General principles of inheritance of characters.
Simply put, every trait in the body (hair color, eye color, blood type, Rh factor) is encoded by two genes.
In reality, the number of genes that determine the trait is much greater. For each trait, the child receives one gene from the mother, another from the father. In genetics, dominant and recessive genes are distinguished. The dominant gene is designated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet, and in its presence the recessive gene, as a rule, does not manifest its properties. A recessive gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet. If for some trait an organism contains two identical genes (two recessive or two dominant), then it is called homozygous for this trait. If an organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested. For example: A is a dominant gene that determines brown eye color and A is a recessive gene that determines blue eye color
Possible genotype options: AA - homozygote, brown eyes Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes aa - homozygote, blue eyes
Example 1:
wife AA - homozygous, brown eyes, both genes are dominant; husband AA - homozygous, blue eyes, both genes are recessive
When germ cells (egg and sperm) are formed, one gene goes into each germ cell (gamete), i.e. in this case, the female body forms two gametes containing one dominant gene each, and the male body forms two gametes containing one recessive gene each. When germ cells merge, the embryo receives one maternal and one paternal gene for this trait.
wife AA + husband aa Gametes: A A a a Child: Aa Aa Aa Aa
Thus, in this situation, 100% of the children will have brown eyes and be heterozygotes for this trait.
Example 2:
wife Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes husband Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes wife Aa + husband Aa gametes: A a A a child: AA, Aa, Aa, aa
In this case, the probability of having children with brown eyes (homozygotes) is 25%, heterozygotes are 50% with brown eyes, and blue eyes (homozygotes) are 25%.
Example 3:
wife Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes husband aa - homozygote, blue eyes Wife Aa + husband aa Gametes: A a a a Child: Aa, Aa, aa, aa
In this case, 50% of children have brown eyes and are heterozygotes and 50% have blue eyes (homozygotes)
How to determine the Rh factor
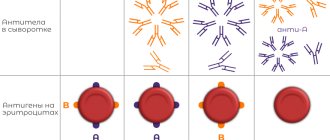
Blood is a biological fluid that contains a huge amount of antibodies and carries genetic information. The Rh factor is a special agglutinogen protein that is part of the blood. There is a distinction between Rh positive and Rh negative. The latter is detected in 15% of people in the world and means the absence of protein in the blood. In medicine, there is the ABO system, which is used to detect antibodies in human blood. The Rh factor is determined by one of the most significant antigens, D. If it is absent in the blood, then the Rh factor is negative. Today in medicine, this research in the laboratory is carried out very quickly and accurately. If, for example, blood containing this protein is transfused to a person who does not have it, then the formation of specific antibodies begins in the blood, which leads to the appearance of disorders called Rh conflict. Repeated injection of blood with incompatible Rhesus promotes agglutination of red blood cells and contributes to the occurrence of severe complications. That is why during transfusion, only blood with the same Rh factor is used.
Patterns of inheritance of blood group and Rh factor.
Inheritance of blood type is controlled by an autosomal gene. The locus of this gene is designated by the letter I, and its three alleles by the letters A, B and 0. Alleles A and B are equally dominant, and allele 0 is recessive to both of them. There are four blood types. The following genotypes correspond to them: First (I) 00 Second (II) AA; A0 Third (III) BB; B0 Fourth (IV) AB
Example 1:
wife has the first blood group (00) husband has the second blood group and is homozygous (AA) wife 00 + husband AA gametes: 0 0 A A child: A0 A0 A0 A0
All children have a second blood group and are heterozygotes for this trait.
Example 2:
wife has the first blood group (00) husband has the second blood group and is a heterozygote (A0) wife 00 + husband A0 gametes: 0 0 A 0 child: A0 A0 00 00
In a given family, in 50% of cases it is possible to have a child with a second blood group, and in 50% of cases the child’s blood type will be first.
Inheritance of the Rh factor is encoded by three pairs of genes and occurs independently of the inheritance of blood type. The most significant gene is designated by the Latin letter D. It can be dominant - D, or recessive - d. The genotype of a Rh-positive person can be homozygous - DD, or heterozygous - Dd. The genotype of a Rh negative person may be dd.
Example 1:
wife has a negative Rh factor (dd) husband has a positive Rh factor and is a heterozygote (Dd) wife dd + husband Dd gametes: dd D d child: Dd Dd dd dd
In a given family, the probability of having a Rh-positive child is 50% and the probability of having a Rh-negative child is also 50%.
Example 2:
wife has a negative Rh factor (dd) husband has a positive Rh factor and is homozygous for this trait (DD) wife dd + husband DD gametes: dd DD child: Dd Dd Dd Dd
In this family, the probability of having a Rh-positive child is 100%.
Analyze it!
