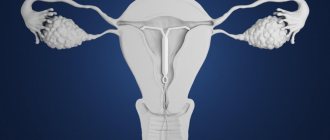
Intrauterine device (IUD) - This is a method of contraception, which consists in the fact that a special device is inserted into the uterine cavity to prevent fertilization of the egg and the attachment of the fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus.
IUDs are divided into two large groups: hormonal and non-hormonal. Non-hormonal ones can be made of polyethylene materials or copper, the latter may also contain silver or gold. Also, IUDs vary in shape, but most often they install “T”-shaped spirals, as they hold better. The installation of hormonal IUDs (for example, Mirena) may be prescribed both for contraception and for the treatment of certain diseases.
Dimensions of the IUD: length from 25 to 35 mm, thickness of the spiral itself from 1 to 2 mm.
Spirals are light in weight, from 100 to 150 mg.
The principle of operation of intrauterine devices.
Basically, the effect of the IUD is due to a mechanical obstacle to the passage of sperm.
In addition, under the influence of the hormonal IUD (Mirena), cervical mucus thickens and ovulation is suppressed. In some cases, fertilization still occurs, BUT in this case, the IUD prevents implantation.
The hormonal IUD can be used not only for contraception, but also for therapeutic purposes, for example, for endometriosis.
With the use of a hormonal IUD, menstruation becomes less abundant and may subsequently disappear completely. This is an expected reaction of the endometrium, and not a side effect. After the IUD is removed, the cycle is restored.
Classification
There are 2 groups of spirals:
- hormonal;
- non-hormonal.
Both perform the same task - protection from unwanted pregnancy. But some of them have additional properties. For example, hormonal IUDs are often used in gynecological practice as a way to treat certain diseases, and non-hormonal IUDs with the addition of silver or gold have a bactericidal effect and protect the female reproductive system from unwanted infections.
There are 3 generations of spirals:
1st generation
- An IUD without any metal or hormone, consisting only of medical grade plastic.
- Their contraceptive effect is achieved only through the mechanical impossibility of attaching the fertilized egg to the endometrium.
- Often cause complications (infectious diseases, ectopic pregnancy and prolapse of the IUD - expulsion).
1st generation IUDs are no longer used because more reliable and effective IUDs exist.
2nd generation
- IUDs containing metal. That is, these are spirals that also consist of medical plastic, but have a contraceptive effect due to additional components - copper, silver, gold.
- Metals act not only on the female body, but also on the male factor - sperm, and thereby reduce the risk of unplanned pregnancy.
3rd generation
- Hormonal IUDs, which at this stage are used as therapeutic and contraceptive agents.
Intrauterine devices have different shapes:
- T-shaped;
- round or semicircular;
- in the form of an umbrella;
- horseshoe-shaped (semi-oval).
Each spiral has its own advantages and disadvantages and is selected individually depending on the characteristics of a particular woman’s body.
All IUDs have the same operating principle – protection against unwanted pregnancy.
When is an IUD installed?
With a regular menstrual cycle, a copper-containing IUD is installed in the first 12 days after the start of menstrual bleeding, and a hormonal IUD in the first 7 days. In the case of a hormonal IUD, the contraceptive effect occurs 7 days after installation, so during these days it is necessary to use an additional method of contraception. After installing a copper-containing IUD, you can have open sex life from the moment of installation.
If the menstrual cycle is irregular, an IUD can be installed on any day, provided that the woman is definitely not pregnant! The IUD can be used during breastfeeding (4 or more weeks after birth).
Indications for use and benefits
The Mirena system can be used in the following cases:
- for the treatment of abnormal menstrual bleeding;
- to protect against unplanned pregnancy;
- treatment of female diseases such as adenomyosis, endometriosis, uterine fibroids.
The main advantages of its use include:
- an effective and reliable method of contraception;
- ease of use, lack of discomfort;
- does not have systemic hormonal effects;
- reduces blood loss during menstruation;
- reduces the likelihood of inflammatory pelvic diseases;
- insertion and removal of the coil does not cause pain or discomfort.
In terms of effectiveness, the use of this type of contraception can be compared to sterilization. Much more effective than other methods of protection against unplanned pregnancy (pills, condoms). There is only 1 case of unwanted pregnancy per thousand women. Women who experience excessive blood loss during menstruation cease to suffer, and the amount of discharge noticeably decreases after a couple of months. Some girls may not have periods at all.
How is an IUD installed?
Before installing an IUD, you must undergo the following examinations:
1. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and ultrasound of the breast
2. Tests for STIs
3. PAP TEST
The installation process itself takes about 20 minutes and takes place on the gynecological chair during the examination. The IUD is inserted into the uterine cavity, leaving control antennae in the vagina (for which the IUD is later removed). They will not cause you discomfort, BUT you need to be more careful when using tampons and removing them, since as a result of lightly tugging on the mustache, the spiral may shift and there will be no contraceptive effect.
The IUD can also be used by nulliparous girls, but there is a risk of the IUD falling out, since the uterus of nulliparous women is smaller.
