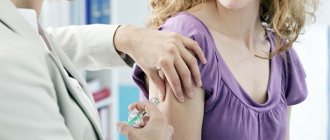
The behavior of animals is often unpredictable, and careless interaction with them can result in bites. Most often, victims consult a doctor with dog bites. In most cases, the culprits of the incident are other people's dogs, but pets often get their teeth into their owner.
According to statistics, dog bites account for more than 90% of all animal bites. According to unofficial data, in Moscow alone, about 35 thousand people suffer from dog bites every year. It is very important to remember about infection prevention and to get tetanus and rabies vaccinations if you are bitten.
1 Dog bite. First aid
2 Dog bite. First aid
3 Dog bite. First aid
Ancient evil
Those who like to walk around Elk Island will notice that there are leaflets posted on the trees along the sides of trails and paths. They urge the population to be vigilant and careful: if you are attacked by stray dogs, you must immediately get vaccinated against rabies. Fortunately, few stray dogs have been spotted in Losiny Ostrov this year. But the danger should not be downplayed. Rabies is still deadly. According to WHO, up to 50 thousand people die from it every year.
This disease has been known since ancient times. In ancient Greece there was even a god of rabies named Aristax, and only Artemis had the gift of curing this terrible disease. The ancient Roman physician Celsus described extensive observations of cases of the disease and proposed preventive measures - washing wounds and cauterization. The latter method was considered the most effective until Louis Pasteur found another way to combat rabies - vaccination.
Pasteur already found out that this disease is caused by a virus. Now scientists count up to a dozen of its varieties, which differ in virulence (infectiousness). The virus is transmitted in saliva when bitten by a sick animal. The likelihood of infection depends on the circumstances (for example, if a rabid animal bites a person through clothing or if the bite causes severe bleeding, the likelihood of infection will be less). The location of the bite also matters - the most dangerous are the head, hands, and genitals - the places richest in nerve endings. First, the virus multiplies in muscle tissue, then enters nerve fibers, along which it spreads at a speed of about 3 mm/h. Eventually it reaches the salivary glands and the brain.
Calm Islands
Rabies occurs in more than 150 countries and territories, on every continent except Antarctica. However, it is not present in the island countries - Great Britain, Malta, New Zealand, Japan - due to strict quarantine measures for imported animals. There is a natural type of rabies, the foci of which are formed by wild animals (wolf, fox, raccoon dog, jackal, arctic fox, skunk, mongoose, bats), and an urban type of rabies (dogs, cats, farm animals). Pets become infected with rabies after contact with sick wild animals. In the vast majority of human deaths from rabies, the source of infection is dogs. In Europe, the natural reservoirs of rabies are foxes and arctic foxes (in the north). In many areas of the United States and Canada, rabies is common among skunks, raccoons, foxes and jackals. Many species of bats are infected with the viral disease in Australia, Africa, Central and Southeast Asia and the Americas. In Sri Lanka, rabies is endemic among martens.
Features of vaccination
Since treatment of rabies at the stage when symptoms appear is no longer effective, to prevent the spread of the virus, prevention of the disease is required by administering a special vaccine.
Rabies vaccinations are prescribed to humans in the following cases:
- if he was injured by objects on which there was saliva of an infected person;
- if he was attacked by an obviously unhealthy animal and received open injuries to the skin;
- if he has been bitten by wild rodents;
- if he was exposed to the saliva of a patient with a pathology such as rabies, a person, and in other cases when the saliva of the alleged carrier could get into an open wound;
- if he has scratches on his body resulting from contact with an animal, which died soon after they were inflicted for an unknown reason.
Rabies vaccinations are prescribed immediately, at regular intervals. They are carried out both on an outpatient and inpatient basis - depending on the patient’s wishes and the severity of the bites.
It should be remembered that vaccination can cause side effects, such as redness of the injection site, increased body temperature, dyspeptic disorders, and general condition. There are special instructions regarding rabies vaccination and alcohol intake - to prevent the development of post-vaccination complications, people are prohibited from drinking alcohol during the vaccination period and six months after it.
Deadly result
A person bitten by an animal can feel safe for a long time. Cases have been described where about a year passed from infection to illness, but most often this period is 1–3 months. The disease begins with the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the bite area (burning, nagging pain, itching, goosebumps), although the wound may already be completely healed. The reason is the multiplication of the virus in the spinal ganglia that innervate the bite area. Bites to the face usually cause olfactory and visual hallucinations. General symptoms - fever, headache, malaise - are accompanied by mental disorders. Apathy and depression are replaced by anxiety, pulse and breathing quicken, and a feeling of tightness in the chest arises.
Article on the topic
Prevention of rabies. What to do if you are bitten by a dog? This period lasts about four days, then specific encephalitis develops. The patient exhibits violence, aggressiveness, muscle spasms, epileptic seizures and paralysis are observed. Bright light, loud sound, touch and even a light breath can provoke an attack in the form of paroxysms of rage, between which consciousness clears up. Symptoms of encephalitis are soon joined by signs of impaired brainstem function, including impaired swallowing (dysphagia). Drooling combined with dysphagia leads to foaming at the mouth. But the most striking clinical symptom of rabies is hydrophobia (hydrophobia): when trying to drink, painful involuntary contractions of the swallowing muscles, diaphragm and auxiliary respiratory muscles occur.