In what situations is it necessary to determine the Rh factor of blood? And in case of emergency, do you need to carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have?
Evgeniya, Voronezh region.
– Such an analysis must be done before planned surgery, blood transfusion and during pregnancy planning.
But it makes no sense to constantly carry with you a reminder about what kind of blood you have. According to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which is valid in all medical institutions in our country, before each blood transfusion, each person entering the hospital must have their blood type and Rh factor rechecked, since there is no guarantee that they were determined correctly.
Features of the course of pregnancy with Rh factor incompatibility. Rhesus conflict.
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn is a condition that occurs as a result of incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus for certain antigens. Most often, hemolytic disease of the newborn develops due to Rh conflict. In this case, the pregnant woman has Rh-negative blood, and the fetus has Rh-positive blood. During pregnancy, the Rh factor with the red blood cells of the Rh-positive fetus enters the blood of the Rh-negative mother and causes the formation of antibodies to the Rh factor in her blood (harmless to her, but causing the destruction of the fetal red blood cells). The breakdown of red blood cells leads to damage to the liver, kidneys, brain of the fetus, and the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. In most cases, the disease develops quickly after birth, which is facilitated by the entry of a large number of antibodies into the baby’s blood when the integrity of the placental vessels is disrupted.
Less commonly, hemolytic disease of the newborn is caused by group incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus (according to the AB0 system). In this case, due to agglutinogen (A or B), present in the fetal red blood cells but absent in the mother, antibodies to the fetal red blood cells are formed in the maternal blood. Most often, immune incompatibility manifests itself when the mother has blood group I, and the fetus has blood group II, and less often, blood group III.
The process of immunization of a pregnant woman begins with the formation of antigens in the red blood cells of the fetus. Since antigens of the Rh system are contained in the blood of the fetus from the 9-10th week of pregnancy, and group antigens - from the 5-6th week, in some cases early sensitization of the mother’s body is possible. The penetration of antigens into the maternal bloodstream is facilitated by infectious factors that increase the permeability of the placenta, minor injuries, hemorrhages and other damage to the placenta. As a rule, the first pregnancy in an Rh-negative woman, in the absence of previous sensitization of the body, proceeds without complications. Sensitization of the body of a Rh-negative woman is possible through transfusions of incompatible blood (carried out even in early childhood), during pregnancy and childbirth (if the fetus has Rh-positive blood), after abortions, miscarriages, and operations for ectopic pregnancy. According to the literature, after the first pregnancy, immunization occurs in 10% of women. If a woman with Rh-negative blood avoided Rh immunization after her first pregnancy, then during a subsequent pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus, the probability of immunization again is 10%. Therefore, after any termination of pregnancy in a woman with Rh-negative blood, it is necessary to administer anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin for prophylactic purposes. During pregnancy, in a woman with Rh-negative blood, it is necessary to determine the titer of Rh antibodies in the blood over time.
What is Rh negative?
Human blood consists of cells: red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets. There is a protein on the surface of red blood cells, which is also an antigen - this is Rhesus. But it may not exist. Cells that have protein on their surface are positive, and those that do not are negative.
80-85% of the world's population lives with positive Rhesus, which greatly simplifies their lives. Because if blood transfusion is needed, it will always be available in treatment centers. People with negative blood should be more prudent about their health, because there are only 15% of them in the world. Moreover, there is a frightening feature of patients with negative indicators. When transfusion of positive blood occurs, the body may attack an unknown protein. This will lead to death or serious complications. Also, pregnant women should be especially careful. Girls who carry a fetus with the opposite rhesus sign expose themselves and the child to mortal danger. Due to the body’s incorrect reaction to a fetus with different indicators. It is very important to register and undergo regular consultations with doctors.
By reporting accurate information about their blood in emergency situations, people with negative Rhesus have a chance to survive or carry a child to term. Not knowing can lead to death for the patient if the laboratory does not have time to conduct analysis in critical situations. We urge you to plan your pregnancy, be vigilant in extreme life situations and notify relatives about negative Rh.
Question 2:
I have a negative Rh factor. I recently had an abortion. Will I be able to have children? Is there a chance that the baby will be sick during the next pregnancy?
Answer
: The presence of a negative Rh factor does not directly affect conception. During an abortion (if it was performed at 9-10 weeks of pregnancy), there was a possibility of sensitization of the body to the Rh factor. Before a planned pregnancy, it is advisable to do a blood test for the presence of antibodies to the Rh factor.
Incredible? Obvious!
My child has negative Rh blood factor, while my husband and I have positive blood. My husband still teases me about this: they say, from whom did she cheat? I know that nothing happened. But the question haunts me: how could this happen? After all, a child will definitely inherit the blood of his parents. Is not it?