Important
Do not forget that the intrauterine device is still a foreign body for the body. Therefore, when using it, women should be attentive to their sensations. You should immediately contact a gynecologist in the following cases:
- you have ceased to feel the tendrils of the spiral;
- your antennae feel longer;
- you feel the presence of a spiral;
- you felt the spiral fall out.
IMPORTANT!
Only a gynecologist can insert and remove an intrauterine device.
Advantages of contraception using the IUD.
- Long-term contraception: IUD is effective for 5 years
- Reliable method of contraception
- There is no need to monitor the regularity of taking pills, or the position of the patch or vaginal ring
- There are not as many side effects as when taking CHCs, including the IUD does not affect libido and does not increase the risk of thrombosis
- The hormonal IUD has a therapeutic effect in some gynecological pathologies (endometriosis, heavy menstruation, recurrent endometrial polyps)
- The IUD can be used during breastfeeding
- Quite an economical method of contraception
Features of intrauterine contraception
The mechanism of operation of the intrauterine device depends on its constituent components. The contraceptive effect of copper-containing IUDs is achieved as follows:
- metal ions released by the IUD inhibit the activity of eggs and sperm;
- the viscosity of cervical mucus increases, this becomes an obstacle to sperm entering the uterus;
- The intrauterine contraceptive enhances the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, which makes it impossible for the implantation of the egg even after its fertilization.
Hormonal types of IUDs are better than metal-containing models, because... additionally protect against pregnancy due to the thinning of the endometrium in the uterine cavity. Microdoses of the hormone secreted by the contraceptive inhibit the proliferation of mucosal tissue, which is why the egg cannot reliably attach to the uterine wall.
Disadvantages of using an intrauterine device.
- After installing the IUD, pain in the lower abdomen may persist for some time, 1-3 months. During this period, NSAIDs can be used.
- With a copper-containing IUD, menstruation may become more profuse, so much so that the IUD has to be removed.
- There is a risk of the spiral falling out or dislodging; this usually occurs within the first 3 months after installation. Therefore, if you feel that the IUD has fallen out or has shifted, consult a doctor immediately!
- Intermenstrual bleeding often appears, which causes inconvenience, but usually disappears in the first 2-3 months after installation.
- A common side effect during the first time after installation of a hormonal IUD is breast tenderness, headaches and slight weight gain.
- There are risks of pelvic inflammatory disease, so it is important to be screened for STIs before inserting an IUD. If you are concerned about persistent pain in the lower abdomen or pain during sexual intercourse, fever or abnormal discharge from the genital tract, then immediately contact your gynecologist.
- Although the IUD is a reliable method of contraception, BUT a low percentage of the probability of pregnancy still exists!
- It is extremely rare, but when installing an IUD, perforation of the uterus occurs - this is damage to the muscular layer of the uterus by the spiral! To avoid this situation, an OMT ultrasound and measurement of the length of the uterine cavity are performed before installation, and also after installation of the IUD, ultrasound control is necessary!
Contraindications and adverse reactions
The Mirena spiral has contraindications for use. These include:
- excessive sensitivity to the composition of contraception;
- malignant tumors of the uterus;
- congenital or acquired uterine anomalies;
- previous serious diseases (cancer) of the mammary glands;
- presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- postpartum inflammatory process in the uterus;
- acute liver diseases;
- uterine hemorrhage for unknown reasons;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
After insertion of the spiral, adverse reactions may occur.
- reduction of the menstrual cycle;
- the appearance of a skin rash;
- gagging;
- gaining a few kilograms;
- dizziness, headache;
- frequent mood swings;
- high sensitivity of the mammary glands.
Such negative consequences usually appear in the first weeks after the installation of the IUD. They disappear over time and do not require treatment.
The use of this hormonal contraceptive in rare cases can lead to complications. If any side effects not listed above occur, you should immediately contact a specialist. Possible complications include ectopic pregnancy, infection, and uterine perforation.
Contraindications to the installation of an IUD.
- Presence of a sexually transmitted infection
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs (including in the postpartum period and the period after termination of pregnancy)
- Cervical cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer
- Anomalies of the uterus - bicornuate uterus, septum in the uterine cavity
- Submucous uterine fibroids
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology
- Pregnancy
- Allergy to copper, Wilson-Konovalov disease - in the case of copper-containing IUDs
- Liver diseases and tumors, hypersensitivity to levonorgestrel - in the case of a hormonal IUD
Author: obstetrician-gynecologist Tarakanova M.Yu.
Rules to follow
Remember, such contraceptives cannot be installed before the onset of the first menstruation, and also for mature ladies after 50 years.
Before the procedure, you should definitely take a smear for flora and infections, and cytology. Make sure that there is no pregnancy at the time of installation of the intrauterine device; to do this, it is enough to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs; if in doubt, an additional hCG blood test.
Avoid sexually transmitted infections and use condoms when changing partners frequently. Understand that even ordinary pathogens behave extremely aggressively in the presence of the IUD and can provoke serious inflammation of the fallopian tubes and uterus.
The University Clinic offers a free consultation with a competent gynecologist online, an appointment with a specialist at a convenient time, a comprehensive examination, and a safe installation or replacement of an intrauterine device.