When convulsions and attacks of hydrophobia stop, those around them mistake this condition for an improvement in the patient’s condition. But in reality it is a sign of imminent death. It occurs after 12–20 hours from paralysis of the heart or respiratory center. The total duration of the disease is 5–8 days, rarely slightly longer.
Etiology
The causative agent of this disease is a large single-stranded RNA virus from the genus Lyssavirus (translated from Greek Lyssa - “rabies”). It has a bullet shape (in some sources it is referred to as rod-shaped). The virus has a glycoprotein shell and a helical ribonucleocapsid with small protrusions on the surface.
For a long time, there was an opinion that this form is the only possible one and that all strains of the virus have the same antigen. Currently, there is an assumption that there are 5 more antigenic variations (African viruses), their exact significance in epidemiology has not yet been established. The virus is classified as neurotropic in its biological properties. When introduced into the body, it induces the release of virus-neutralizing antibodies due to the internal nucleoprotein.
An infected animal releases a huge amount of virus along with the secretion of the salivary glands. In it, the virus is able to maintain its virulence for a day. High resistance in the external environment is not typical for this pathogen. The best preservative for it is low temperatures down to minus 200C. The rotting process inactivates the virus in the corpse within 2 weeks. Conventional disinfectants are suitable for inactivation. A temperature of 1000C instantly leads to the death of the virus.
Delay is like death
If you become the target of an attack by any animal: cats, dogs, foxes, etc., you need to take immediate action. The first step is to immediately wash the bite site with laundry soap. The procedure should be long, at least 10 minutes, and as intense as possible. It is recommended to wash deep wounds with a stream of soapy water using a syringe or catheter. Cauterization of the wound and suturing it are strictly not recommended. Suturing is indicated exclusively for large wounds, to stop threatening bleeding and for cosmetic reasons (skin sutures on facial wounds). You will have to go between Scylla and Charybdis - the risk of great blood loss and the danger of infection. After washing, you need to treat the wound with medical alcohol or iodine. And - immediately to the emergency room.
The emergency room will require a description of the animal, the circumstances of the bite, information about the presence of a collar, so if possible, you need to carefully examine the bitten animal.
If the animal is killed, its corpse must be taken to a virology laboratory, where the presence of the rabies virus can be quickly detected using the immunofluorescent method. If an animal is captured, it should be observed without killing it. It is believed that the animal was not rabid at the time of the bite if it did not die after 10 days.
Article on the topic
4 myths about rabies: an animal can behave normally - but be infectious In case of saliva falling on intact and damaged skin, in case of single superficial bites or scratches of the torso, upper and lower extremities (except for the hand, fingers and genitals), treatment is not prescribed. But only if the animal is healthy at the time of the bite and for 10 days of observation. If within 10 days it gets sick, dies or disappears, then treatment should begin with the appearance of the first signs of illness or disappearance of the animal: 1 ml rabies vaccine on the 0, 3, 7, 14, 30, 90th day. If the animal is suspected of rabies at the time of the bite, was sick with rabies and ran away, was killed, or the diagnosis is unknown, then treatment begins immediately: 1 ml vaccine according to the same regimen. Pregnancy and infancy are under no circumstances contraindications for emergency immunization.
When saliva falls on the mucous membranes; any bites or injuries to the head, face, neck, hand, fingers, upper and lower extremities, genitals; with multiple bites and extensive damage to any location; For single deep bites and scratches, the vaccination schedule remains the same. But the treatment also includes anti-rabies immunoglobulin, which is injected around the bite site. Doses and immunization schedules are the same for children and adults. If the patient is taking corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, the effectiveness of vaccine therapy may be reduced. In these cases, an additional course of treatment will be required (after determining the level of antibodies in the blood). For preventive purposes, laboratory workers working with the rabies virus, veterinarians, hunters, foresters, dog catchers, slaughterhouse workers, and taxidermists are immunized.
The effectiveness of specific treatment is directly dependent on how quickly after the bite it was started. If on the first day, then you can hope for success in most cases. According to the chief researcher of the State Research Institute for Standardization and Control of Medical Biological Preparations named after. L.A. Tarasevich Nikolai Medunitsyn, in the absence of accurate data on the mechanism of development of the infection, it is still believed that as long as the virus has not entered the cells of the nervous system, treatment will be successful. A study of more than 3,000 cases did not provide information on the duration of the existence of antibodies to the rabies virus in the blood of people, so if a second bite occurs more than a year after vaccination, treatment should be carried out as usual.
Diagnosis of rabies
This diagnosis can be made when symptoms of the disease appear after an animal bite. Rabies is confirmed by examining a skin sample taken from the back of the head and isolating the virus from tear, cerebrospinal fluid, and saliva.
Laboratory tests required to diagnose rabies:
- general blood test (excluding ESR and leukocyte formula);
- general urine analysis;
- a blood test to determine antibodies to the rabies pathogen;
- Determination of the causative agent of rabies through examination of tissues and biological fluids of the body:
— examination of fragments of skin tissue on the back of the head, cornea imprints;
— study of the genetic material of the virus using PCR;
- examination of brain tissue using electron microscopy.