Olga, Kostroma
- No not like this. There is nothing supernatural in your situation. It is explained by the fact that a person with a positive Rh factor may be a carrier of a negative Rh gene, which is suppressed by a stronger positive gene.
But when this negative gene is present in the blood of both parents, then, doubling its strength, it can be passed on to the child and form a Rhesus with a minus sign. According to statistics, for Rh-positive parents this situation is possible in 25% of cases.
Question 3:
What dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin and in what time frame is administered to a woman with Rh-negative blood after childbirth? Is it true that the administered dose of the drug should be increased after a caesarean section?
Answer
: Women with Rh-negative blood after childbirth are given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin in an amount of 1-1.5 ml (200-300 µg) no later than 24-48 hours after birth for prophylactic purposes. During surgical interventions, transplacental bleeding may increase, and therefore the administered dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is increased by 1.5 times.
Rhesus conflict. Prevention
Laboratory control of Rh immunization is carried out by determining Rh antibodies in the blood of a pregnant woman:
- If both the father and mother have Rh negative blood, it is not advisable to determine antibodies during pregnancy; — If the Rh-negative genotype of the fetus is determined based on the results of a non-invasive test, antibody determination is not carried out; — Rhesus immunization is determined when the antibody titer is 1:4 or more; — There is a risk to the fetus when the antibody titer is 1:16 or more; — Determination of antibodies is carried out upon registration, at 18-19 and 28 weeks, with the appearance and increase in titer - the frequency of studies increases. ⠀
Prevention of Rh immunization in Rh negative women
1) Administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin 2) Preservation of the first and subsequent pregnancies, the woman should avoid abortion.
Anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin (antibody) protects against the immune reaction without having a negative effect on the fetus and newborn.
Application schemes
— A dose of 300 mcg is administered intramuscularly at 28 weeks of pregnancy (provided there are no antibodies in the blood) — If prophylaxis is not carried out at 28 weeks, it is carried out as soon as possible — Additional prophylaxis 125 mcg (I trimester) or 300 mcg (II, III trimester ) after invasive procedures during pregnancy (amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, cordocentesis, cervical suturing, embryo reduction), after abdominal trauma and after the appearance of bleeding
What else is worth knowing
- Prevention is also carried out in case of unsuccessful completion of pregnancy - instrumental or medical abortion, spontaneous miscarriage and intrauterine fetal death - After birth, the Rh factor of the child is determined and in the case of positive blood - the woman is administered 300 μl of immunoglobulin, no later than 72 hours after birth, with negative blood - prophylaxis is not carried out - The dose of immunoglobulin is increased in case of placental abruption, during cesarean section, during manual examination of the postpartum uterus - If for some reason prophylaxis after childbirth is not carried out, it is possible to administer immunoglobulin up to 10 days of the postpartum period.
Prevention is carried out to prevent immunization in the future, when carrying subsequent children.
Blood transfusion: who can be a donor and who can be a recipient?
According to WHO [Official Source], more than 118.5 million blood transfusions are performed worldwide every year. They are carried out in connection with complex injuries accompanied by blood loss, cardiovascular operations, during difficult childbirth, transplant operations and other circumstances.
A healthy person (18 - 60 years old) can become a blood donor. It is allowed to donate blood no more than once every 3 months, no more than 400 ml.
Of course, it is better to transfuse blood of an identical group and Rh factor, but if it is not available, then you can use the following rules [Verified source]:
- I (O) group is poured into all groups. People with this group are universal donors , but they can only be transfused with blood of group II.
- Group II (A) should be used for transfusion to owners of blood groups II and IV. However, she can only take I and II. The group is the most common.
- III (B) group is a donor for groups III and IV, although I and III can accept.
- People with group IV (AB) are universal recipients, but are donors only for group IV.
In addition to the above-mentioned transfusion laws, you need to remember that donor blood must undergo mandatory testing for HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, and coronavirus.
How does blood type affect character?
In the twentieth century, Japanese scientists became interested in the influence of blood type on a person’s character. They conducted several studies, putting forward the theory of "ketsu-eki-gata", which analyzes the influence of blood type on the behavior of an individual.
The main conclusions of this theory:
- According to “ketsu-eki-gata”, representatives of group I are: serious, creative, reserved, patient, responsible, but stubborn and tense.
- People with blood type II are passionate, creative, strong, have an active character, but are selfish and irresponsible.
- III (B) group is found in controlled, rational, indecisive and forgetful individuals.
- IV (AB) blood group promotes the manifestation of confidence, well-developed intuition and strong-willed qualities, but sometimes its representatives are selfish and unpredictable.
"Ketsu-eki-gata" is very popular in Japan, but there is no scientific evidence that character type is related to blood type.
