Beta hemolytic streptococcus does not reproduce by spores - these bacteria are immobile. The main condition for their growth is the presence of meat-peptone nutritional conditions. For example, it could be a pot of yesterday's soup.
However, some types of streptococci are also used for good purposes. Hemolytic streptococci are capable of fermenting lactose, as a result of which lactic acid is formed, which is used to produce fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk.
But for the most part, the streptococcus is very dangerous. The fact is that it produces toxins that have a very detrimental effect on human health. Toxins produced by streptococcus are capable of triggering autoimmune reactions that develop into serious diseases: rheumatism, glomerulonephritis.
Detailed description of the study
The diagnostic method is cultural (bacteriological). Inoculation is carried out on a pathogen-specific - selective - dense medium with the addition of blood. After a few days, a quantitative and qualitative assessment is carried out: the fact of colony growth, the intensity of growth, a change in coloring - discoloration - of the differential diagnostic medium are noted.
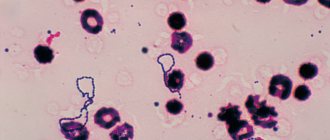
Streptococcus pyogenes (β-hemolytic streptococcus group A or GABHS) is a round-shaped bacterium - the diameter does not exceed 1 micrometer - arranged in chains or pairs. Individual representatives of this group are capable of forming a capsule.
GABHS is one of the most common causes of acute pharyngitis and tonsillitis - inflammation of the pharynx and tonsils. According to modern data, in different age categories the incidence of ENT diseases caused by pyogenic streptococcus varies from 10-15% to 70%. Children aged 5-15 years are most susceptible to infection. In some cases, the microorganism is constantly detected in the microflora of the oropharynx and nasopharynx: in persons suffering from chronic tonsillopharyngitis.
The disease in its acute form occurs with characteristic symptoms:
- Sharp pain when swallowing;
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- Enlarged submandibular and cervical lymph nodes;
- Purulent plaque of varying severity on the tonsils, the back wall of the pharynx;
- Increase in temperature to febrile levels (38.5 ° C) and above;
- Lethargy, lack of appetite, headache.
Three mechanisms are involved in the development of infection: infectious, toxic and allergic. There are rheumatogenic and nephritogenic strains of the pathogen. The former can provoke complications of acute tonsillopharyngitis in the form of damage to the joints and tissues of the heart, the latter - damage to kidney structures (glomerulonephritis).
The main cause of the disease is infection from a sick person, the route of infection is airborne droplets. The pathogen is transmitted with microparticles of saliva when sneezing or coughing. Also, the cause of an acute disease may be activation of streptococcus in bacteria carriers (with suppression of local immune defense factors). This usually occurs with general hypothermia, as well as as a consequence of a previous viral infection.
Streptococcus pyogenes is also capable of infecting the skin, causing the development of pyoderma. In this case, bubbles filled with cloudy contents appear on the surface of the skin, surrounded by an area of inflammation. Subsequently, they open, are replaced by crusts and fall off without the formation of defects. The disease is accompanied by general intoxication. The pathogen penetrates the skin when its integrity is violated (microtraumas, scratches, abrasions) or when local immunity is reduced. The risk group is people suffering from chronic diseases and young children.
The bacteriological, or cultural, method is the gold standard for diagnosing infections caused by GABHS (detection of streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis). The sensitivity—correct identification of patients—of the method exceeds 95%. Timely isolation of GABHS in a smear is essential for prescribing effective therapy, and also prevents the development of complications and, in most cases, the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Streptococcal infections and the role of healthy microflora in their prevention
Theodor Billroth and the equally famous French chemist and microbiologist were the first to encounter these bacteria that parasitize humans . The first discovered them in 1874, when he was treating erysipelas, the second - several years later when examining patients with purulent diseases and sepsis. Over time, it became clear that these microorganisms also live in animal bodies and represent a whole family that has one thing in common: they provoke various diseases.
References
- Handbook of infectious diseases in children / ed. Yu.V. Lobzina - St. Petersburg. : SpetsLit, 2013. - 591 p.