Other research methods used to diagnose rabies:
- EEG or electroencephalography is a method that allows you to evaluate the electrical potentials of the brain.
The path to salvation
According to Rospotrebnadzor, every year in Russia from 250 to 450 thousand people who have suffered from animal bites receive anti-rabies treatment, about a quarter of whom are children. The following rabies vaccines are used in our country: Rabivak-Vnukovo-32 Culture-inactivated rabies vaccine for human immunization (FSUE NPO Microgen of the Russian Ministry of Health); KOKAV Anti-rabies vaccine, cultured, concentrated, purified, inactivated (FSUE NPO Microgen, Ministry of Health of Russia); Rabies vaccine culture concentrated purified inactivated dry (Enterprise for the production of bacterial and viral preparations of the M.P. Chumakov Institute of Poliomyelitis and Viral Encephalitis of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Federal State Unitary Enterprise). Rabipur is also registered in Russia (Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics GmbH and Co.KG, Germany). The total market capacity of the Russian Federation (treatment + prevention) is in the range of 1.8–3 million doses.
In accordance with WHO recommendations, the immunological activity of the domestic non-concentrated vaccine (CAV) is at least 0.5 IU/ml, and the concentrated COCAV vaccine is at least 2.5 IU/ml. According to Rina Timerbaeva, deputy director for production and technology of the branch of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise NPO Microgen of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Immunopreparat (Ufa), the use of COCAV made it possible to reduce the number of injections (up to 6 times) and administration doses (from 5 ml in 2 places to 2 .5 ml to 1 ml per injection). This significantly reduces the antigen load, reduces adverse reactions and post-vaccination complications. The local reaction is characterized by slight swelling, redness, itching, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. The general reaction can manifest itself in the form of malaise, headache, and weakness. In very rare cases, the possibility of neurological symptoms is expected. In this case, the victim should be urgently hospitalized so as not to miss the development of encephalitis.
“Post-vaccination complications are caused, first of all, not by the insufficient quality of the domestic drug, but by the intensity of the immune response, individual characteristics and reactivity of the vaccinee,” Rina Timerbaeva is sure. Therefore, when carrying out urgent rabies prophylaxis, it is worth abandoning the search for imported vaccines, since delay can cost lives. For preventive immunization, it is possible to use an imported vaccine if there is time and money to find it.
Article on the topic
World Rabies Day. What to do if you are bitten by an animal? When summarizing observations of vaccinated people (1,708 cases), an amazing pattern emerged: vaccination with the Fermi rabies vaccine stimulates the immune system, as evidenced by a sharp decrease in the number of cases of bronchial asthma, gastric ulcers, collagenosis, herpetic lesions and periodontal disease, while influenza and ARVI were milder.
Anti-rabies immunoglobulins, which are the second component of urgent rabies prevention, are divided into homologous, obtained from human donor blood, and heterologous, obtained from the immune blood of horses. The negative side of all heterologous AIH is the risk of developing allergic complications. After the administration of rabies immunoglobulin, anaphylactic shock and a local allergic reaction may occur, since it is produced on the basis of horse protein. Its administration is recommended in a hospital setting. The homologous drug "Imogam Raj" produced in France is registered in some CIS countries. However, it is almost inaccessible due to its high cost and small production volume, which are caused by the objective difficulties of immunizing volunteers and the insufficient raw material base. There are no plans to produce homologous AIG in Russia in the near future.
Experts emphasize that rabies remains a real and formidable danger. According to the Ministry of Health, of those who died from hydrophobia in 2008–2011, 40 people (70.2%) did not seek medical help and, accordingly, did not receive timely anti-rabies treatment; 10 people (17.5%), having sought medical help on time, refused anti-rabies treatment. In one case, after dangerously localized bites inflicted by a wolf, rabies immunoglobulin was not prescribed, which contributed to the development of the disease.
“Despite the apparent simplicity of specific anti-rabies treatment, quite often there are serious violations in the prescription and implementation of a course of anti-rabies treatment, associated primarily with unsatisfactory knowledge of the instructions for using the drugs,” says Rina Timerbaeva. Only active educational work among the population, as well as improving the qualifications of medical workers, can reduce mortality.
Figures and facts
The average annual number of rabies cases in animals is highest in Europe and South America and lowest in Africa, while the incidence rate in humans is highest in Asia and lowest in North America. Rabies kills more than 55,000 people each year, mostly in Asia and Africa. At the same time, more than 15 million people in the world receive vaccination to prevent the development of the disease. This prevents hundreds of thousands of deaths from rabies each year. In the first quarter of 2013, animal rabies was detected in 37 constituent entities of the Russian Federation, including Moscow and the Moscow region. Traditionally, St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region remain rabies-free. The sad leaders are Belgorod region (79 cases in animals), Saratov region (64 cases), Moscow region (40), Voronezh region (37) and Tambov region (36). Two people fell ill (and died) in the Kursk and Vladimir regions.