Finally, a little disclosure.
Genetic features of the Rh factor and diagnostic capabilities
As part of the Rhesus blood group Rh factor), C, c, E and e. The proteins that form these antigens are encoded by 2 genes: RHD (D antigen ) and RHCE (antigens C, c, E and e). These genes and the proteins they produce are very similar. This similarity complicates genotyping for these genes. The fact is that to assess the risk of developing a Rh conflict, you need to know the probability of an Rh+ embryo in each couple planning a pregnancy. To calculate this probability, it is necessary to establish the genotype of the father and mother for the RHD gene.
Women with a negative Rh factor are primarily at risk . If the partner also has an Rh-negative status, then the pregnancy will definitely proceed without the development of an Rh conflict and such a couple will not need additional examinations. Women with a negative Rh factor are primarily at risk . If the partner also has an Rh-negative status, then the pregnancy will definitely proceed without the development of an Rh conflict and such a couple will not need additional examinations.
If the father is homozygous, that is, both homologous chromosomes carry a full-fledged RHD gene, then the probability of obtaining an Rh+ embryo in such a pair is 100%, since for a positive Rh factor you need at least one chromosome with this gene, which will definitely come from a homozygous Rh+ father . In this case, the geneticist will not be able to offer anything as a way to prevent Rh conflict and the couple should consult a doctor managing the pregnancy. The doctor will draw up an individual plan for the prevention of Rh conflict.
If a man does not have the RHD , then there is a 50% chance that among the embryos there will be Rh negative ones, with which the pregnancy will proceed without complications from the Rh factor.
However, the high similarity in the sequences of the RHD and RhCE genes complicates not only the diagnosis of these genes and the Rhesus blood group, but also the assessment of the risks of developing a Rhesus conflict. Other mammals have only one gene, which is more similar to human RhCE. Presumably, in humans, the RHD gene appeared as a duplicate of RhCE and changed slightly over time, finding its function in the body. Thus, one of the main features of the genetic diagnosis of the Rh factor is the analysis of several loci of this gene. The fact is that due to the similarity of genes, analysis of one locus with a high probability for a diagnostic test can give a false positive answer, that is, instead of a heterozygote for deletion of the RHD gene, we will see a homozygote with two copies of RHD due to the fact that a false contribution will be made to the analysis RhCE gene. For accurate diagnosis, our laboratory uses the modern MLPA , based on the analysis of a large number of points in these genes at once, which allows not only to accurately diagnose the absence/presence of the RHD gene, but also to identify its other features, which we will discuss further in the next article on our website. Using this method, it is possible to genotype future parents with high accuracy and carry out invasive prenatal diagnostics during natural pregnancy in order to begin timely preventive measures to eliminate the development of Rh conflict.
For preimplantation embryo diagnosis (PGD), we perform the analysis in two different ways for even greater confidence. First of all, using a test system developed in our laboratory for direct mutation analysis : we genotype precisely the presence/absence of the RHD gene deletion. However, PGD uses a very small amount of biomaterial, which can lead to false results, so the results of direct mutation analysis in our laboratory are always complemented by linkage group testing. The fact is that in the human genome there are such sequences, short repeats of nucleotides, the length of which is very different from person to person. Therefore, if you find out the length of several such repeats in one person, with a high probability it will be possible to distinguish him from all other people on Earth by the set of lengths of these sections. Moreover, by the lengths of these sections we can distinguish not only people, but also homologous chromosomes of one person. Therefore, we select such variable regions that are closest to the gene in order to avoid the effects of recombination, find out the lengths of these regions from the parents and obtain four sets of lengths that describe each of the four parental chromosomes - two from mother’s and two from father’s. This is a characteristic of each chromosome. At the same time, we clarify which of the paternal chromosomes the RhD gene, which is dangerous for the pregnancy of a Rh-negative woman, is located on. Indirect diagnosis consists of looking at which chromosomes the embryo received from its parents and calculating whether it received the paternal chromosome on which the gene we do not need is located or not. Accordingly, if a woman is Rh negative, and her partner is a heterozygous Rh positive carrier of the RHD gene, then to prevent Rh conflict we select embryos that do not have the RHD gene on any of the chromosomes. Double checking of the result with two independent test systems based on different principles allows you to obtain a highly accurate, reliable result even on small quantities of biomaterial that you have to work with as part of PGD.
We will talk about rare variants of the RHD gene and the accuracy of biochemical and genetic analysis of Rh factor status, as well as how to protect yourself and your family in such cases in the next article on our website.
Previous article on the topic: Rh factor and pregnancy
Next article on the topic: Unusual variants of the RHD gene and what is their danger during pregnancy
Author: Zhikrivetskaya Svetlana
research biologist