- Kaspranskaya, G.R., Lopatin, A.S. Chronic tonsillitis: different views on an old problem. Medical Council, 2013. - No. 5-6. — P. 69-71.
- Finogeev, Yu.P., Pavlovich, D.A., Zakharenko, S.M. and others. Acute tonsillitis in infectious patients. Journal Infectology, 2011. - T. 3. - No. 4. - P. 84–91.
- Bakradze, M.D., Darmanyan, A.S. Differential diagnosis of acute bacterial and viral tonsillitis. Diagnostic algorithms in pediatrics, 2009. - T. 1, No. 2. — P. 56-61.
- Pokrovsky, V.I., Briko, N.I., Ryapis, L.A. Streptococci and streptococcosis. - M.: Geotar-media, 2008. - 540 p.
- Gieseker, KE Evaluating the American Academy Pediatrics diagnostic standard for Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis: Backup culture versus repeat rapid antigen testing. Pediatrics, 2003. -Vol. 111. - P. 66–70.
Meet streptococcus!
As you guessed, we will talk about streptococcus, one of the rather widespread microorganisms in nature. But it’s hardly necessary to get to know him in the literal sense of the word. Is it just informational, to a) try to avoid infection with these bacteria; b) correctly treat the ailments they cause, if an unpleasant “meeting” could not be avoided.
Streptococcus or, in Latin, Streptococcus , is, scientifically speaking, a genus of spherical or ovoid gram-positive facultative anaerobic bacteria. Arranged in pairs or in the form of chains of varying lengths. They belong to the Streptococcaceae family. It includes numerous species with certain differences. Both physiological and biochemical characteristics, including the degree of pathogenic effects on humans.
| INTERESTING TO KNOW. Favorite habitats in the body: respiratory tract, digestive tract. They especially prefer the mouth and nose, as well as the large intestine. They are also found in the vaginal environment. Streptococci are “capricious” when it comes to nutrient substrate. That is, as long as they don’t “eat” anything and don’t reproduce anywhere. Their most preferred environments are blood or sugar. |
Capable of forming small colonies (this is on the surfaces of solid media). Bottom growth occurs in liquid media. They are divided into three ecological groups. The first group includes S. Pyogenes, its representatives are pathogenic only for humans, the second group includes S. Faccalis, S. agalactia, etc., which are pathogenic for both humans and animals. The third group is represented by opportunistic oral streptococci S. Mitis, S. mutans and others.
Probiotics can help
However, often the problem of dysbiosis as one of the possible factors favoring the emergence and development of streptococcal infections cannot be solved only by proper nutrition . Especially if a person has previously suffered one or another of them, his body is additionally weakened by antibiotic therapy and there is a risk of relapse of the disease. In such cases, probiotics - live lactic acid microorganisms (lacto- and bifidobacteria, including yeast) - become a real help . In addition to improving digestion, overall gastrointestinal health and strengthening the immune system, they produce biotin, folic acid, vitamin K and other essential nutrients.
All this becomes one of the foundations of antistreptococcal preventive measures. Taking probiotics directly during drug therapy for streptococcal infections is like a breath of fresh air for a person weakened by a serious illness. Entering the intestines (it is advisable to use their liquid forms), probiotics prevent antibiotics and other strong drugs entering the body from completely destroying the beneficial microflora. On the contrary, they allow it to get stronger, stimulating its growth and development. Practice convincingly shows that the inclusion of probiotics in the complex therapy of diseases caused by streptococcal bacteria allows patients to recover faster, regain their strength and become less susceptible to such infections in the future
Back to list Previous article Next article
Healthy flora against streptococcus
The occurrence of any streptococcal infection signals trouble in the body. For example, about a decrease in general immunity. Or a disruption of the normal intestinal microflora (dysbacteriosis), when lactobacilli and bifidobacteria that are beneficial to humans lose their positions, giving way to living space to opportunistic microflora. This actually includes streptococcus bacteria . Therefore, along with other methods of prevention (primarily maintaining personal hygiene, avoiding direct contact with sick people, as well as identifying hidden carriers), intestinal health should not be neglected.
