by periods when no movements are felt. Baby's height is 20 cm and weight is up to 250 g.
Recommendations from a gynecologist for a future mother
First of all, try to sleep at least 8-10 hours, go to bed early and try to rest during the day. All this is necessary so that the future baby is comfortable in your stomach and receives the necessary amount of nutrients and oxygen (and all this comes to him through your blood). Spend more time in the fresh air, for example, take a walk with your husband before going to bed. If you feel nauseous in the morning, eat a cookie or an apple before getting out of bed. This problem often occurs due to the fact that blood sugar levels are low in the morning, and a small “snack” will help you quickly bring it back to normal.
Radical life changes will be needed only if your work involves the risk of contracting infections, if you spend a lot of time in contact with chemicals or with a computer. In this case, you should think about taking a vacation without waiting for maternity leave. The fact is that in the first 8 weeks, all the organs and systems of the unborn child are formed, and any harmful influence (chemicals, radiation, viruses, nicotine, alcohol) can disrupt this important process. And one more thing: during the first ultrasound examination, the doctor will determine where the placenta is: if it is located normally and there are no problems during pregnancy, then you should not deny yourself sex.
Embryo 20 weeks -30 weeks
Did you feel the kick? Now the baby communicates with his mother this way. If mom is sad, upset about something, or there is loud music around, it’s smoky, stuffy, the baby violently expresses his opinion. At first it’s timid, but by the end of pregnancy this method of communication will no longer cause tenderness. Constantly getting kicked from the inside can be quite painful. A sudden noise or fright of the mother leads to a similar response from the child. Protective reflexes arise.
In the lungs, the formation of respiratory alveoli is completed. Fingerprints form on hands. Brain development occurs at the fastest rate. Neural connections are formed. The baby can blink. The immune system is formed. The respiratory organs are developed enough to provide breathing in the event of premature birth, but sometimes only with medical assistance and special equipment. Adipose tissue appears. By 30 weeks, growth reaches 40-43 cm, weight up to 1.5 kg.