Streptococci , as already mentioned, love a sugar environment. This means that you should not overuse sweets, baked goods and other products that can inhibit beneficial microflora and provoke putrefactive processes in the intestines. The more you pay attention to the health of your gastrointestinal tract by eating healthy foods (vegetables, fruits, dairy products, etc.), the less chance these harmful bacteria will have to “take over” in your body. After all, a healthy body presupposes a strong immune system – right?
Consequences and complications
Streptococcal infection can be complicated by autoimmune and toxicoseptic secondary lesions of systems and organs. As a result, complications may develop:
- glomerulonephritis;
- rheumatism;
- sepsis;
- necrotic myositis;
- meningitis;
- vasculitis;
- inflammation of the heart muscle;
- purulent otitis media;
- lung abscess;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- pulpitis;
- erysipelas;
- lymphadenitis;
- sepsis.
Tests and diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the patient needs not just a test for streptococcus, but a whole series of necessary studies. They are needed to determine the specific causative agent of the disease and its reaction to drugs. Therefore, the doctor not only prescribes a test for streptococcal infection, but also conducts a comprehensive diagnosis.
An analysis to detect streptococcus in a throat smear is carried out, as a rule, in cases where a person has symptoms indicating a suspicion of such an infection. In this case, an important factor in the diagnostic process is not the very fact of the presence of the pathogen in the biomaterial, but its quantity. This analysis makes it possible to determine the number of pathogenic bacteria, as well as whether Streptococcus viridans and other types of streptococcus are normal in the throat.
When analyzing the data obtained, it should be taken into account that the microflora normally contains a certain number of streptococci. Thus, a Streptococcus viridans indicator of 10 5 CFU/ml (pharynx) can be considered normal, while at higher levels subsequent research and treatment are required.
The degree of infection is determined by the amount of microorganism that was found in the biomaterial:
- 10 in grade 1 CFU/ml - 10 in grade 2 CFU/ml - the amount of microorganism in the oral cavity is normal and cannot cause disease.
- 10 to grade 3 CFU/ml – 10 to grade 4 CFU/ml – the amount in the oral cavity is normal and safe if there are no clinical symptoms.
- 10 to 6 degrees CFU/ml - 10 to 7 degrees CFU/ml - the amount is high and can cause an infectious lesion.
- “Confluent growth” is the definition of too high a quantity of a microorganism, corresponding to a high degree of infection and requiring immediate treatment.
Before taking a throat swab for streptococcus, you should adhere to the following rules:
- The smear must be taken in the morning.
- Do not drink or eat before donation.
- Don't brush your teeth.
- Do not use topical antiseptics or chew gum.
Streptococci in a smear in women are most often determined in swabs from the nose and throat. The causes of streptococcus in a smear in women may be associated with the development of various diseases. But the presence of this pathogen is most dangerous when analyzing urine in pregnant women. Streptococcus agalactia can cause infection in a child and cause serious illness.
If Streptococcus agalactiae is 10 in grade 5 or if Streptococcus agalactiae is 10 in grade 6 or more, the doctor prescribes treatment for the expectant mother on an individual basis.
When collecting urine for the determination of streptococcus, it is necessary to adhere to important recommendations on which the accuracy of the analysis depends. Failure to comply with hygiene rules may result in a false positive result. The following must be taken into account:
- Before collecting urine, you should wash your genitals using only running water.
- Before collecting urine, a woman should spread her labia minora wide apart. The first portion of urine is flushed into the toilet, as it contains microorganisms from the surface of the urethra. For research, only the middle portion of urine is taken.
- It is important to take into account that the presence of streptococcus in the urine is influenced by the time of day, the phase of the monthly cycle and other factors.
If there is a suspicion of the development of a septic process, a bacteriological blood test is performed. If a positive growth of streptococci is observed in the blood (on blood agar), this is evidence of a serious infection, because a healthy person should not have this bacterium in the blood. If its presence is confirmed, an additional study is carried out to determine the type of streptococcus. Also conducts serological testing to determine antibodies.
As for the possibility of buying a streptococcus test at a pharmacy, certain rapid tests exist (for example, the Strep A test for streptococcus). But accurate results can be obtained only after all tests have been carried out in medical conditions. institutions.